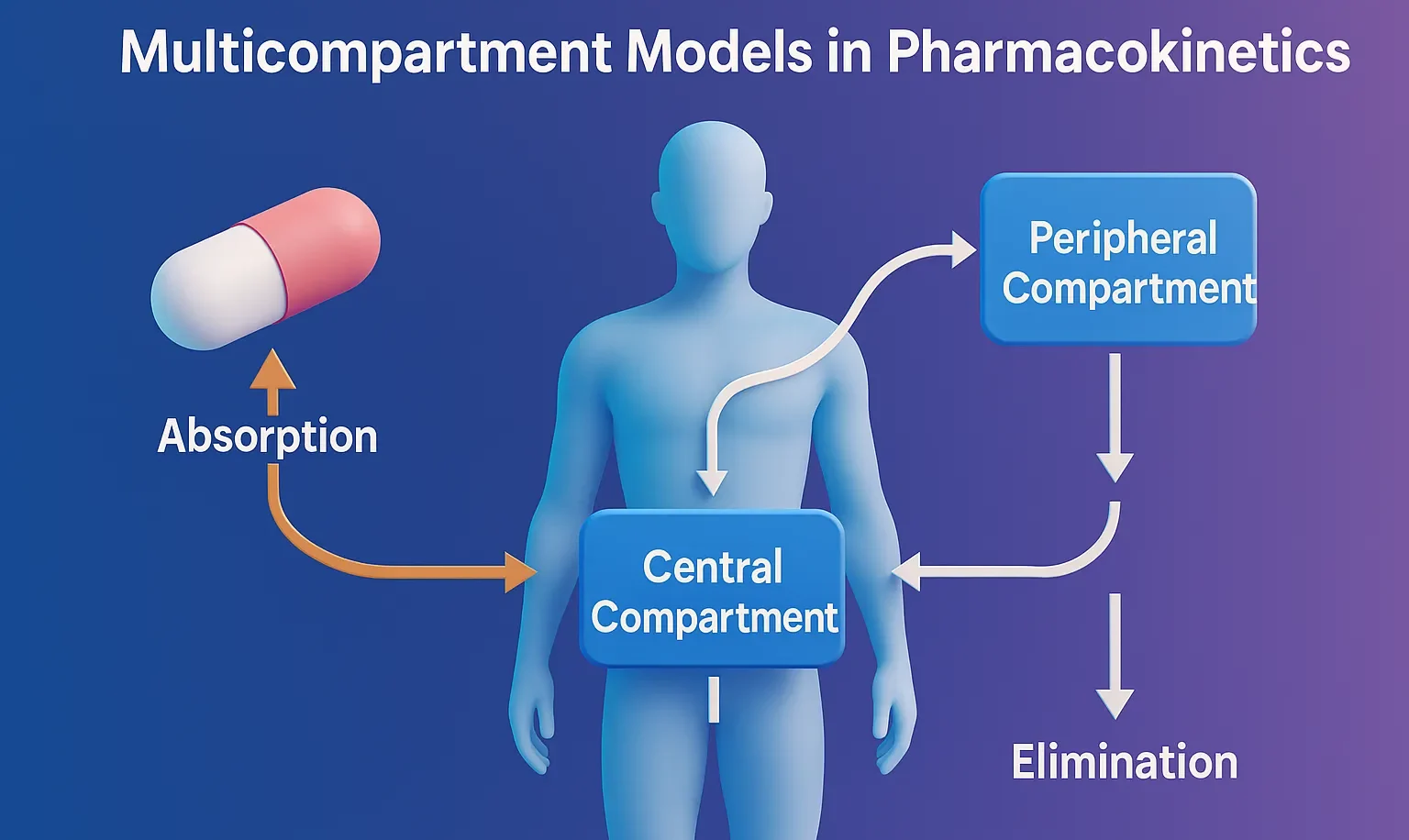
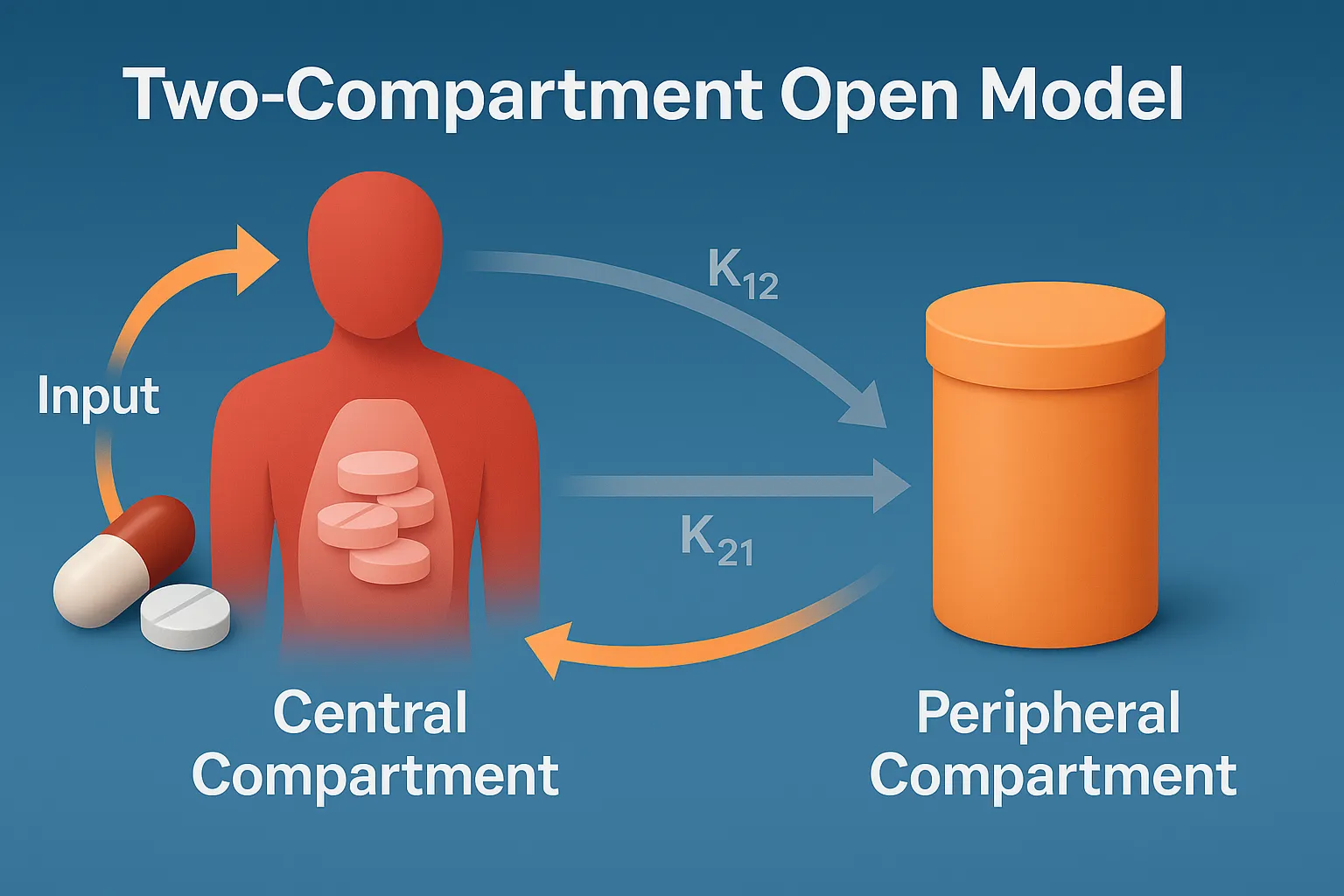
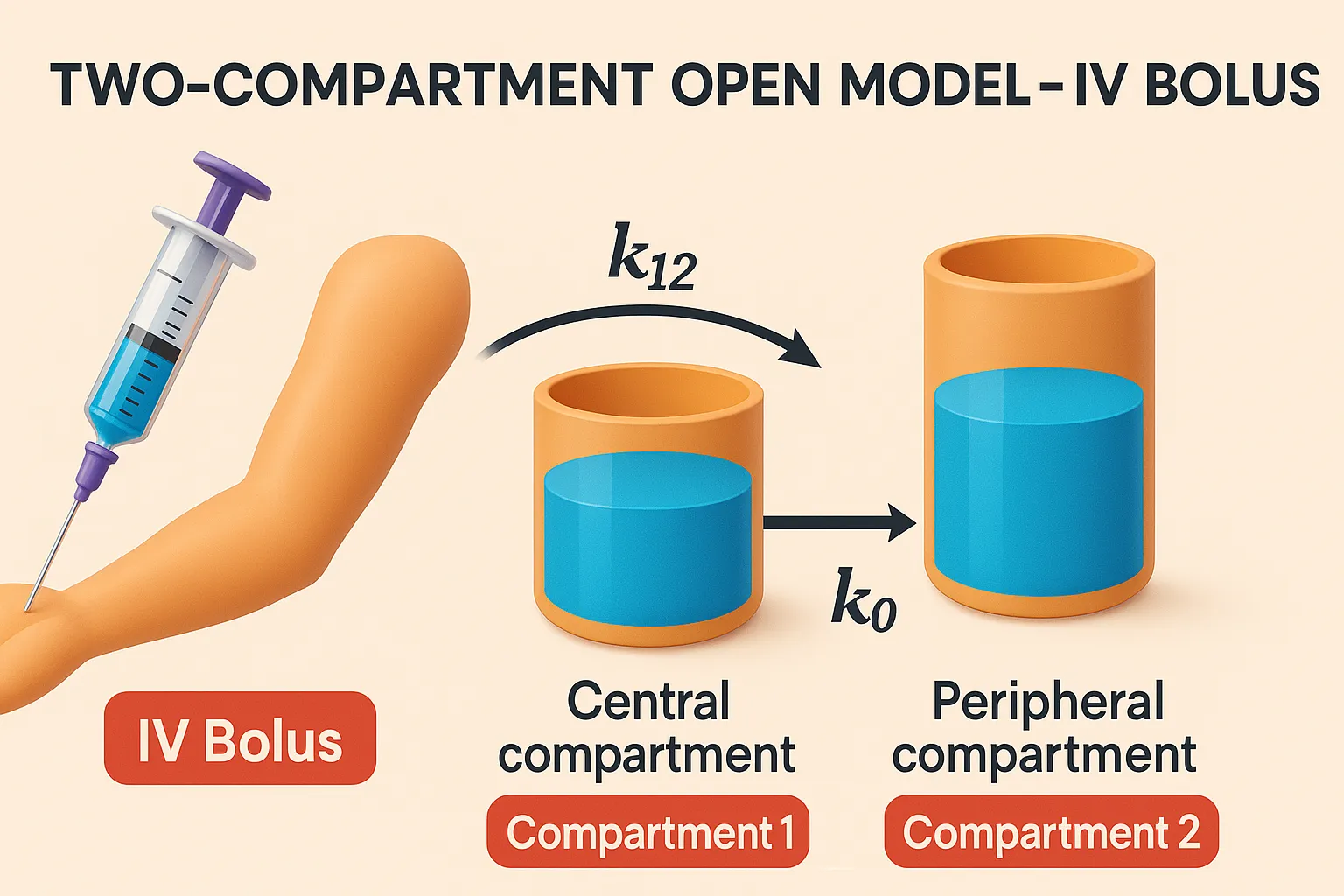
Efflorescent Powders
Efflorescent powders refer to a class of pharmaceutical powders that contain hydrates, which are substances that have water molecules incorporated into their crystal structure. When these hydrates are exposed to a low-humidity environment or are subjected to heat, they can release water molecules, a process known as efflorescence. Although efflorescent powders aren’t a specific type … Read more