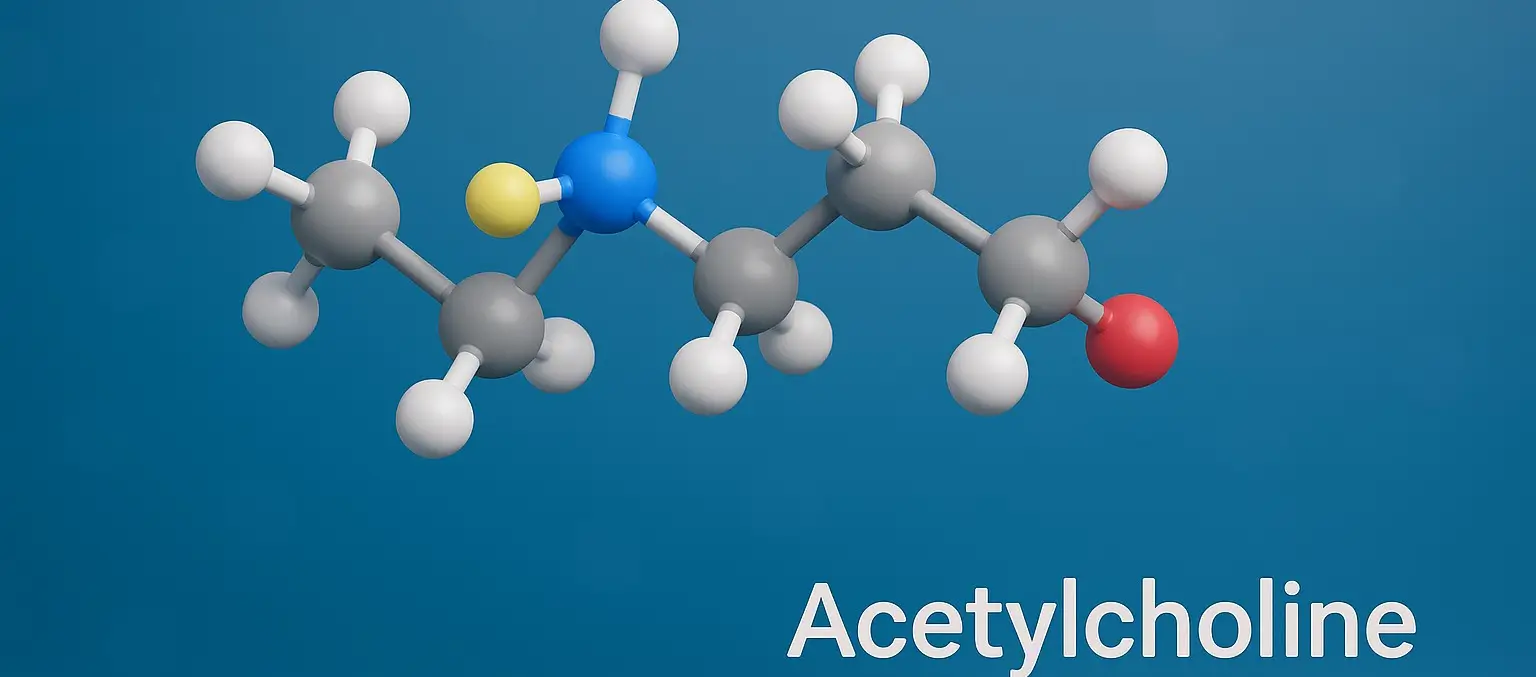
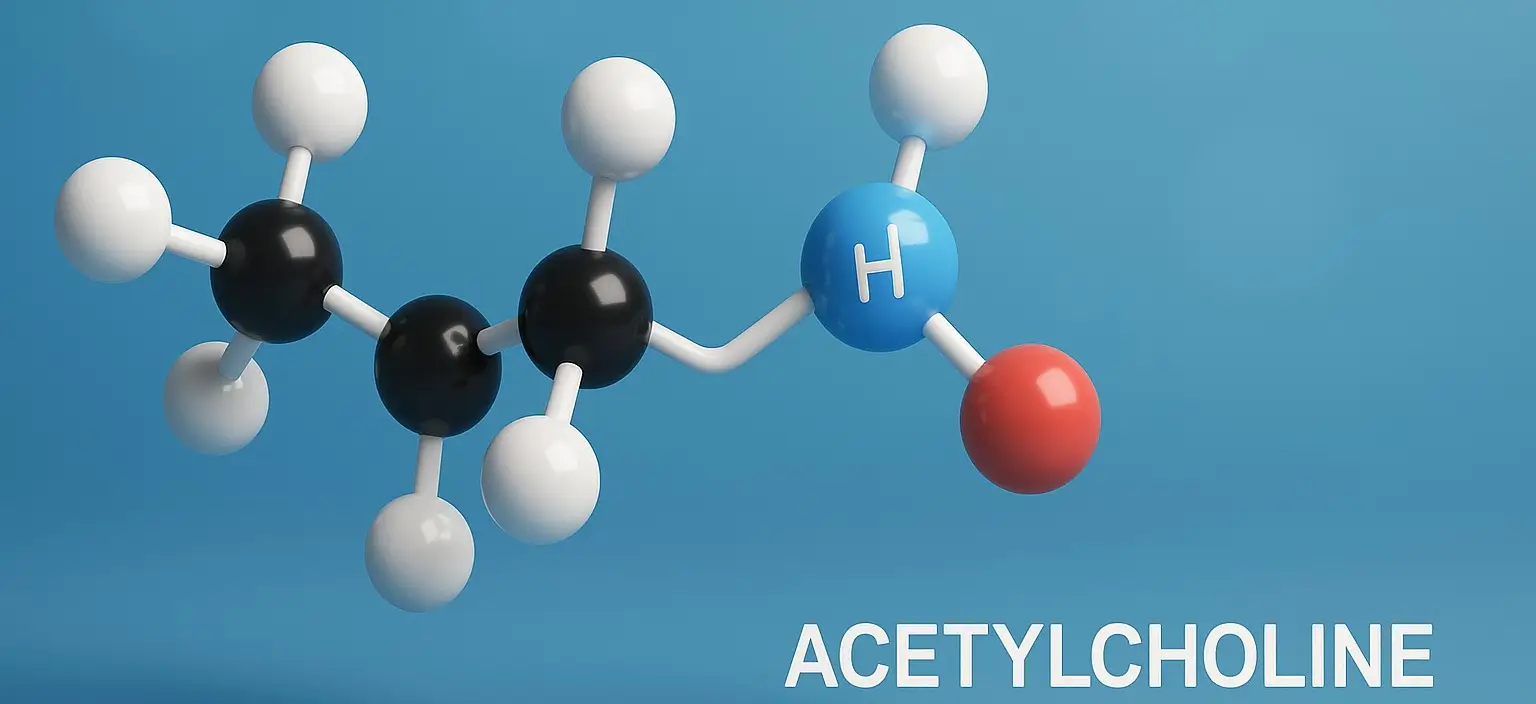
Acetylcholine
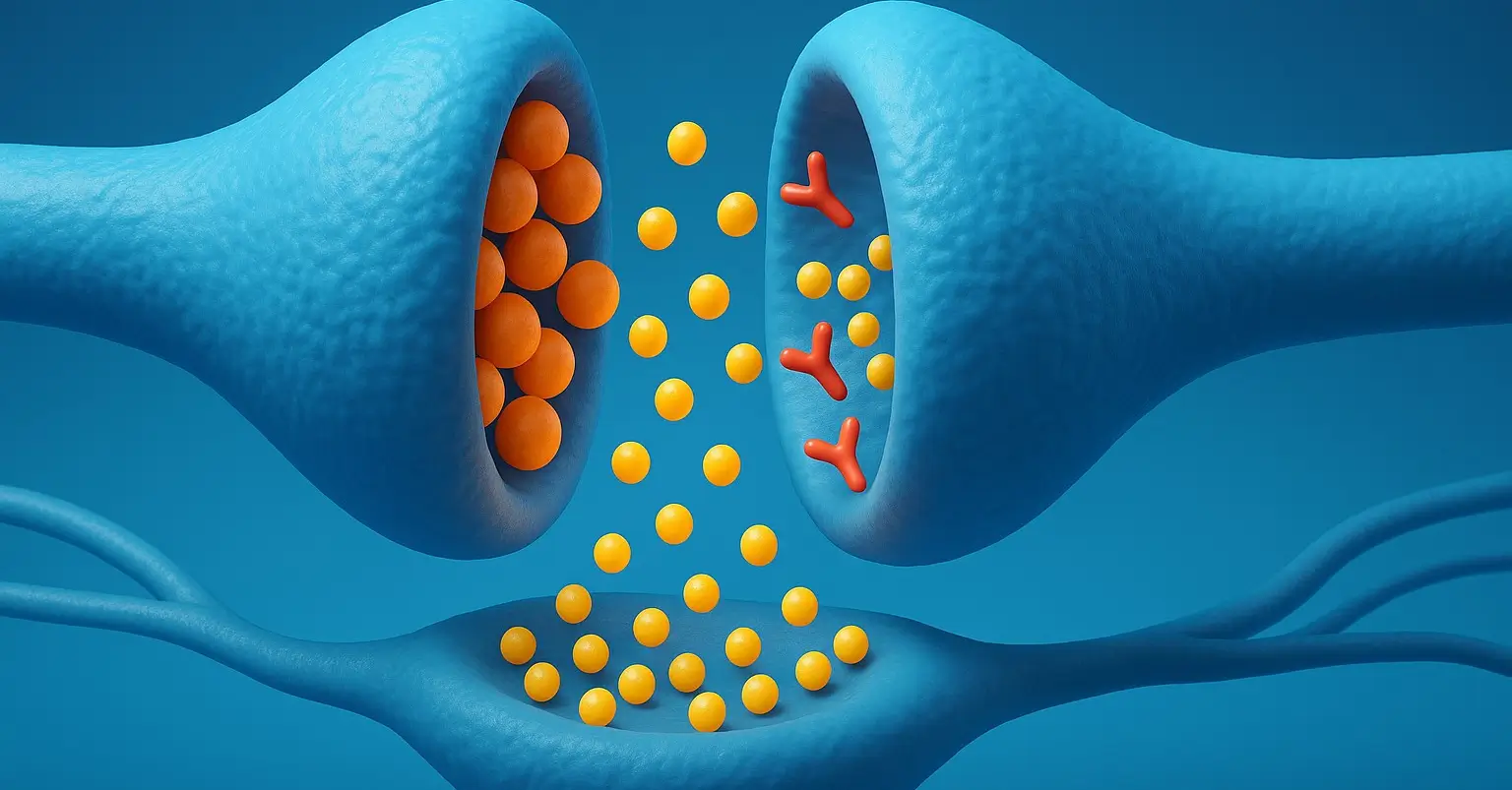
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter a chemical messenger that plays a key role in both the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). It is involved in transmitting nerve impulses across synapses, particularly at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, and within the brain. Chemical Formula: C₇H₁₆NO₂⁺ Mechanism of Action: Mimics acetylcholine at muscarinic and … Read more