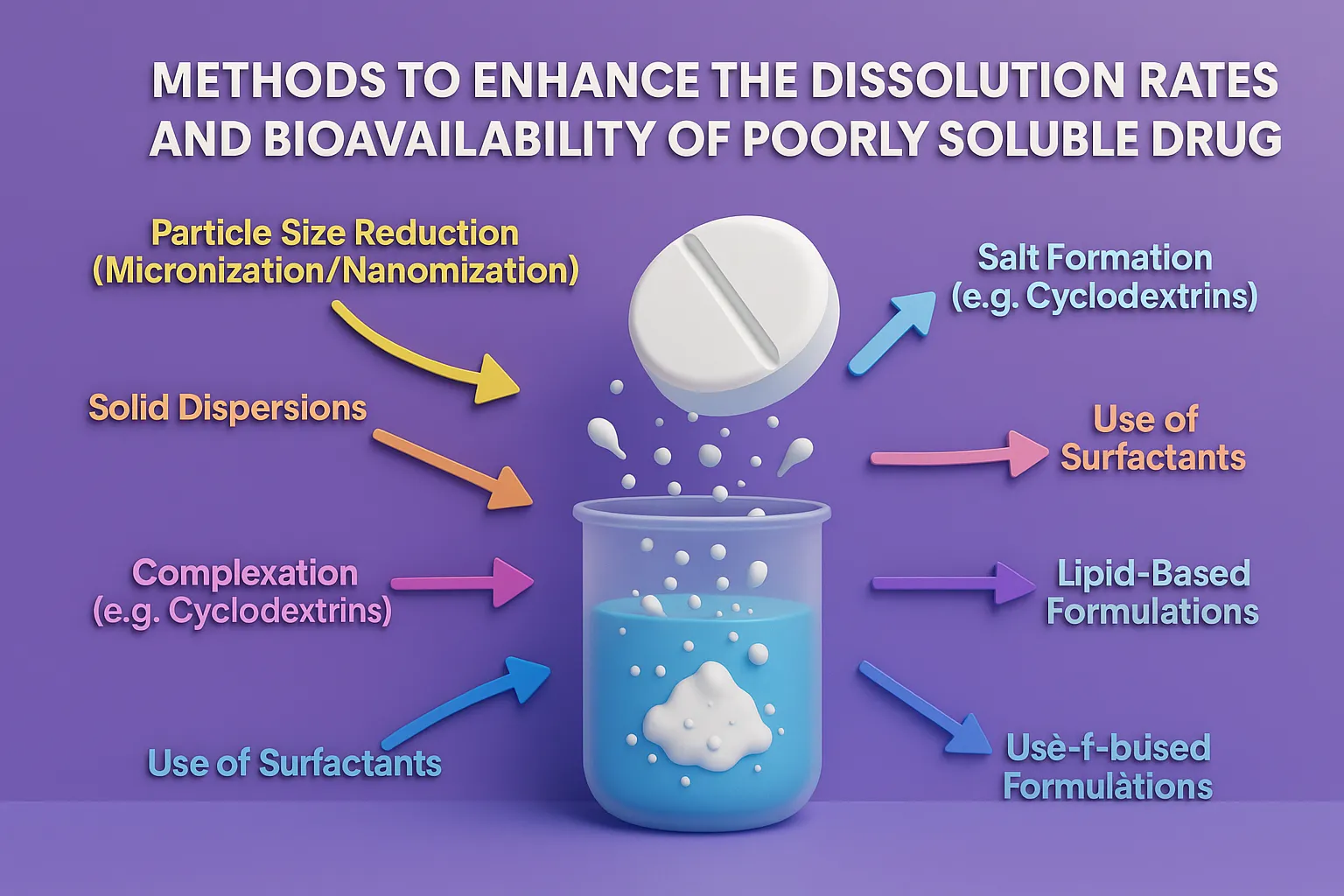
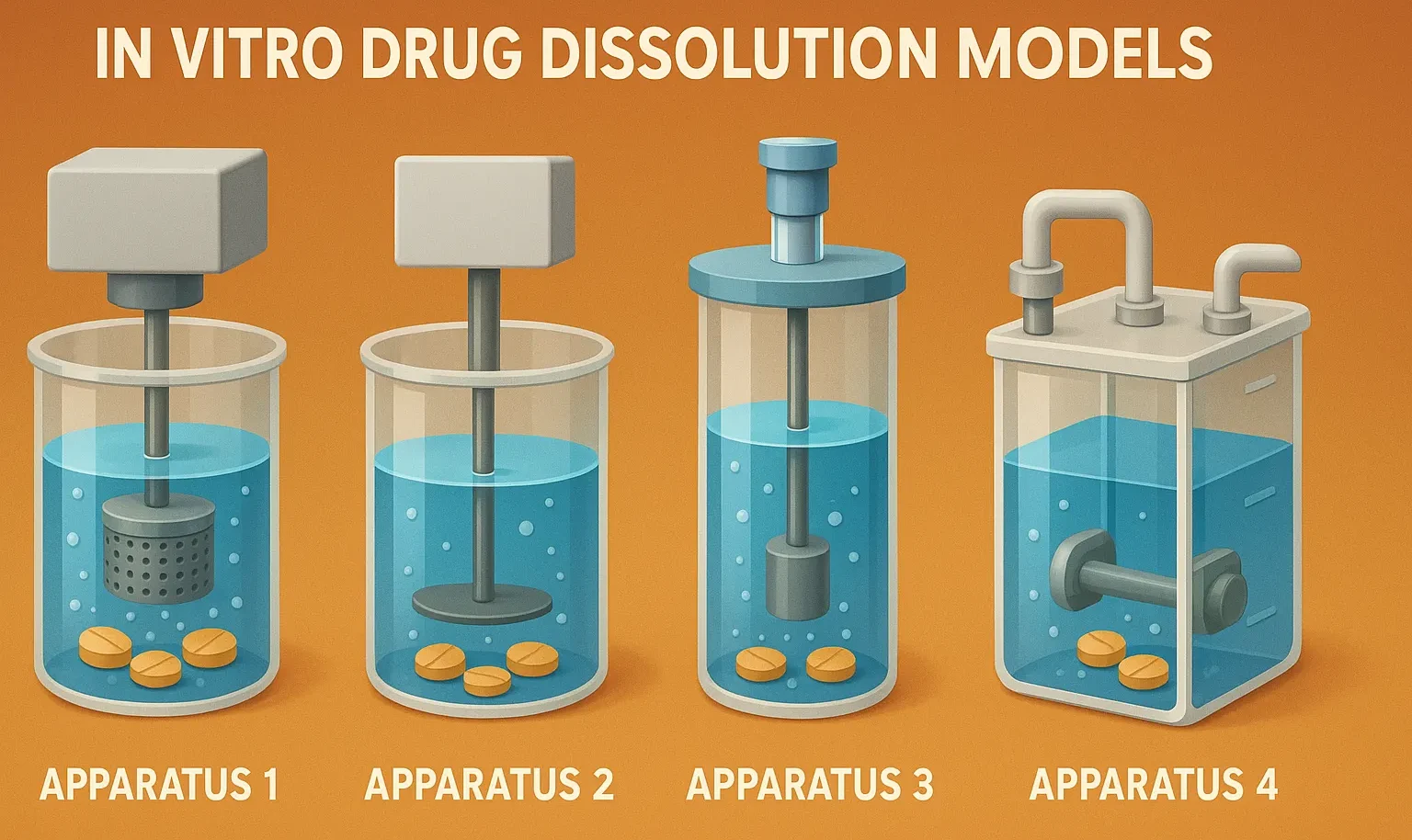
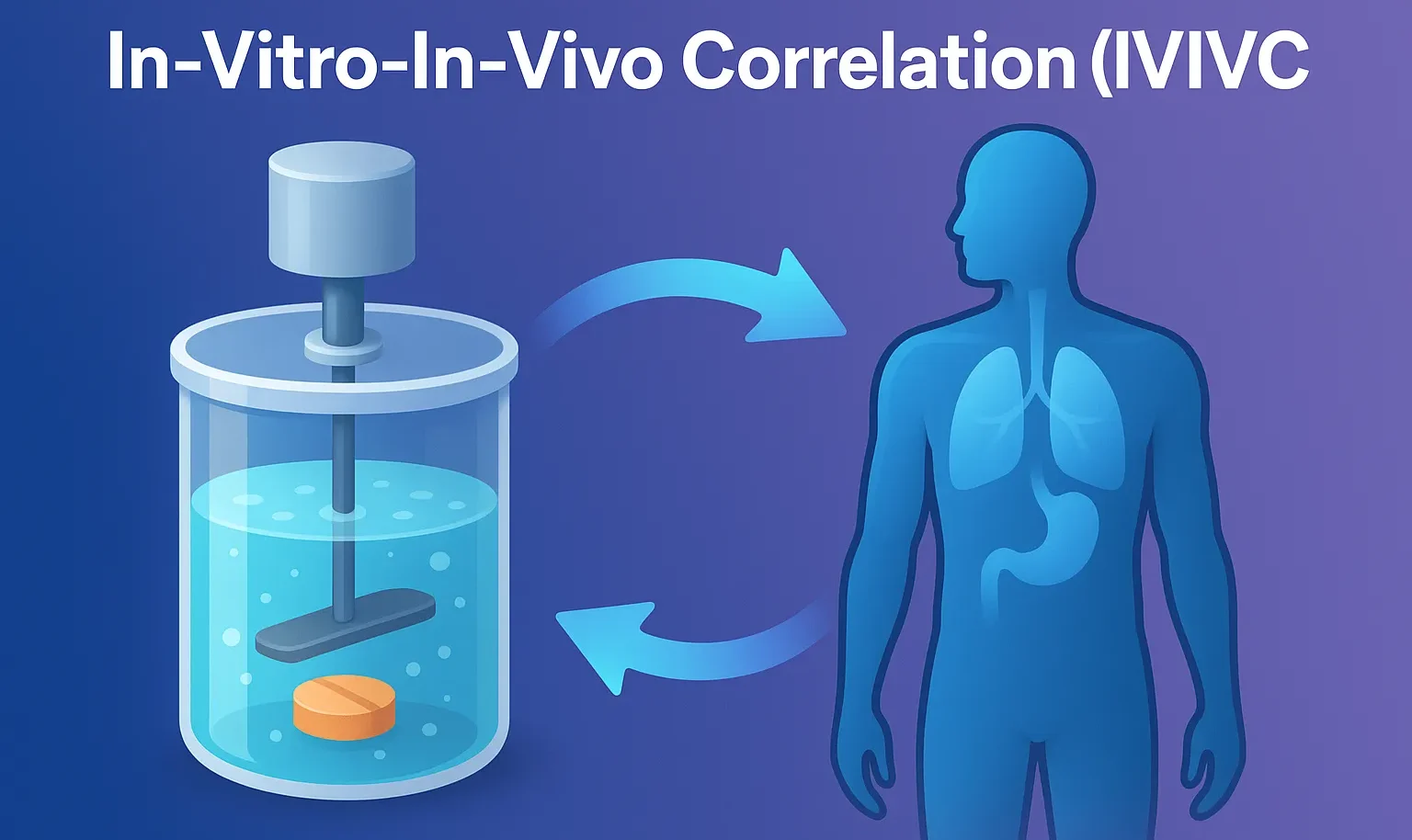
