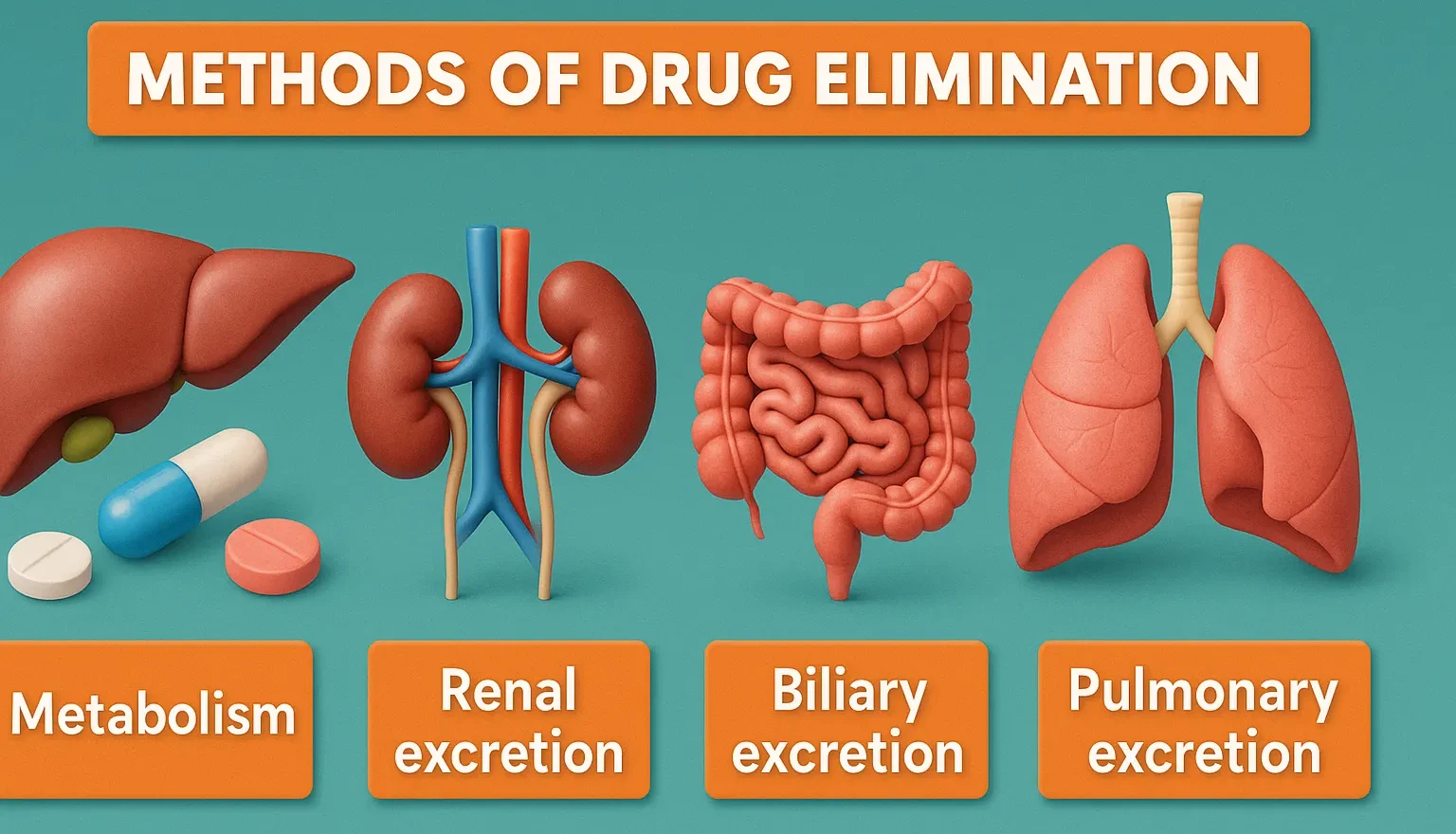
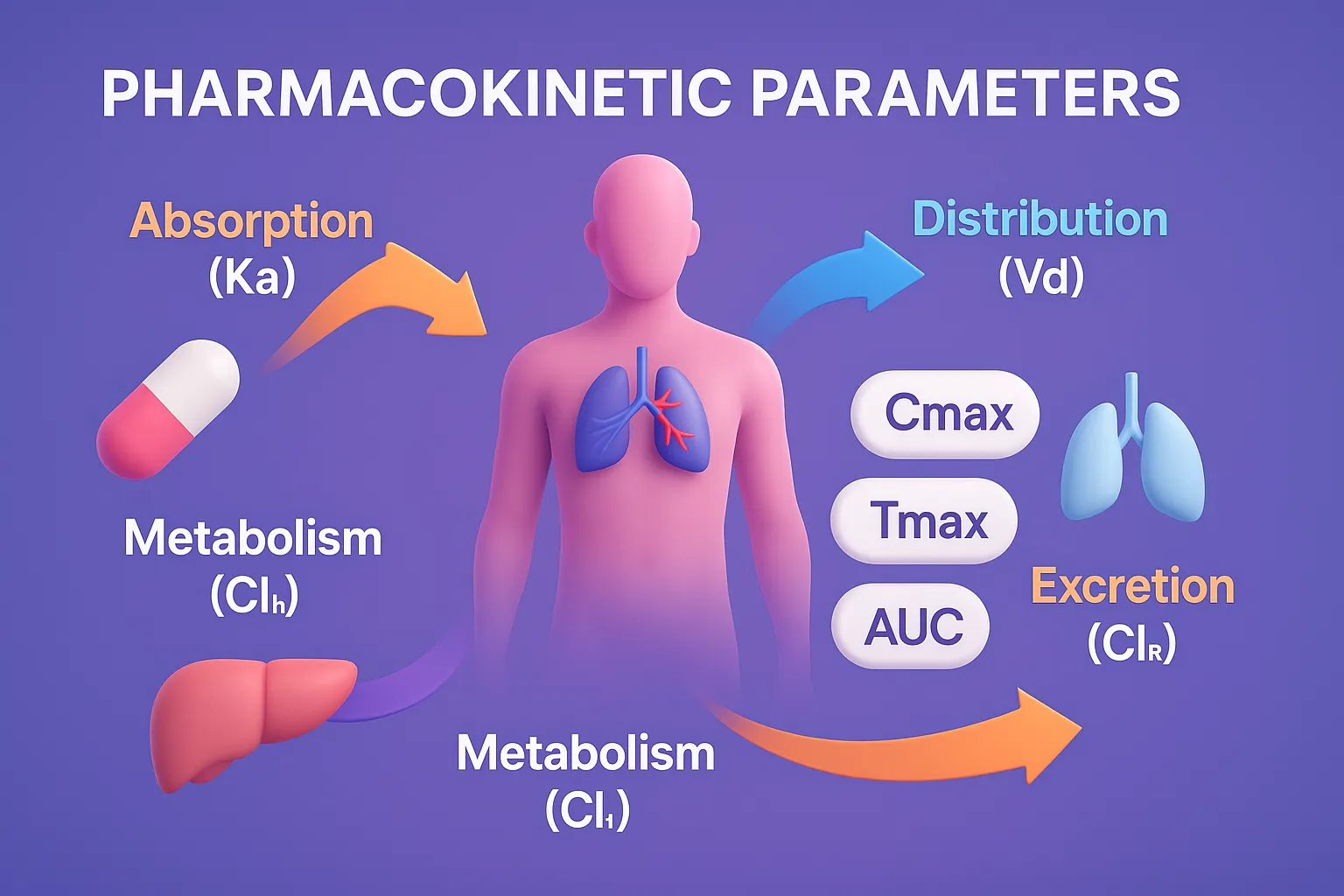
