Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR) Of Sympathomimetic Agents
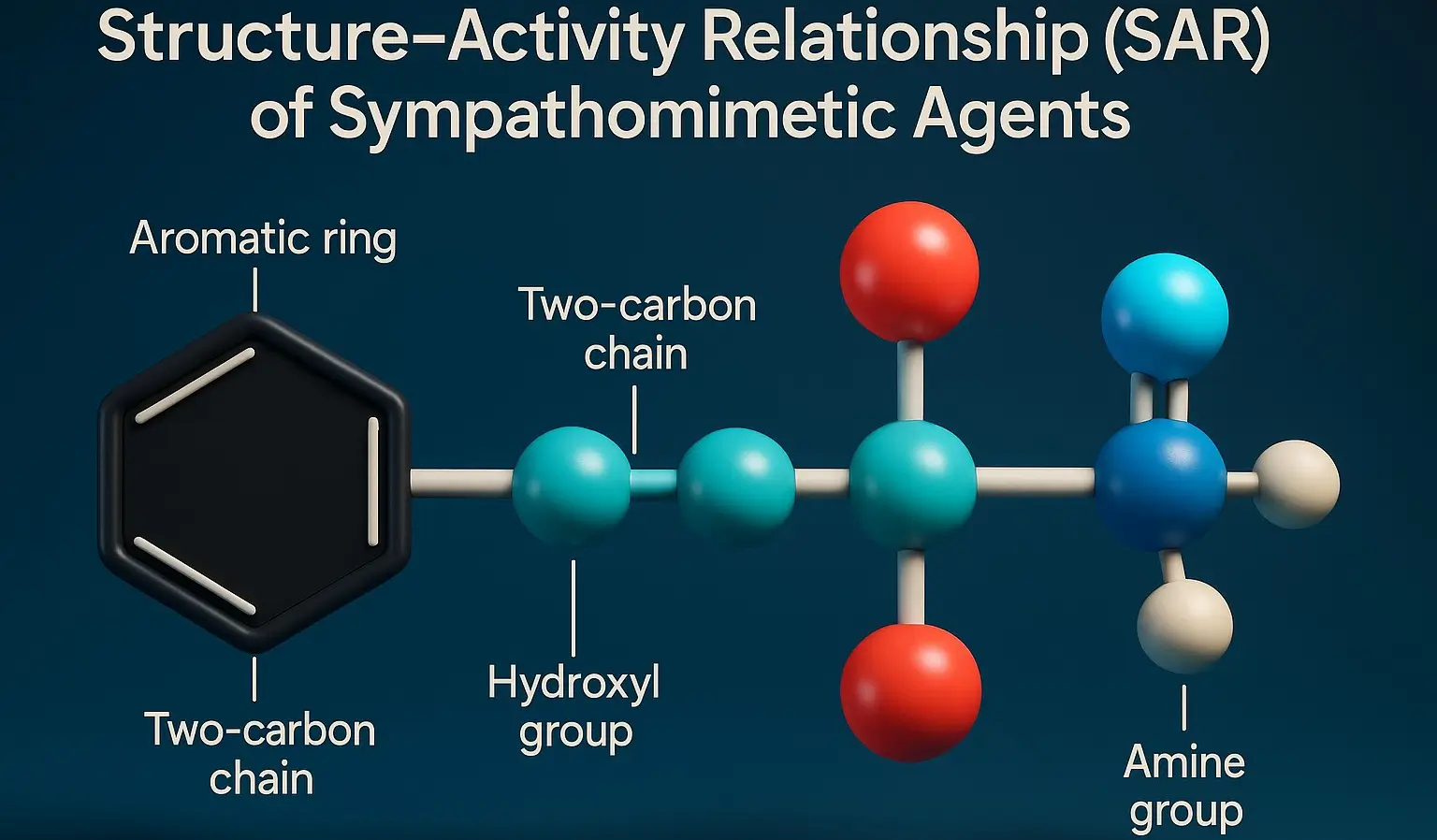
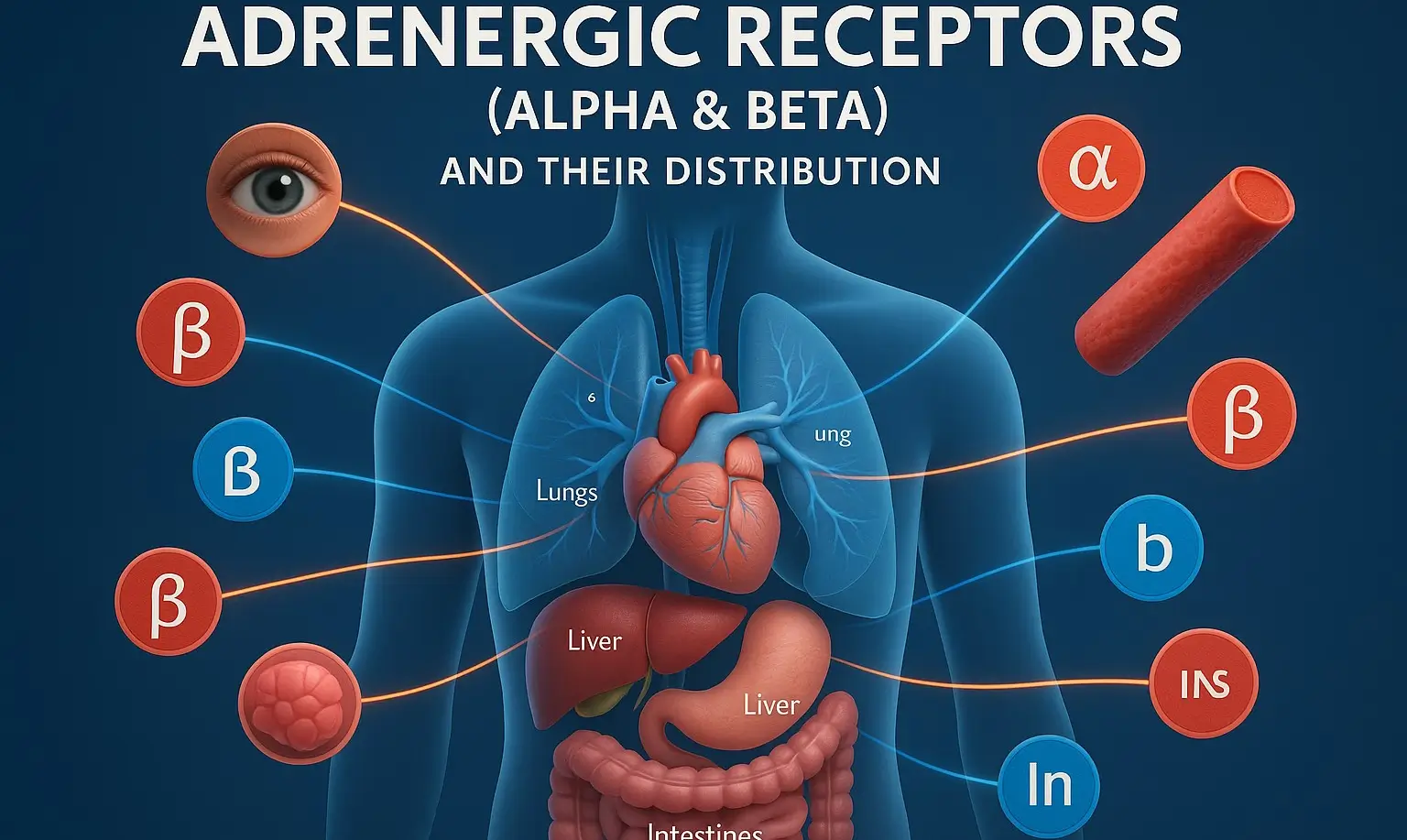
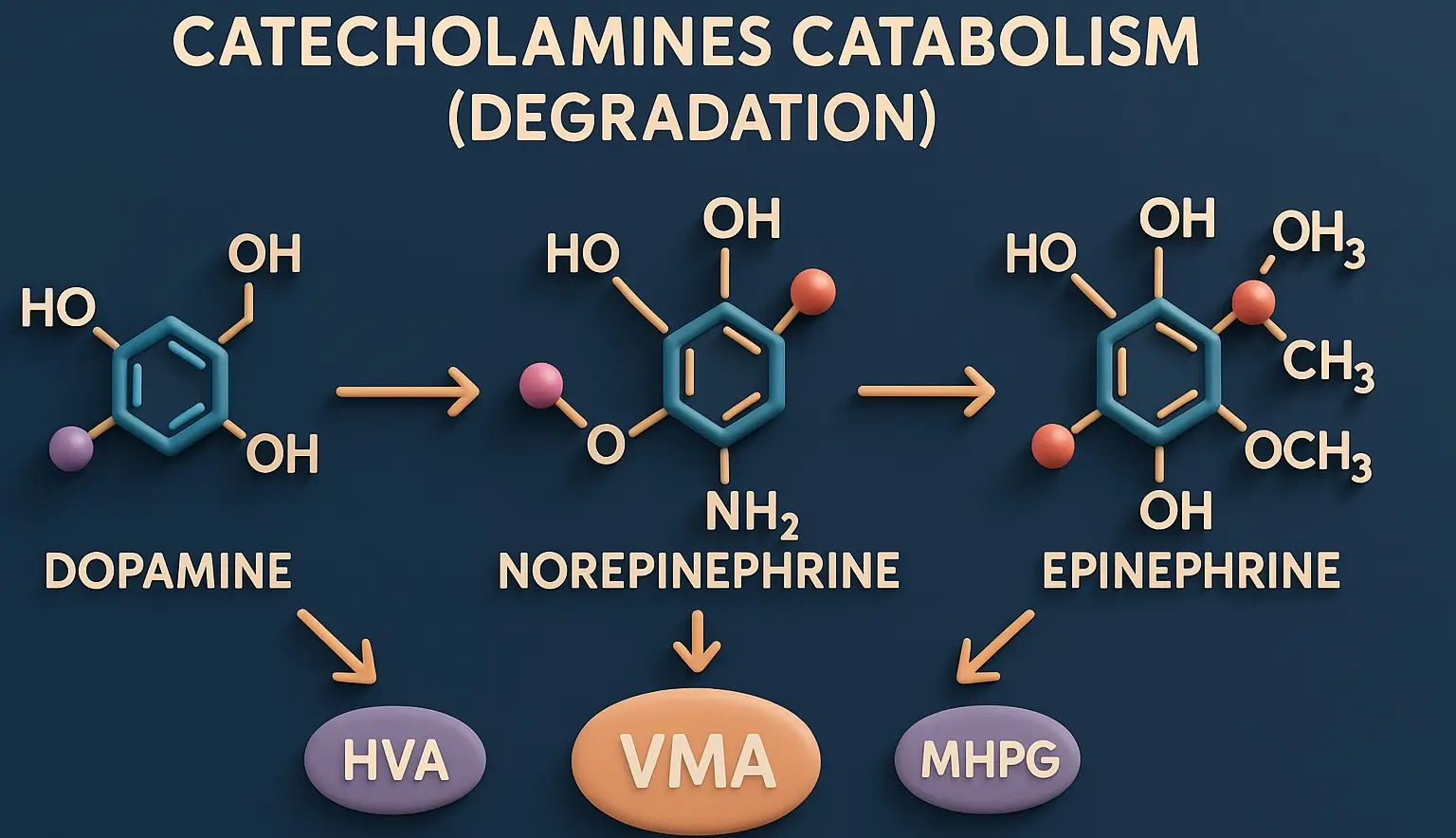
