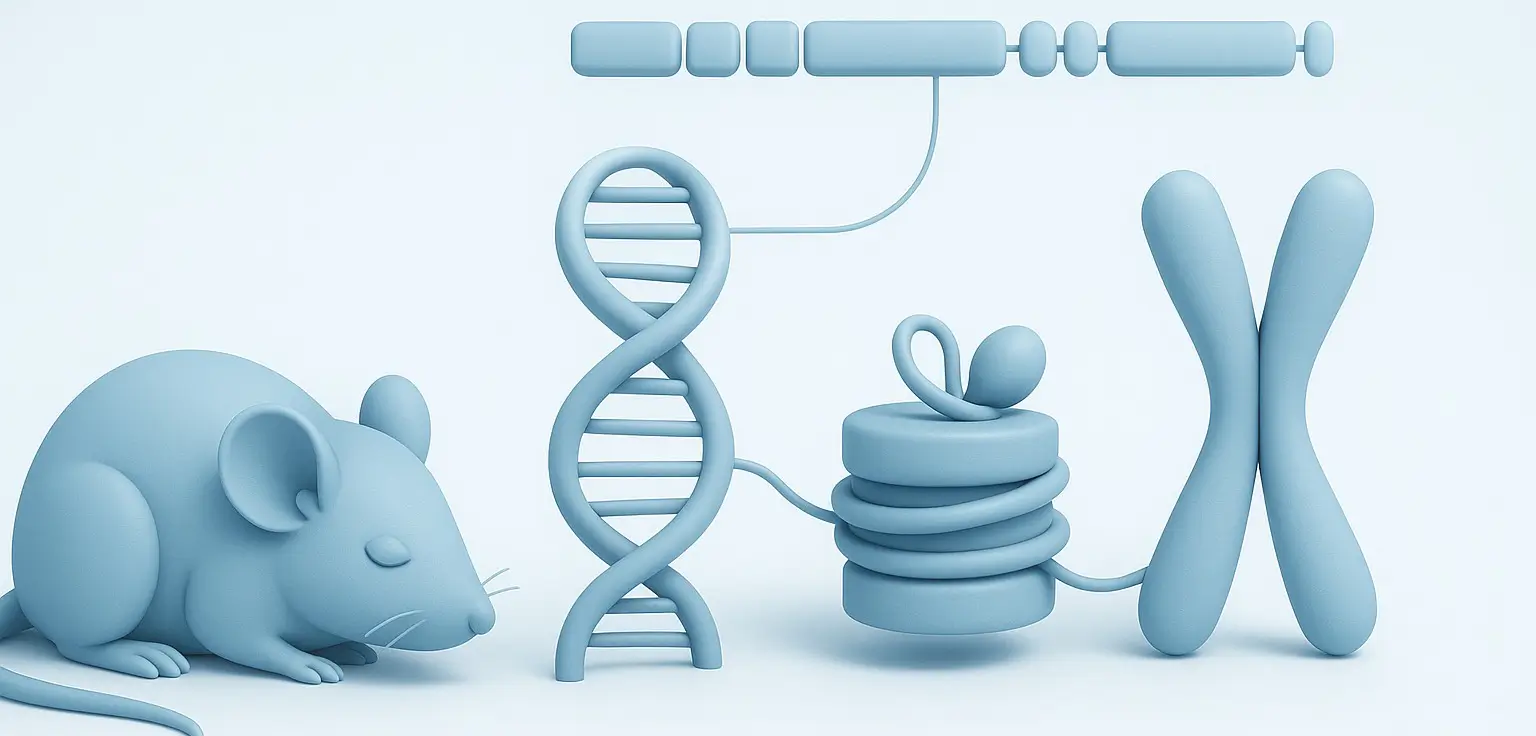
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): Structure & Functions
DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is a long, double-stranded molecule that carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) is composed of two strands forming a double helix, made up of repeating units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), … Read more