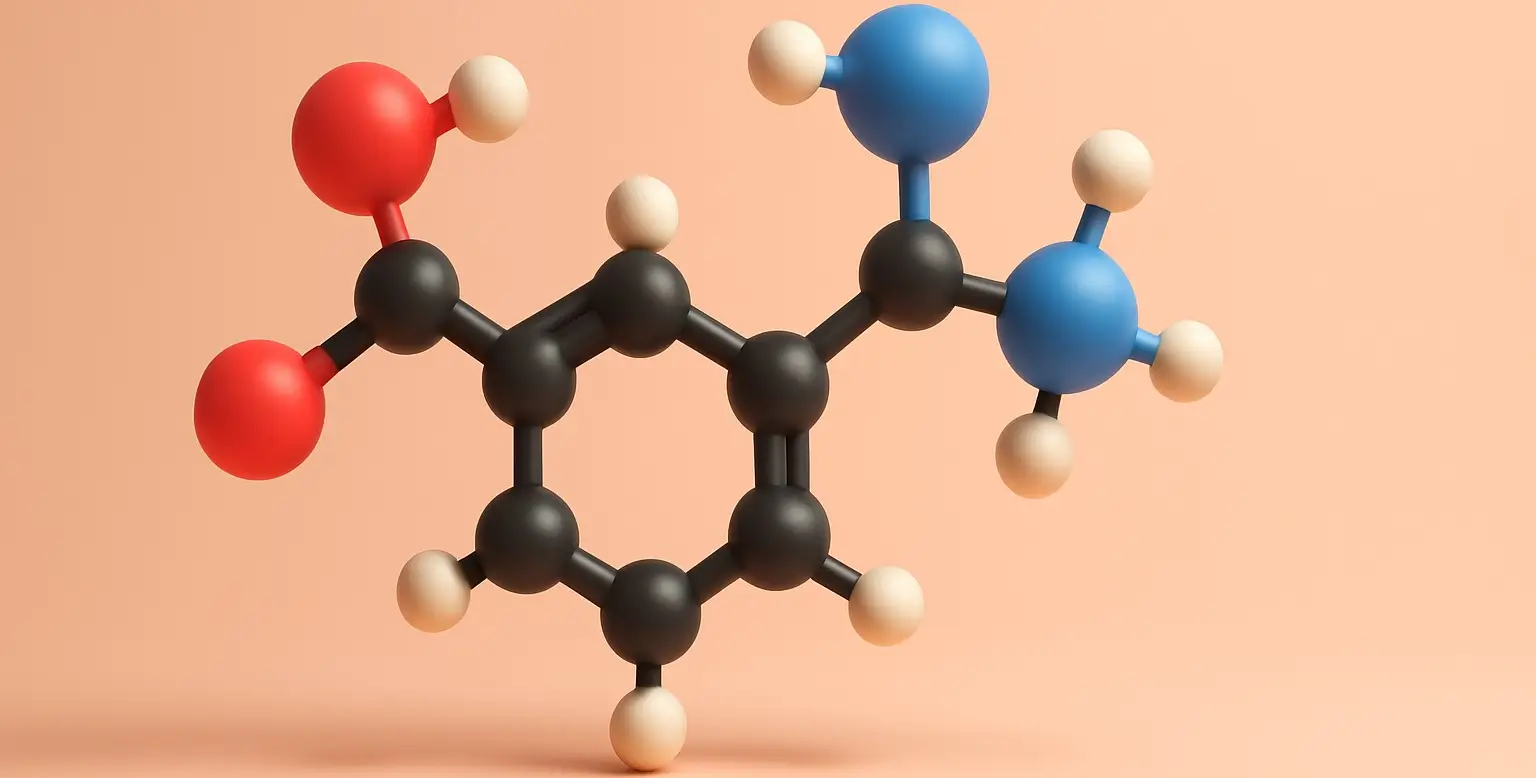
Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
Adrenaline (also known as Epinephrine) a hormone and neurotransmitter produced by the adrenal glands, located on top of the kidneys. It plays a key role in the body’s “fight or flight” response by increasing heart rate, expanding airways, dilating pupils, and mobilizing energy stores. It prepares the body to respond quickly to stressful or dangerous … Read more