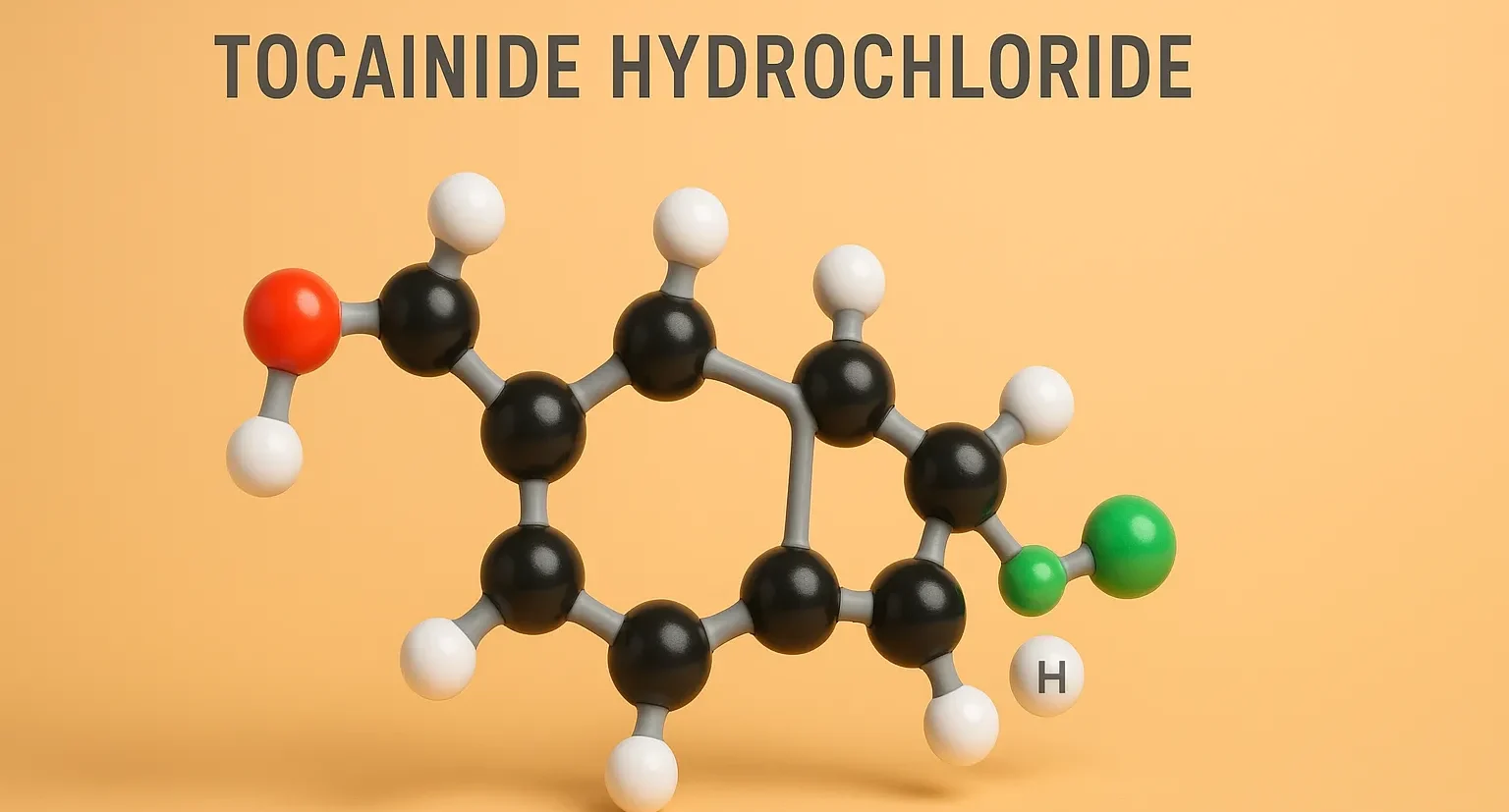
Tocainide Hydrochloride
Tocainide Hydrochloride is a class Ib anti-arrhythmic used to manage ventricular arrhythmias by inhibiting sodium influx. Structure of Tocainide Hydrochloride Tocainide hydrochloride is an amide-type antiarrhythmic agent structurally related to procainamide. It features a diethylaminoethyl side chain attached to a 2,6-dimethyl-p-aminobenzoic acid core. Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₁₅N₃O₂S·HCl Mode of Action Class IA Antiarrhythmic: Blocks fast sodium … Read more