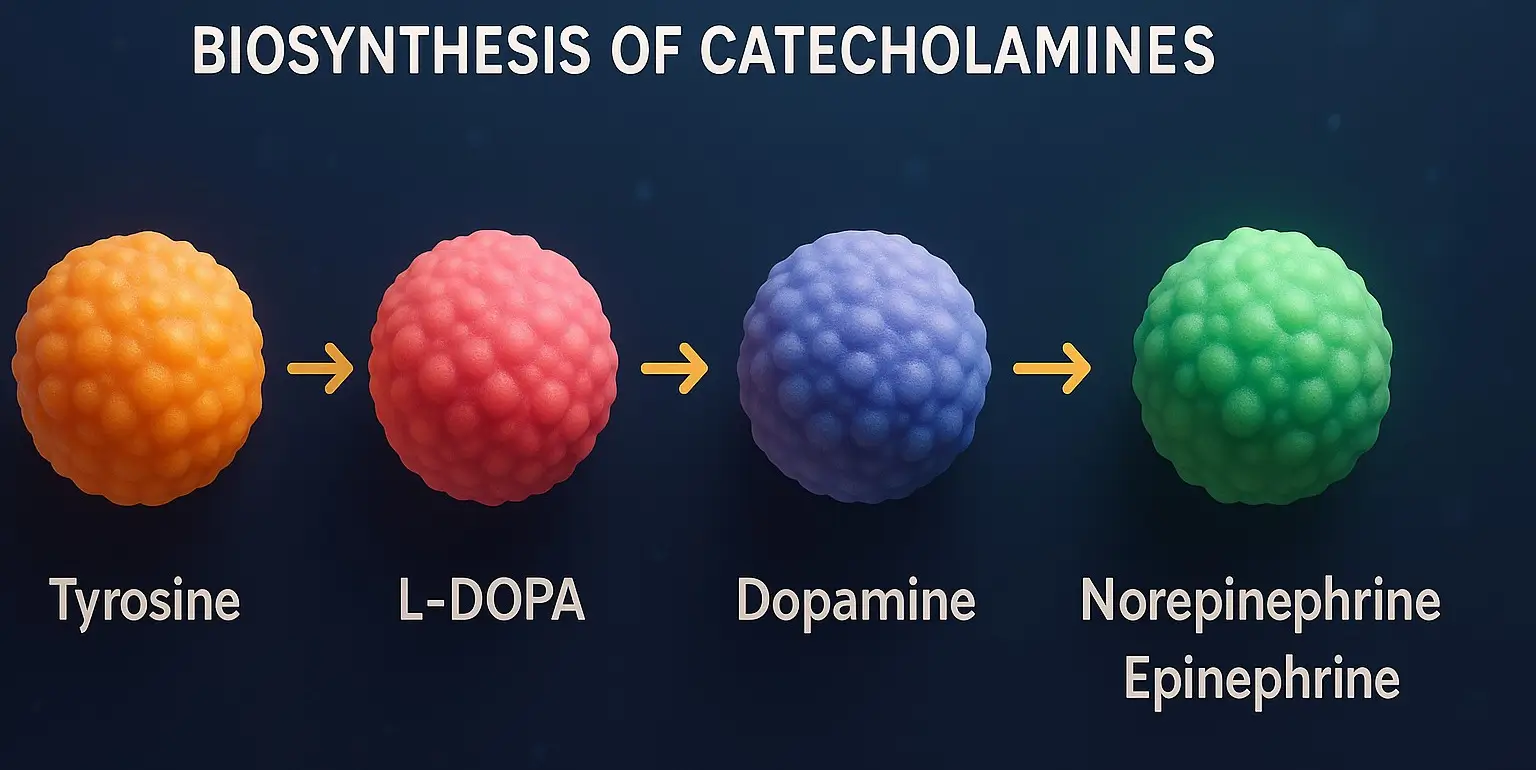
Structure-Activity Relationship mimic catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine) by stimulating adrenergic receptors (α and β). Their activity depends on structural modifications affecting receptor selectivity, metabolism, and CNS penetration. Key Structure-Activity Relationship Features Catechol Ring Substitutions 3,4-Dihydroxy (Catechol): High α/β activity, rapid metabolism (e.g., Epinephrine, Norepinephrine). Single Hydroxyl (-OH) Group: Reduces metabolism, increases α1 selectivity (e.g., Phenylephrine). No … Read more