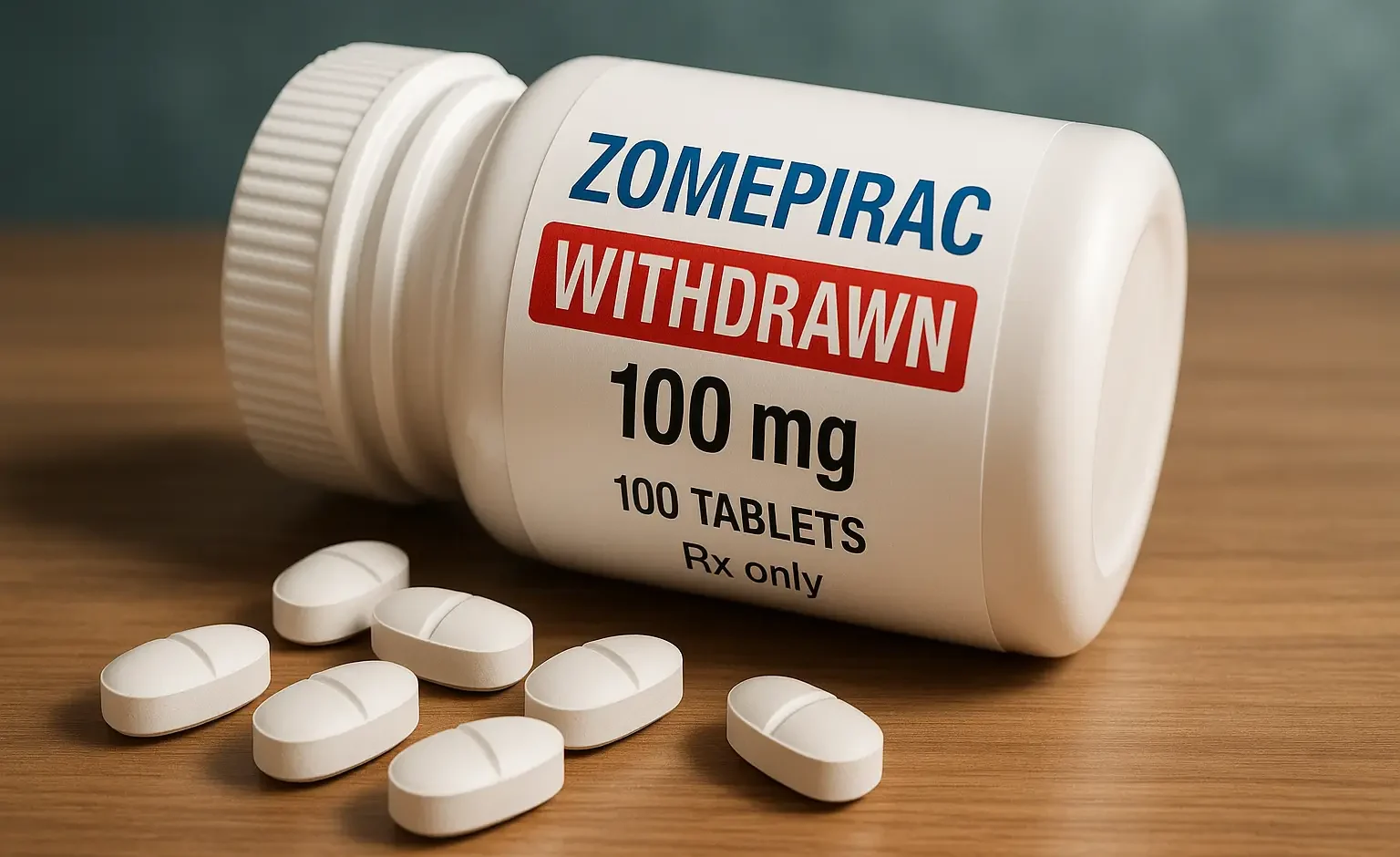
Zomepirac (Withdrawn)
Zomepirac (Withdrawn) was discontinued due to severe anaphylactic and hypersensitivity reactions. It was an NSAID once used for pain relief in arthritis and acute conditions. Chemical Formula: C₁₁H₁₂N₂O₃ Mechanism of Zomepirac (Withdrawn): Non-selective COX inhibitor Uses of Zomepirac (Withdrawn): Formerly used for moderate to severe pain Side Effects: Fatal anaphylactic reactions GI toxicity Notes: Withdrawn … Read more