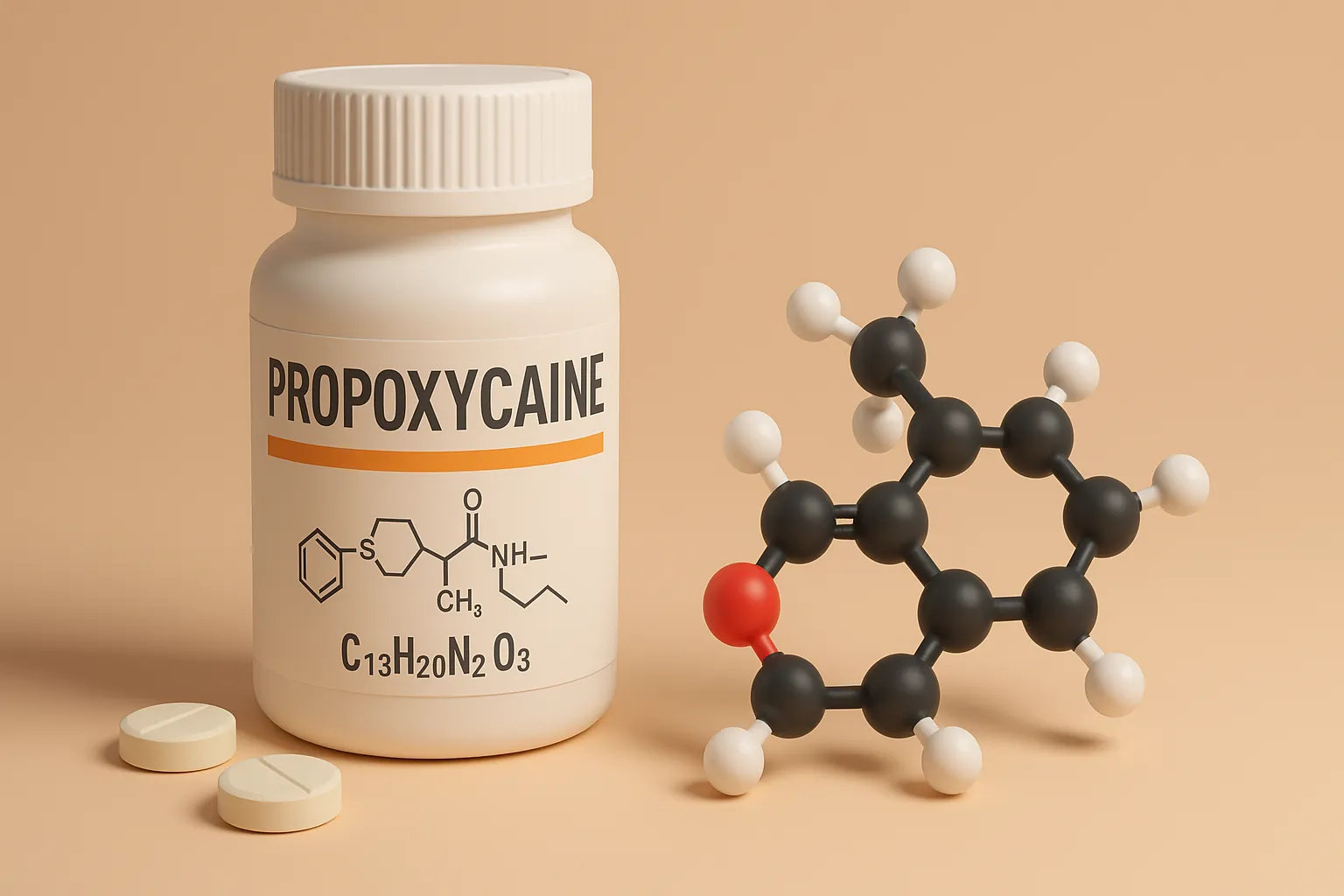
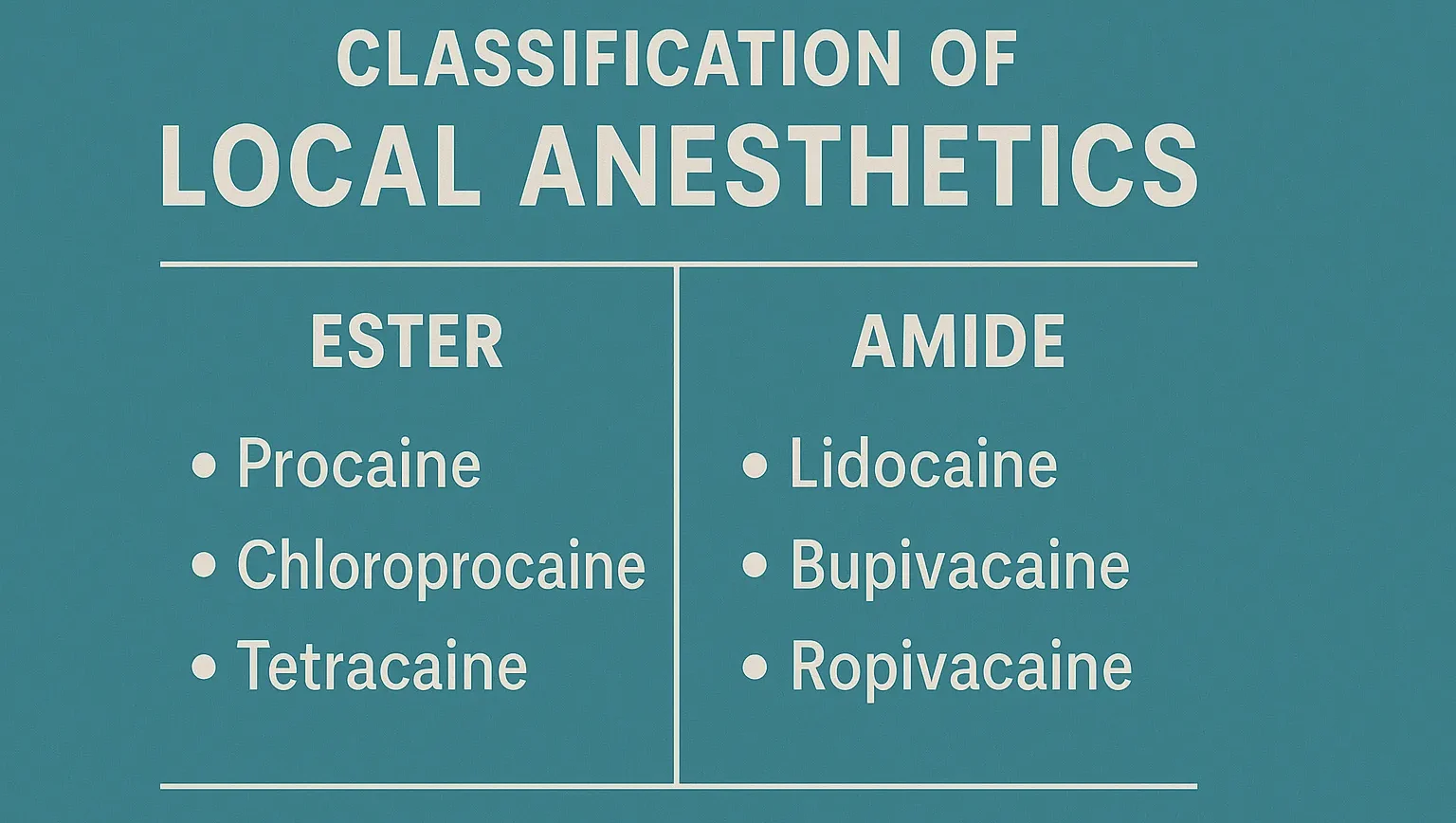
Tetracaine
Tetracaine is a potent ester local anesthetic used for spinal and ophthalmic anesthesia by blocking nerve signals. Structure of Tetracaine It is a potent amino benzoic acid derivative with a butyl ester group, providing long-lasting local anesthetic effects. Chemical Formula: C₁₂H₂₉N₃O₂ Mode of Action Sodium Channel Blockade: Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing nerve impulse conduction. … Read more