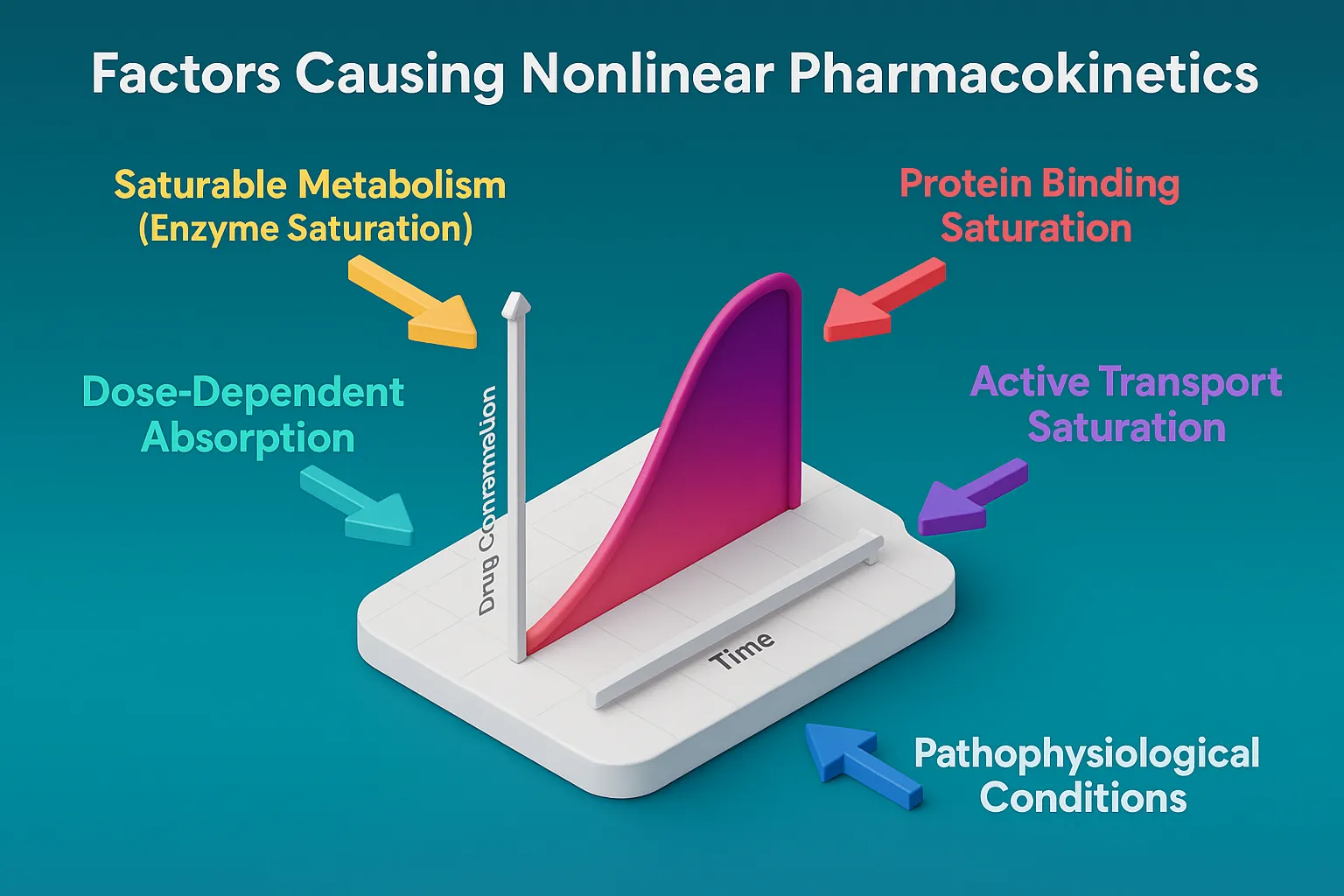
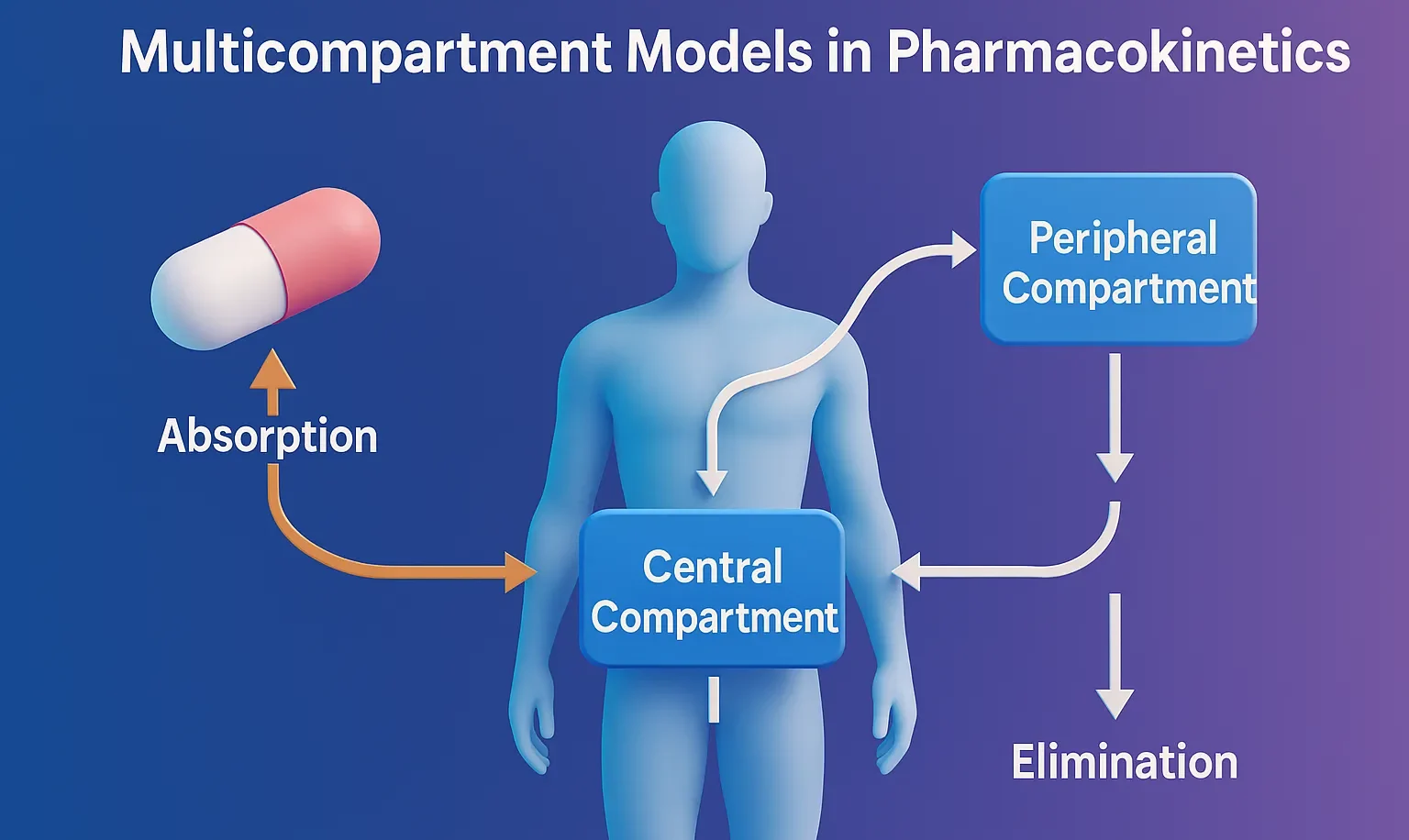
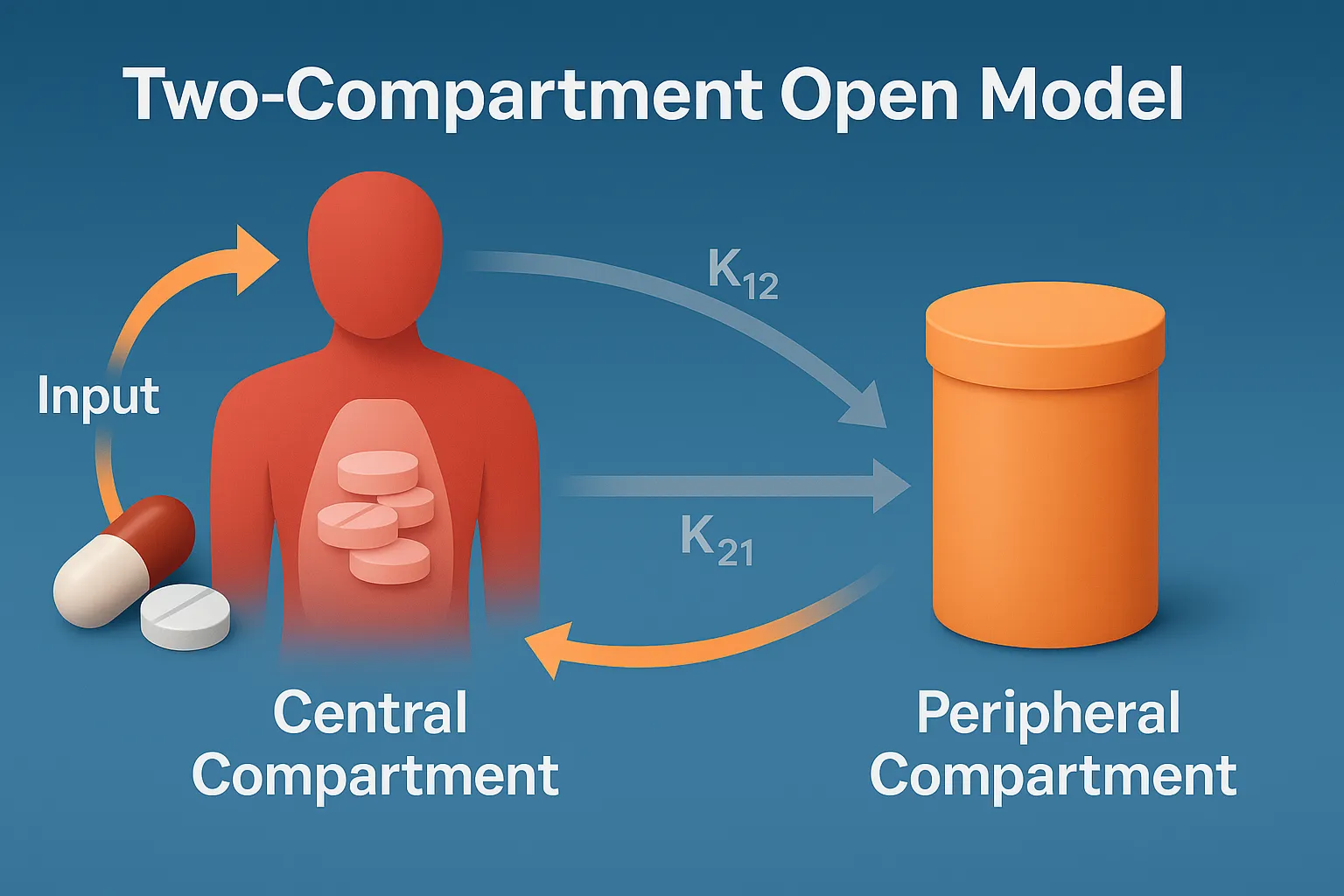
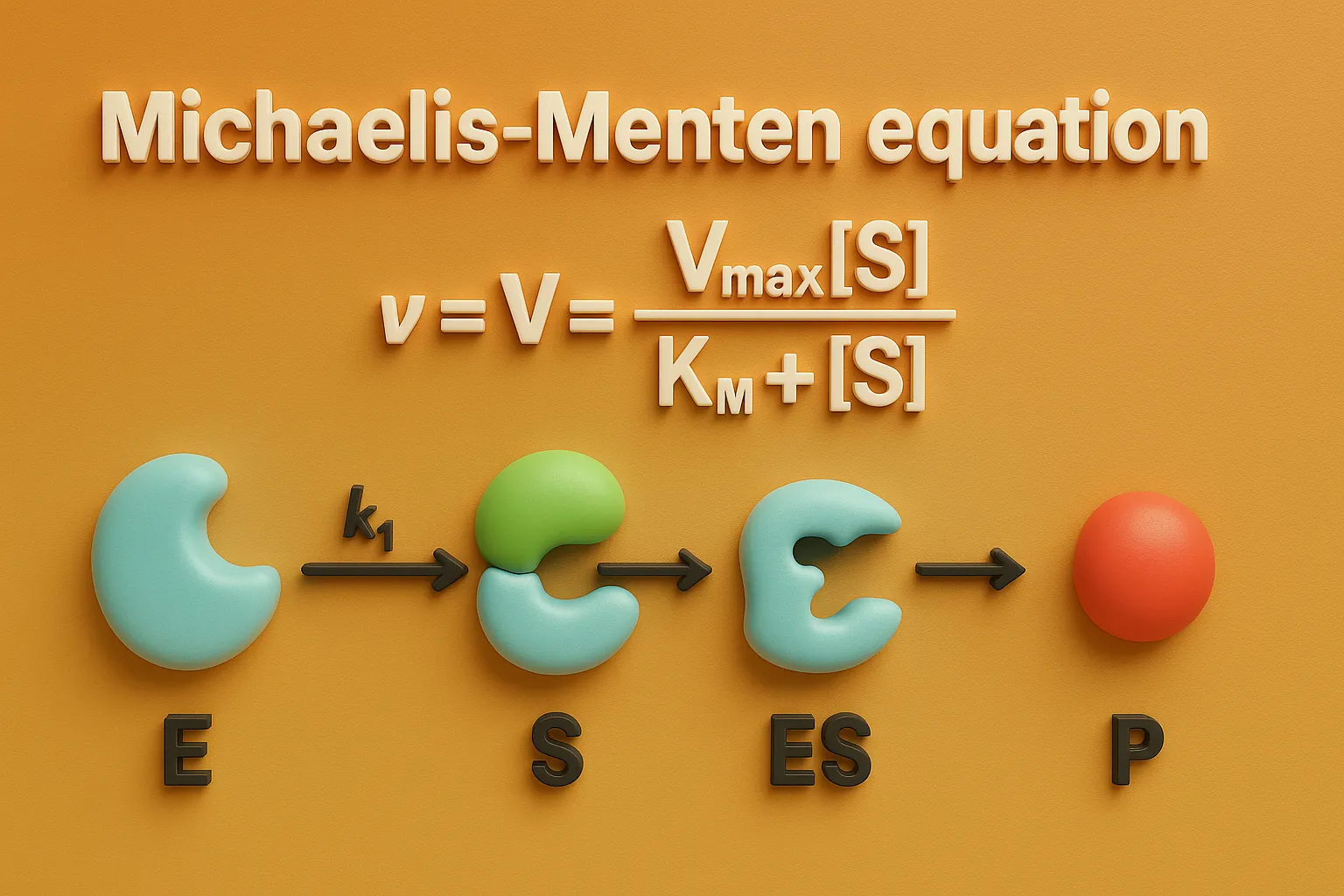Factors