Reaction Kinetics: Rate, Rate Constants, and Order
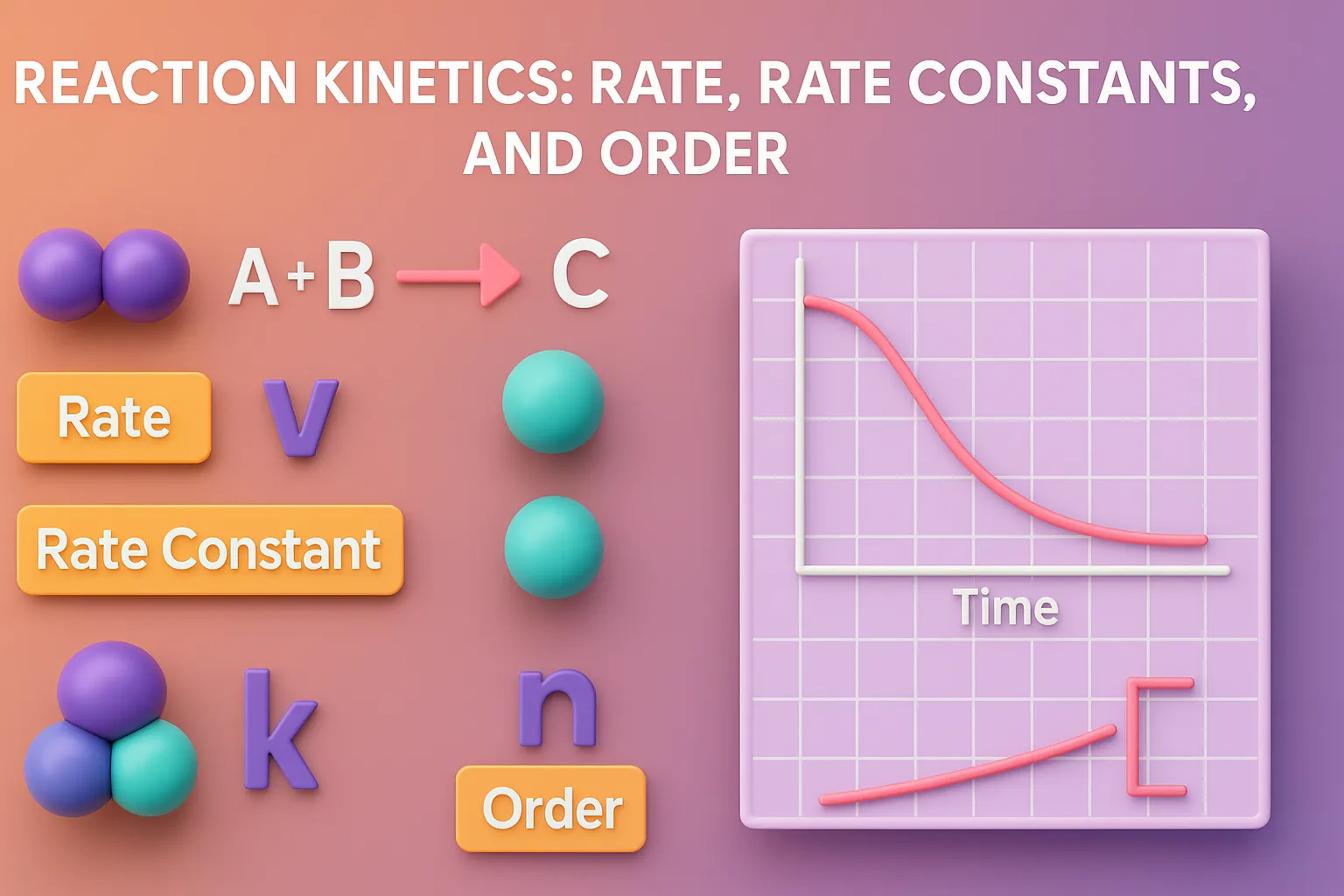
