Isoflurane
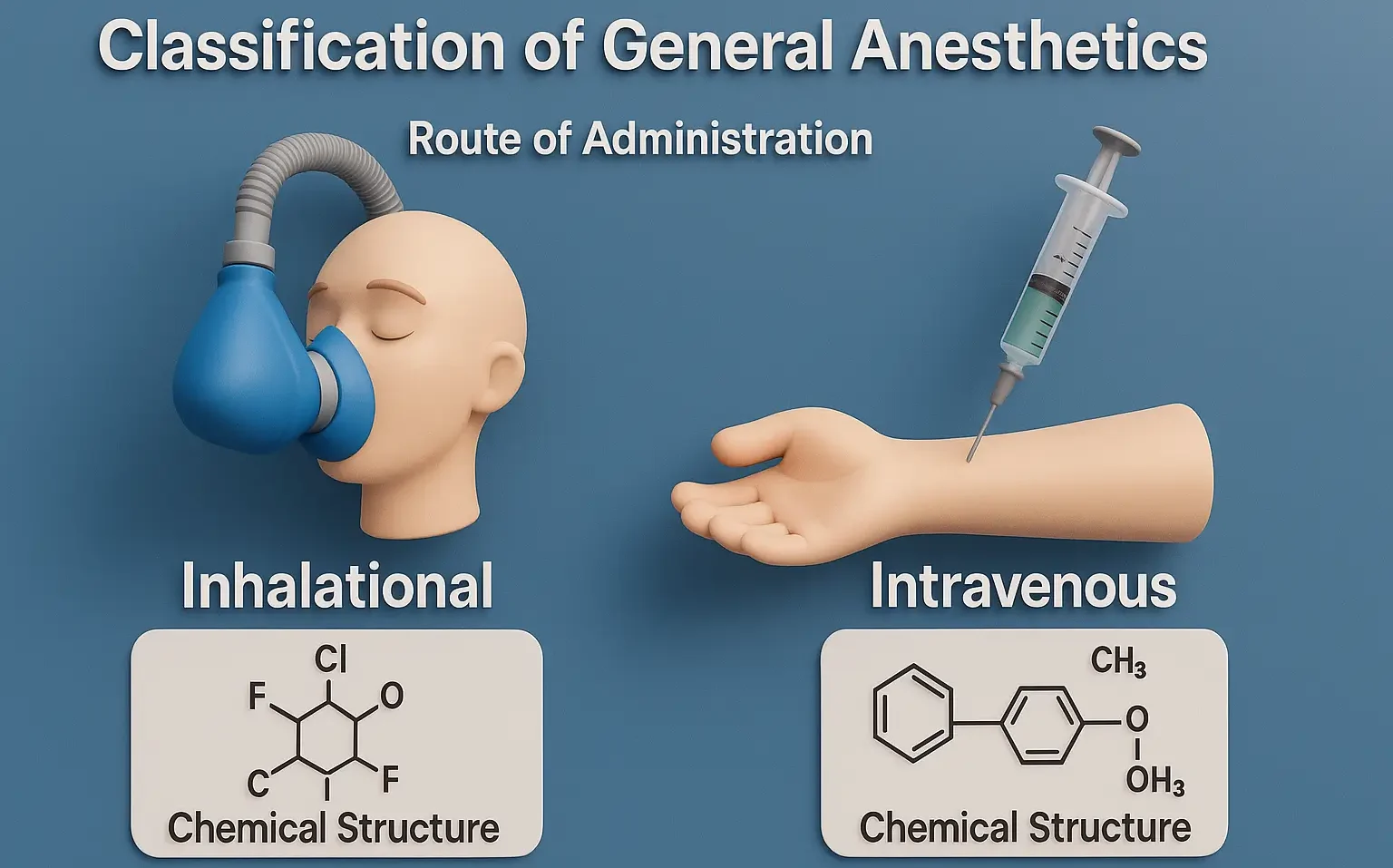
Isoflurane enhances GABA activity, causing CNS depression with rapid onset and smooth recovery. It is an inhalation anesthetic used for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. Chemical Formula: C₃H₂ClF₅O Mechanism of Isoflurane: GABA-A receptor potentiation Inhibits NMDA receptors, 2-pore domain K+ channels Uses of Isoflurane: Maintenance of anesthesia Side Effects: Airway irritation (not ideal for … Read more