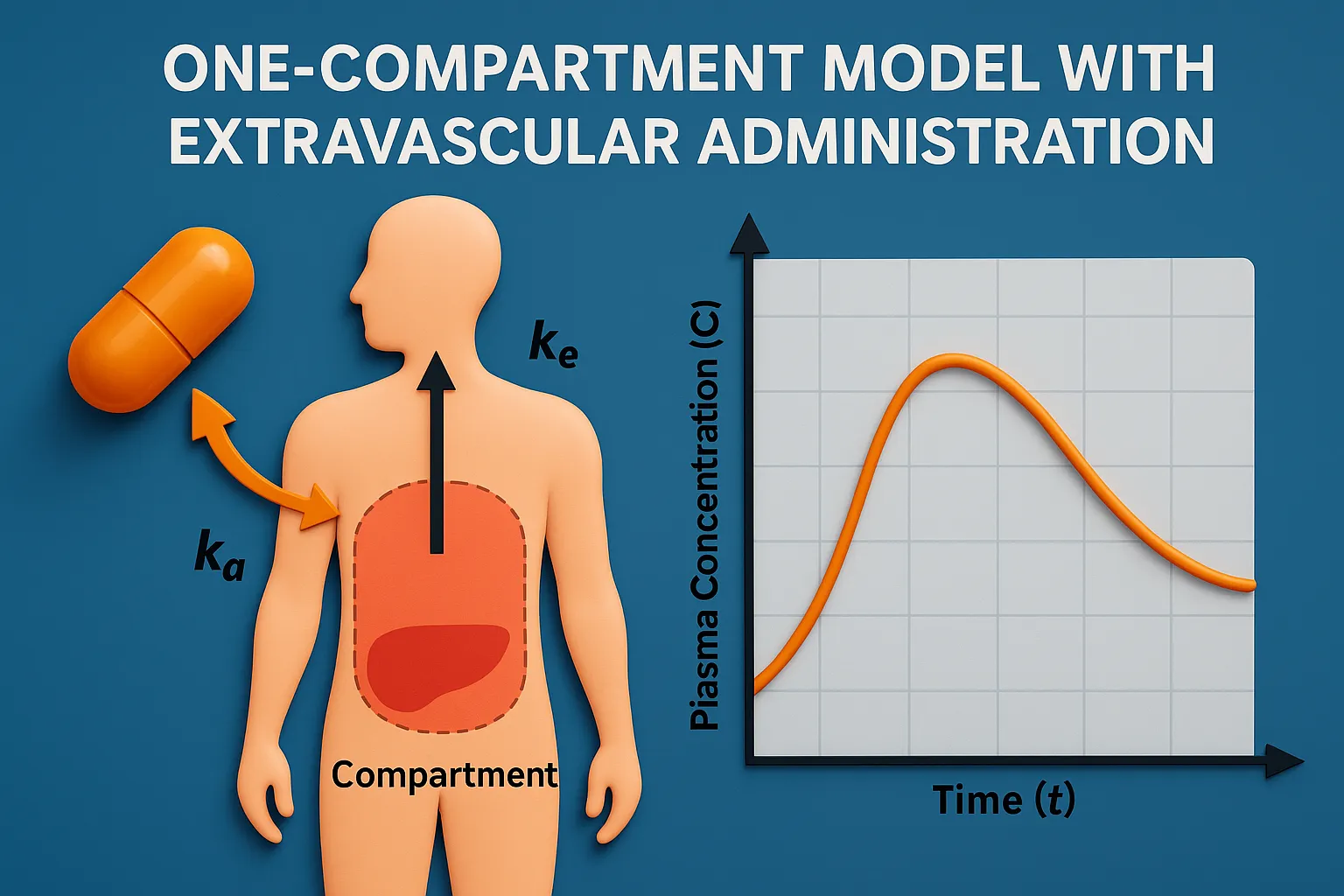
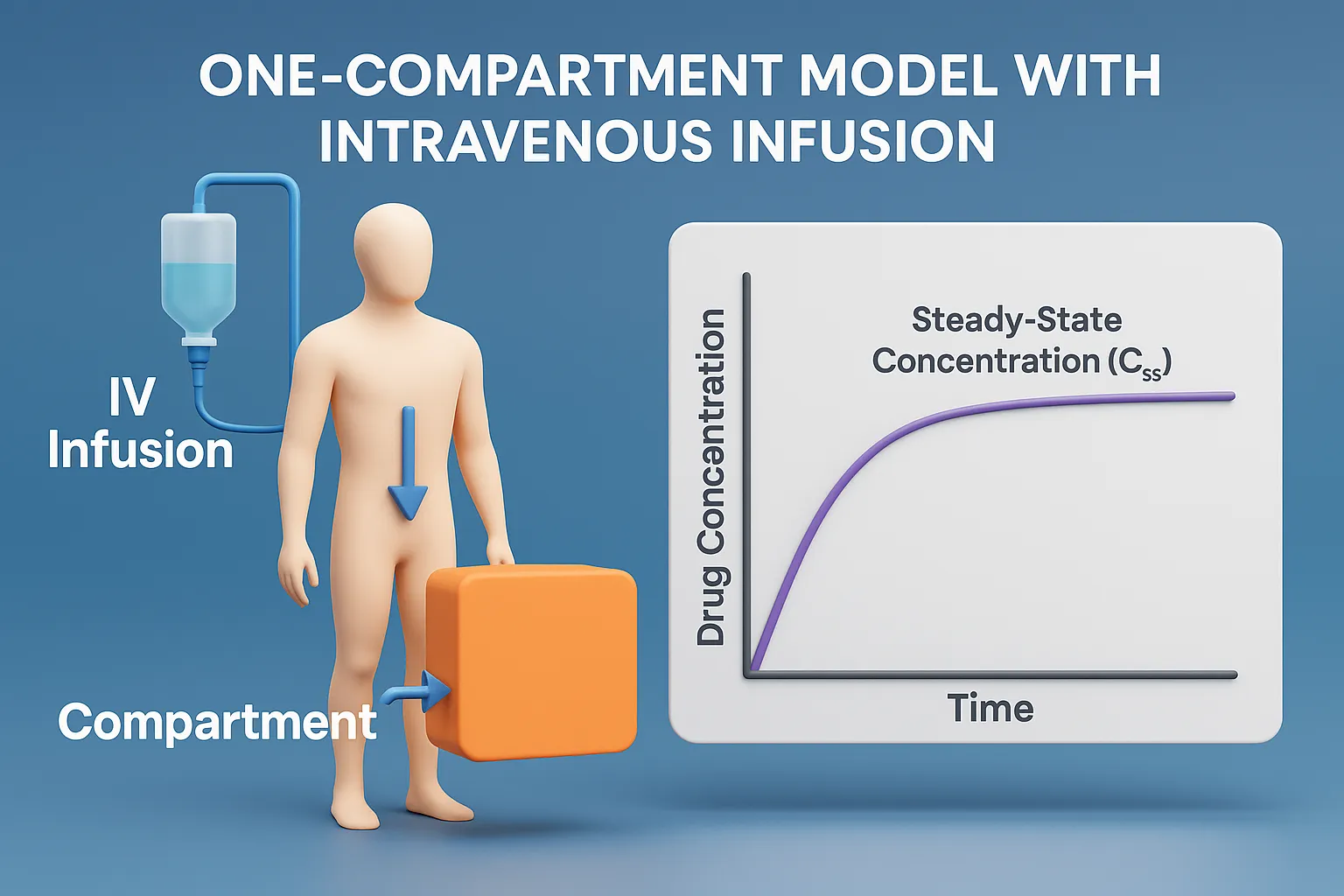
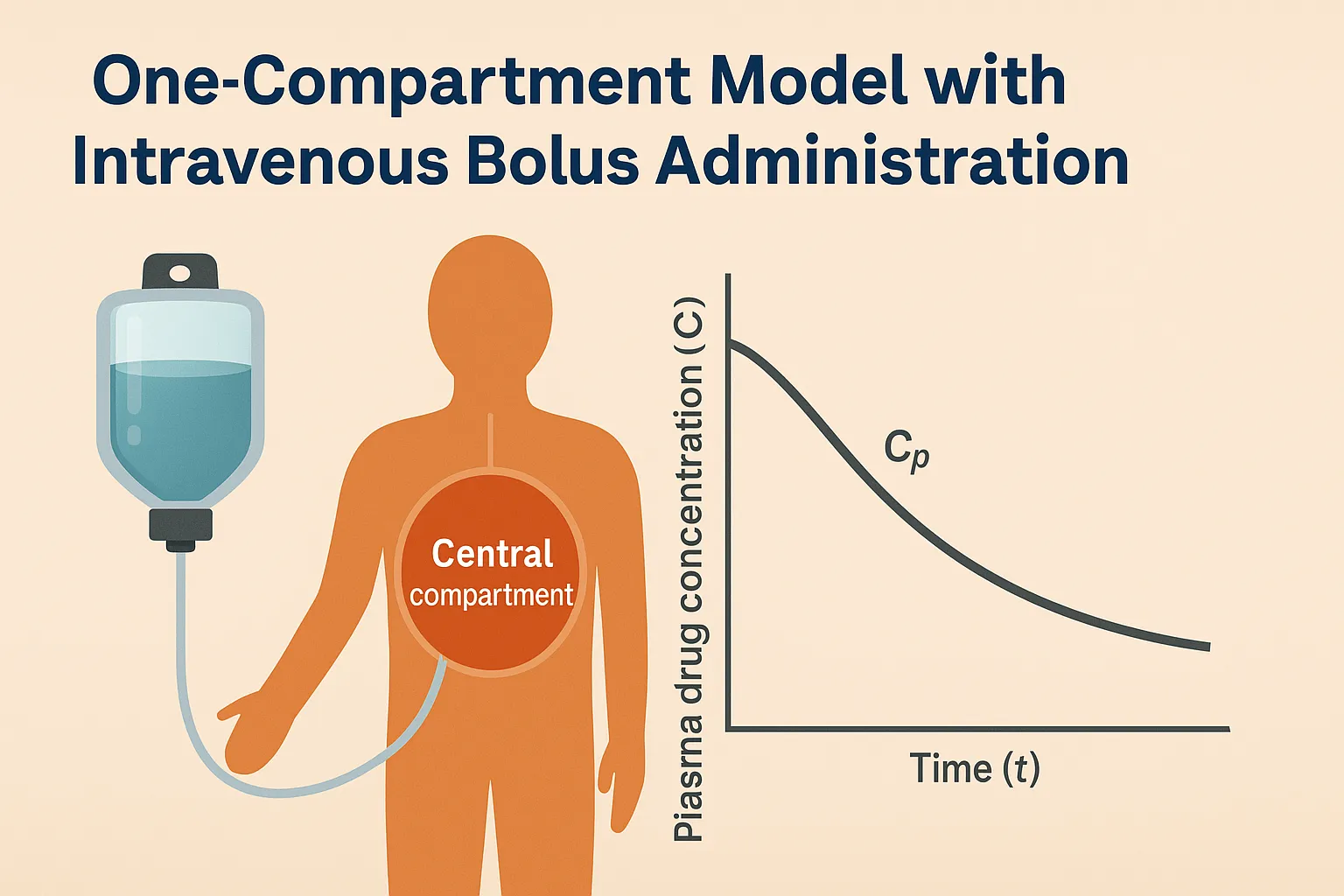
