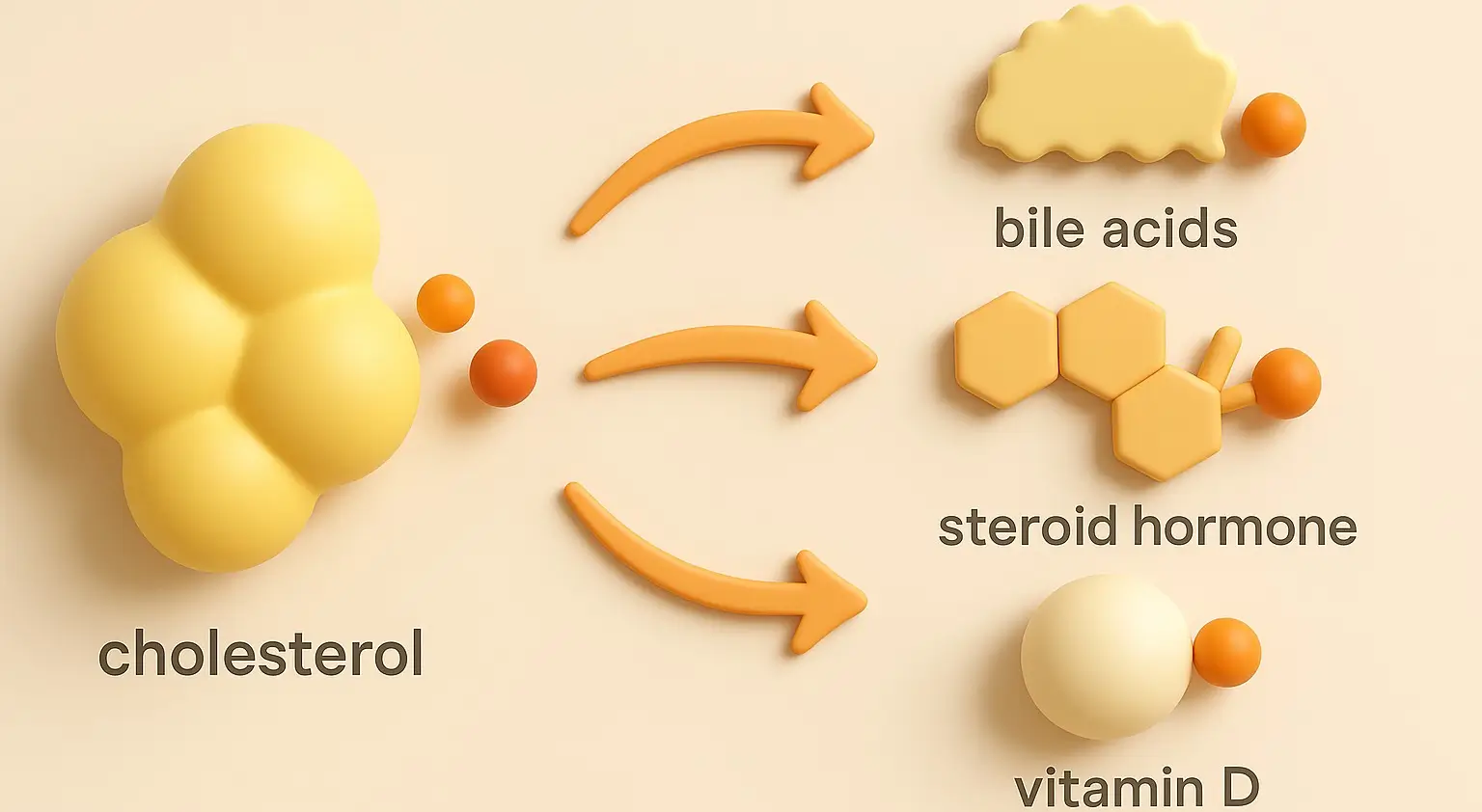
lipid metabolism Disorders
Lipid metabolism disorders can significantly impact health, leading to various conditions such as hypercholesterolemia, atherosclerosis, fatty liver, and obesity. Here’s a brief overview of each lipid metabolism Disorders: 1. Hypercholesterolemia: Definition: An abnormally high level of cholesterol in the blood. Causes: Genetic factors, poor diet, lack of exercise, and other health conditions like diabetes. Risks: … Read more