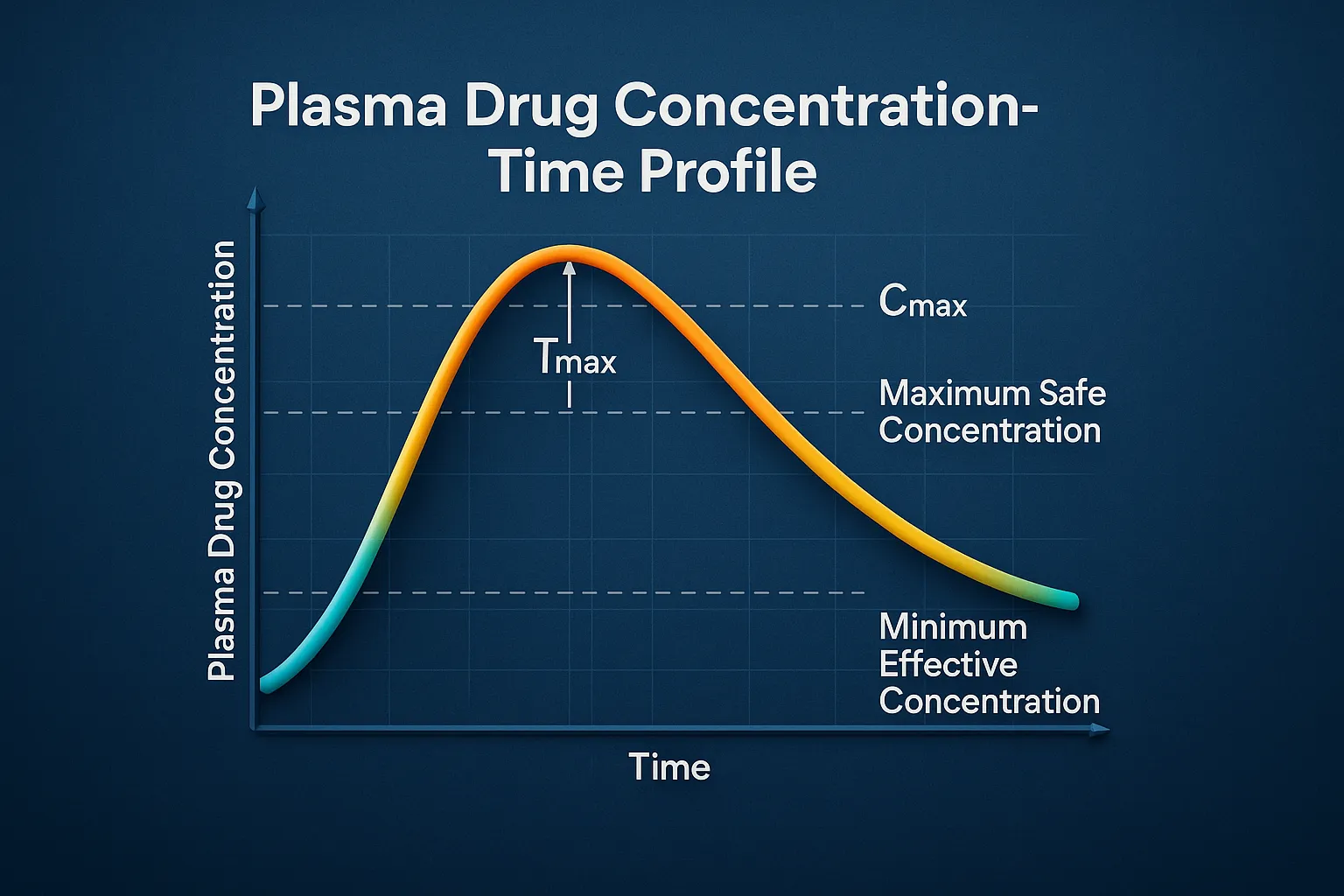
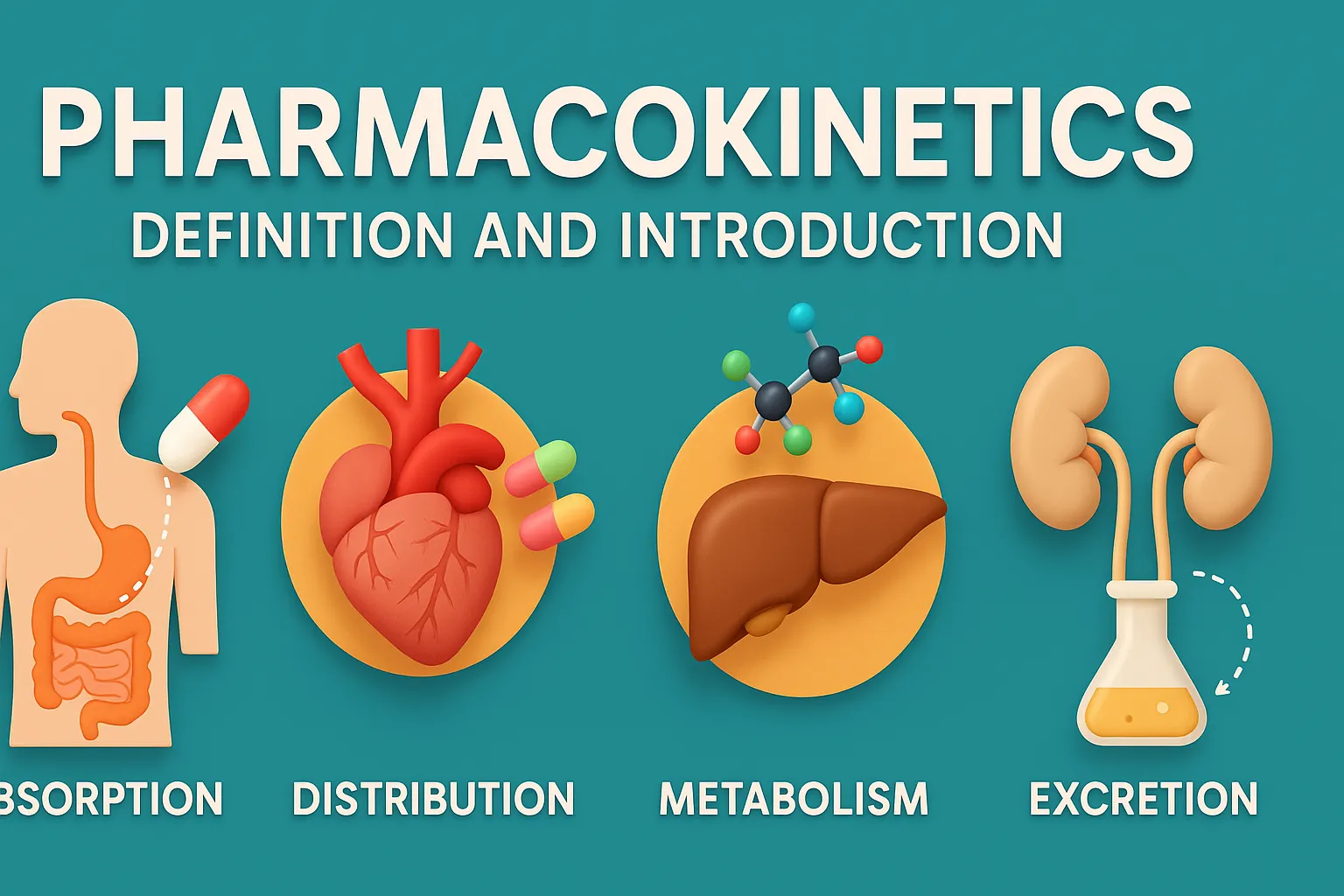