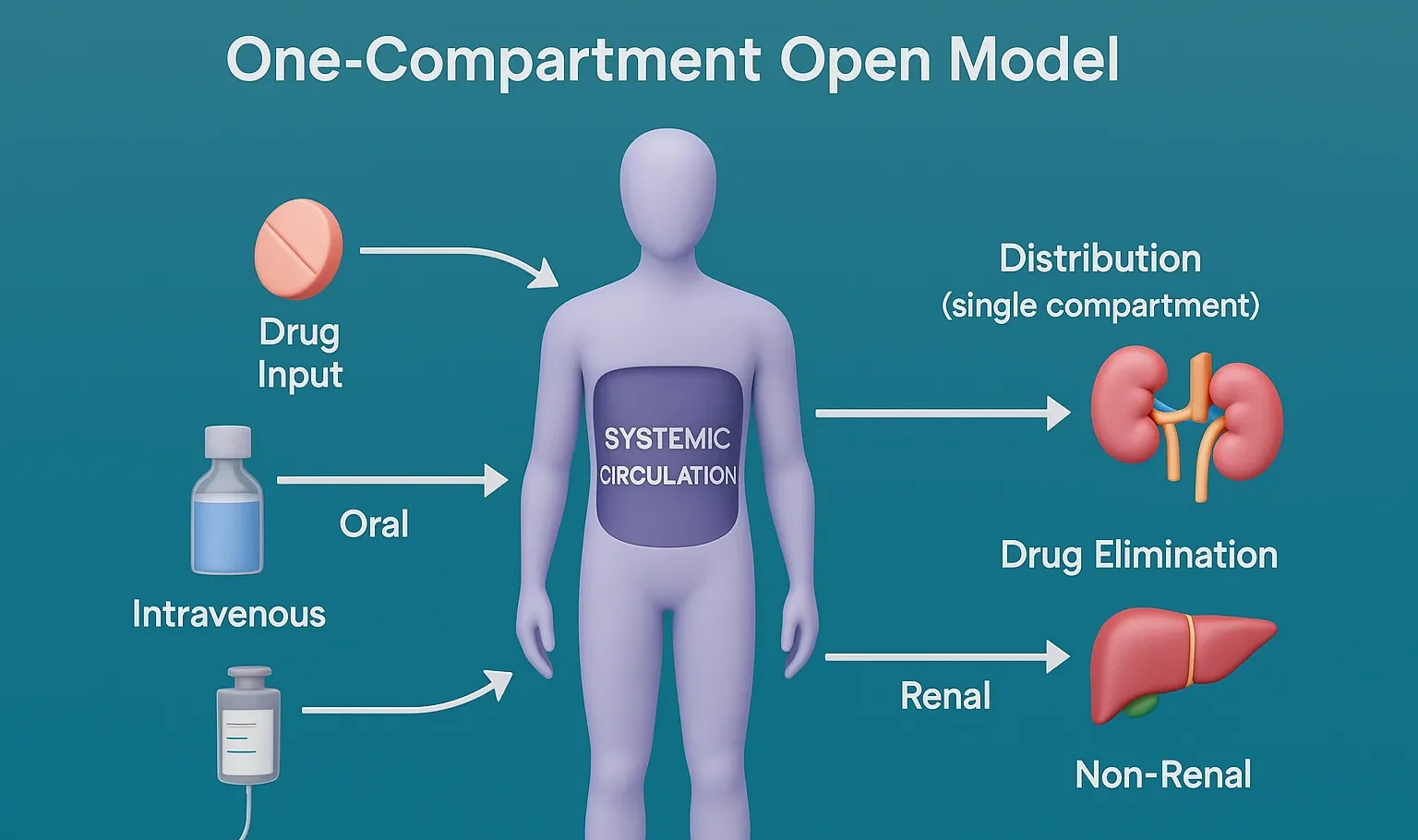
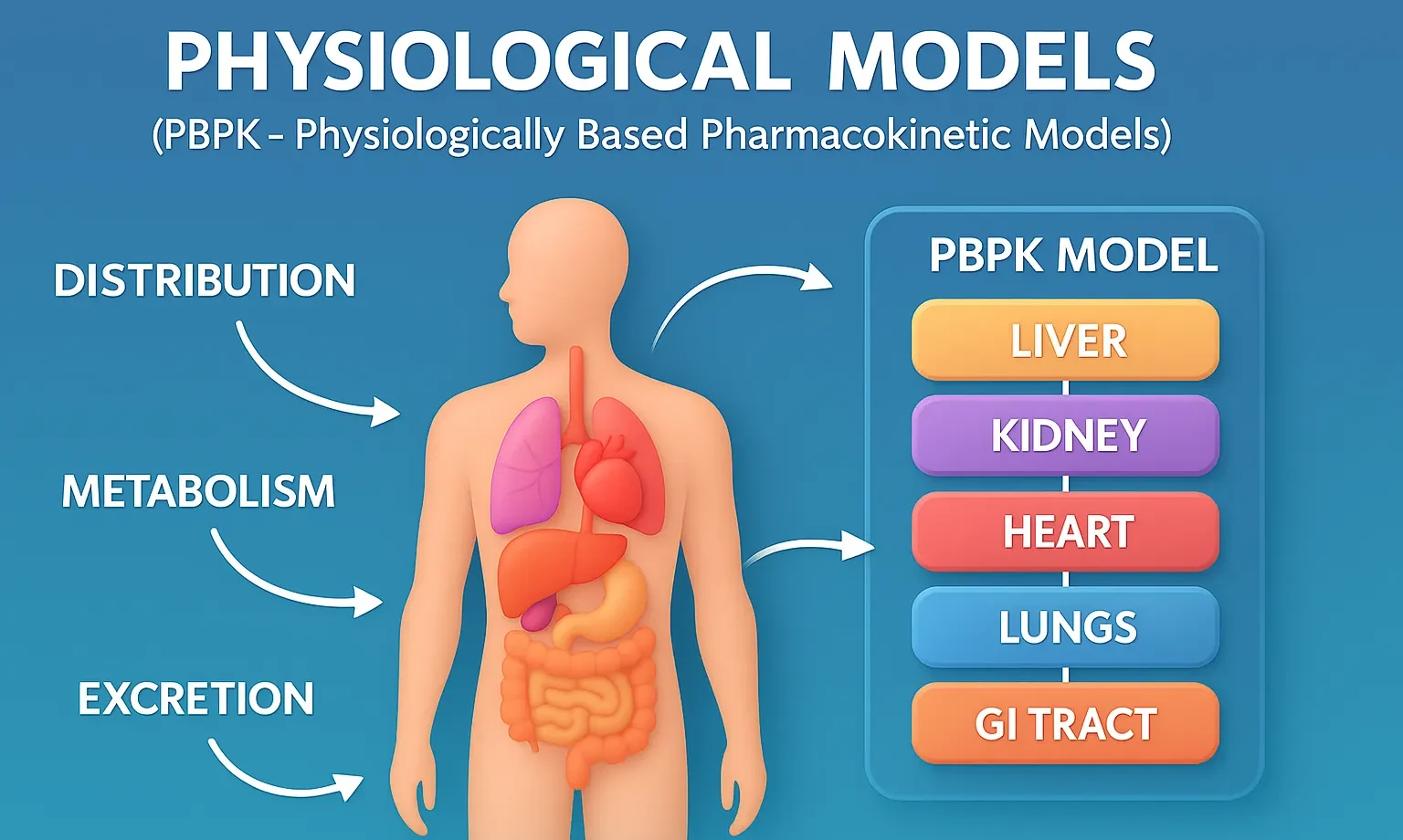