Causing Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics
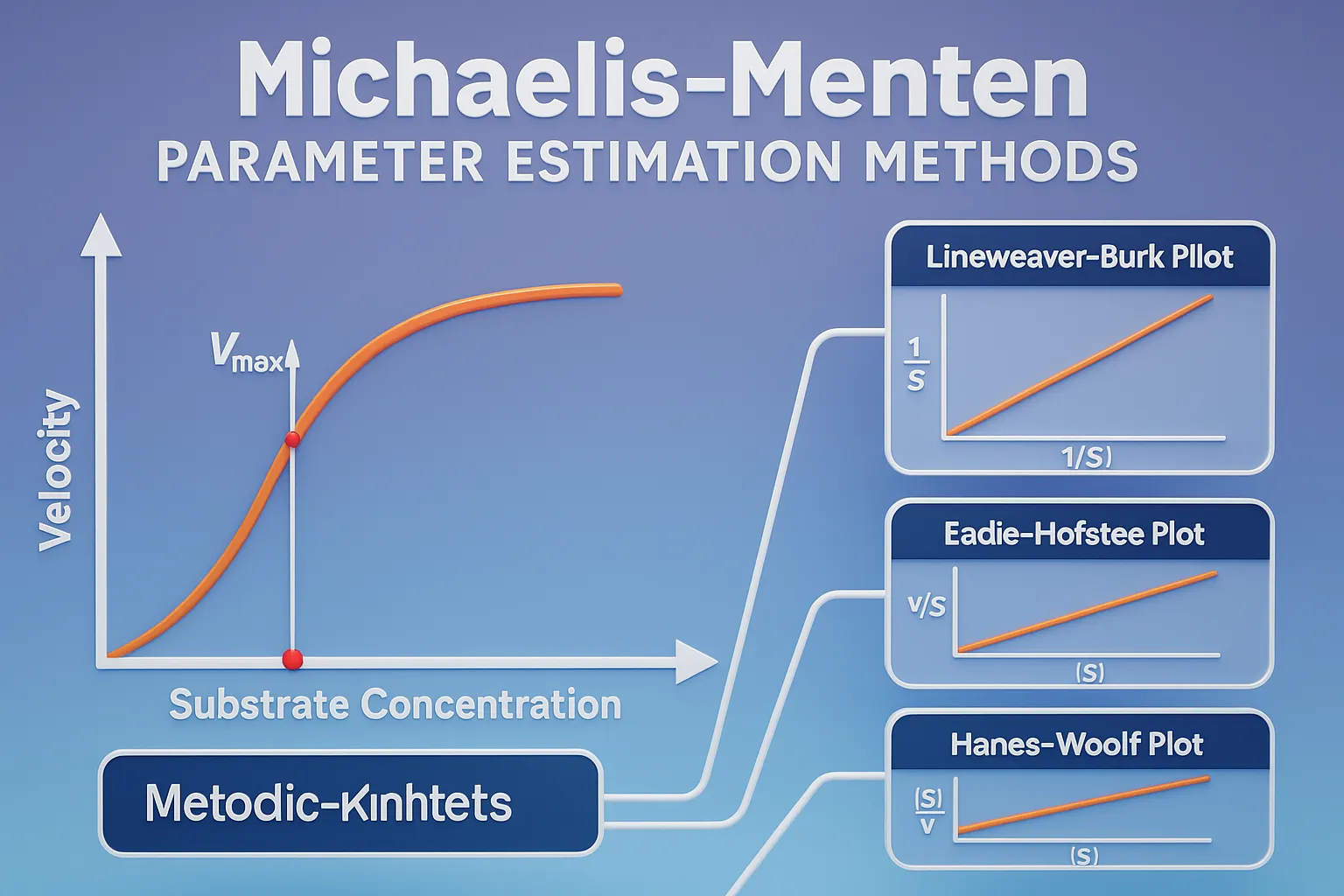
Factors Causing Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics include enzyme saturation, protein binding, transport limits, and metabolic pathway shifts. Factors Causing Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics Nonlinear pharmacokinetics arises from the saturation of physiological processes involved in drug metabolism, absorption, distribution, or excretion. Key mechanisms include: Saturable Metabolism (Capacity-Limited Metabolism) Enzymes (e.g., CYP450, alcohol dehydrogenase) become saturated at high drug concentrations. Once … Read more