Nandrolone
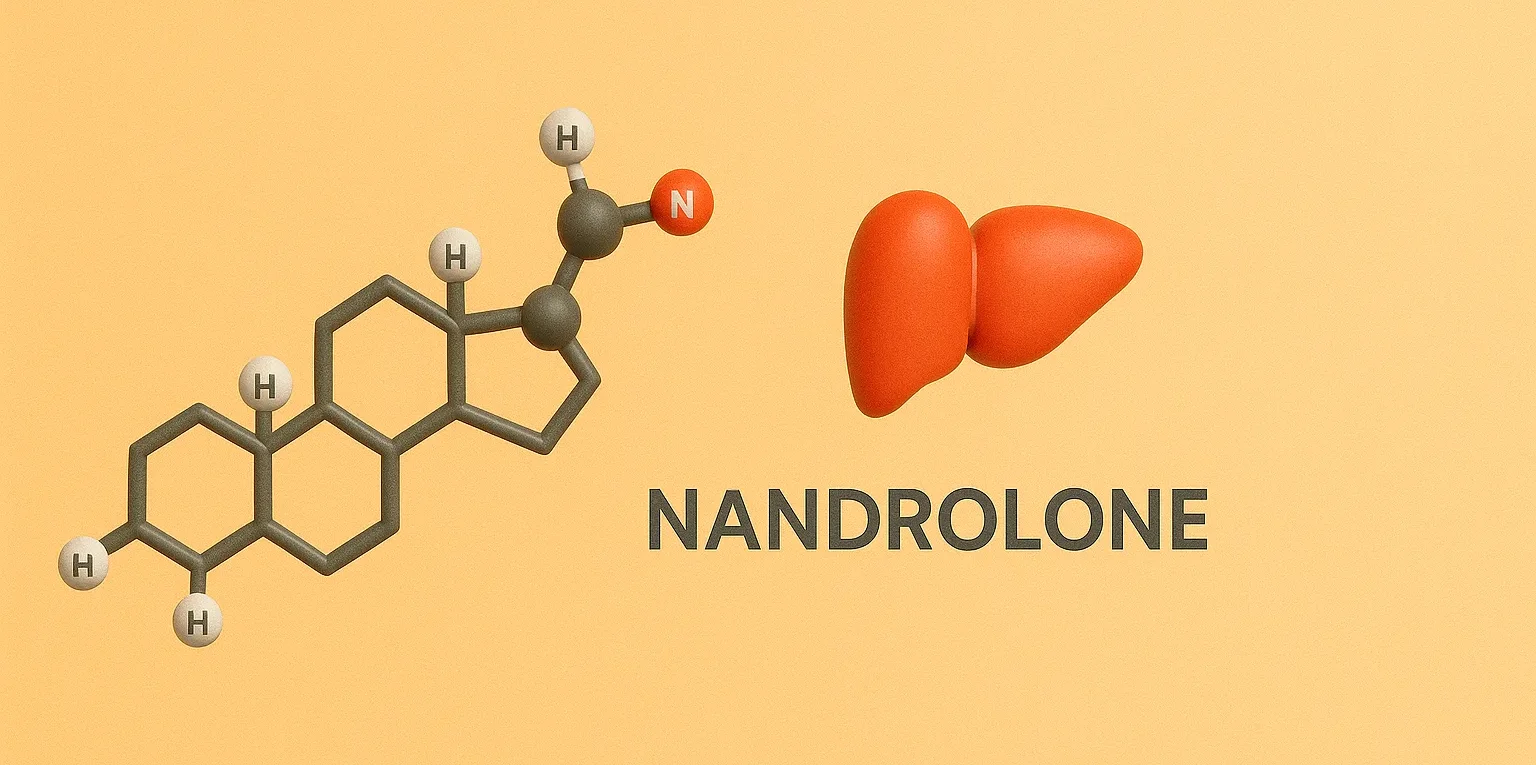
This article explains about the Nandrolone is an anabolic steroid used to promote muscle growth and treat certain anemia types. Structure of Nandrolone Andralone is an anabolic androgenic steroid with a modified cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene structure. It typically includes additional functional groups to enhance its anabolic properties. Chemical Formula: C₂₀H₂₈O₂ Mode of Action Androgen Receptor Activation: Similar … Read more