Isotonic solutions
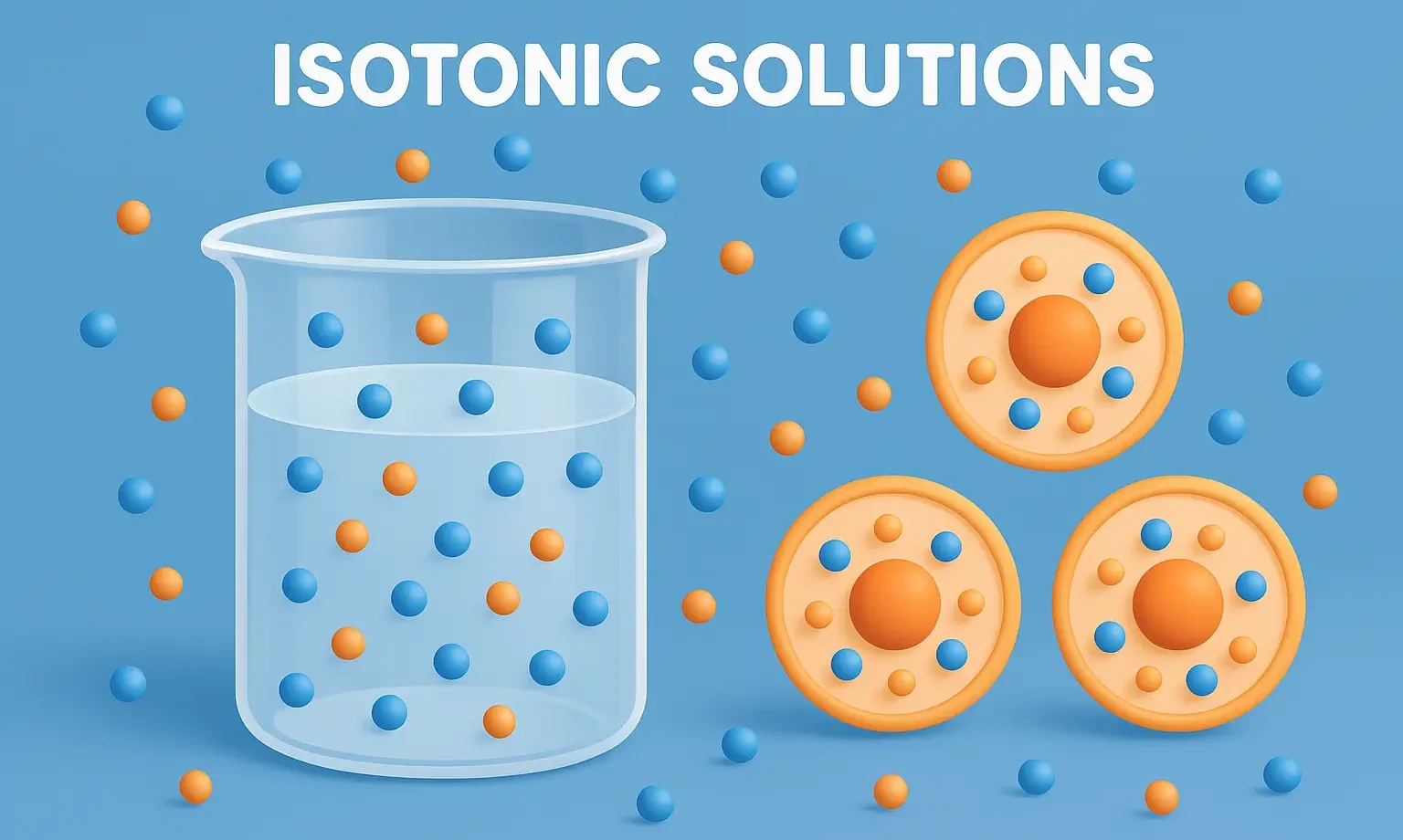
An Isotonic Solutions has the same osmotic pressure as body fluids, preventing cell damage by maintaining balance between fluids. Isotonicity and Freezing Point Depression Isotonic solutions match the freezing point depression of body fluids, around -0.52°C. Example: 9 Percent NaCl solution is isotonic with blood (normal saline). Isotonicity and Molecular Weight The osmotic pressure depends … Read more