Formulation Considerations for Ophthalmic Preparations
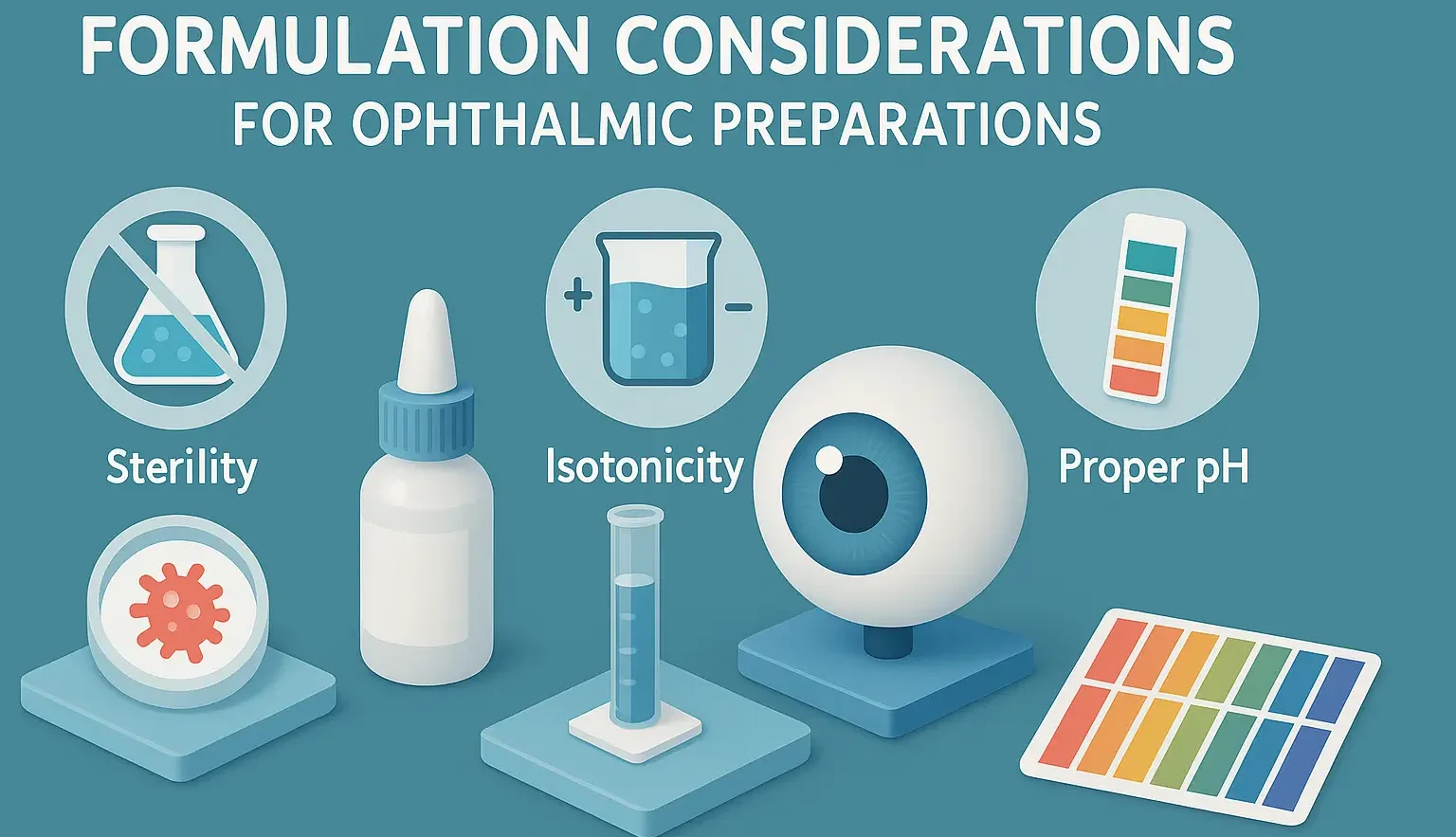
Introduction to Formulation Considerations for Ophthalmic Preparations Formulation Considerations for Ophthalmic Preparations involve ensuring sterility, isotonicity, proper pH, and particle size for safety and efficacy. It focusses on viscosity enhancers, preservatives, and minimizing irritation for patient comfort. Formulating ophthalmic preparations involves addressing unique challenges due to the sensitivity of ocular tissues and the need for … Read more