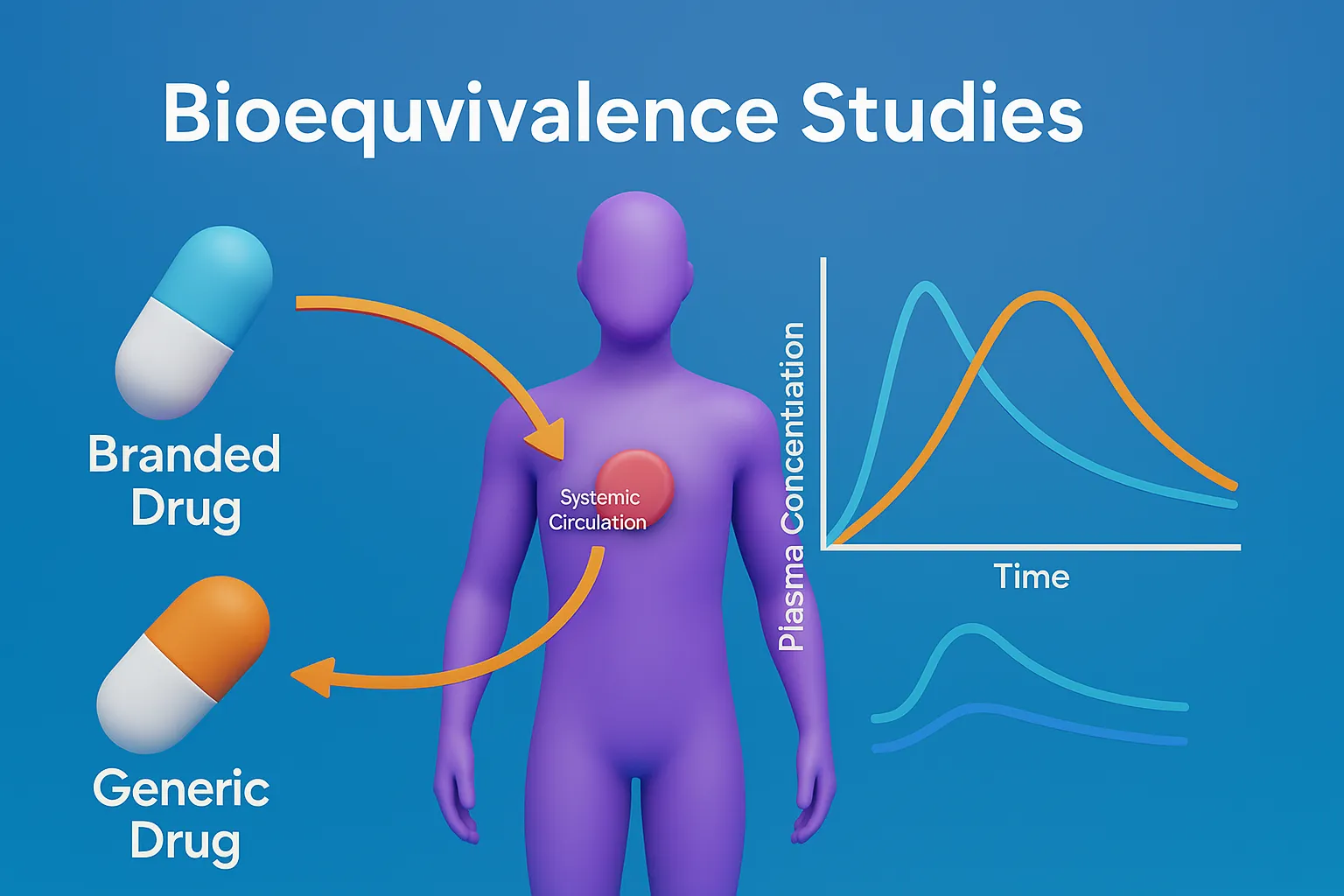
Reaction kinetics rate rate constants and order describe how drug concentration changes over time in pharmaceutical chemistry. Basic Concepts of Reaction kinetics rate rate constants and order Rate of Reaction: Measures how fast reactants are converted into products. Influenced by temperature, concentration, catalysts, and surface area. Rate Constant (k): A constant specific to a given … Read more