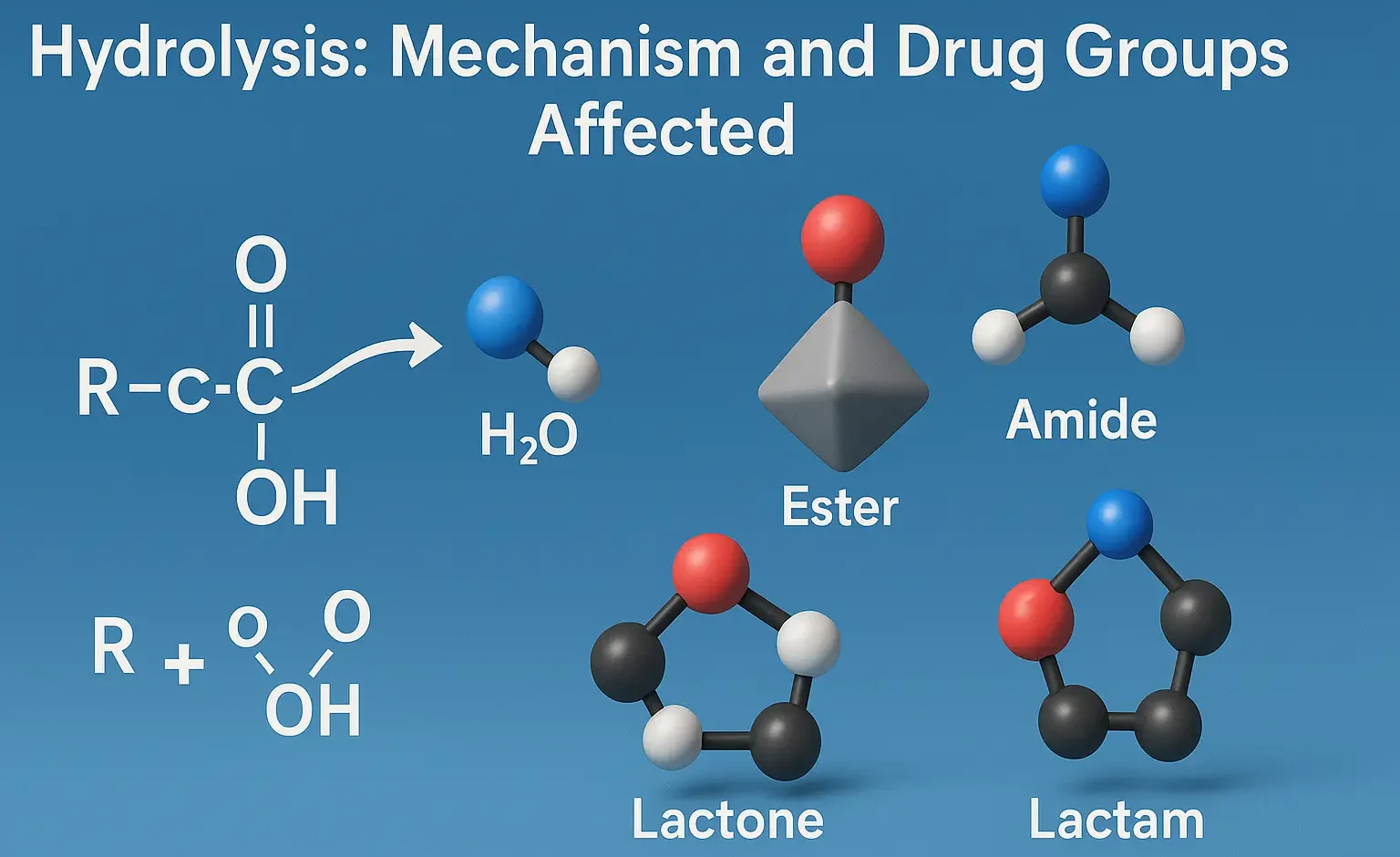
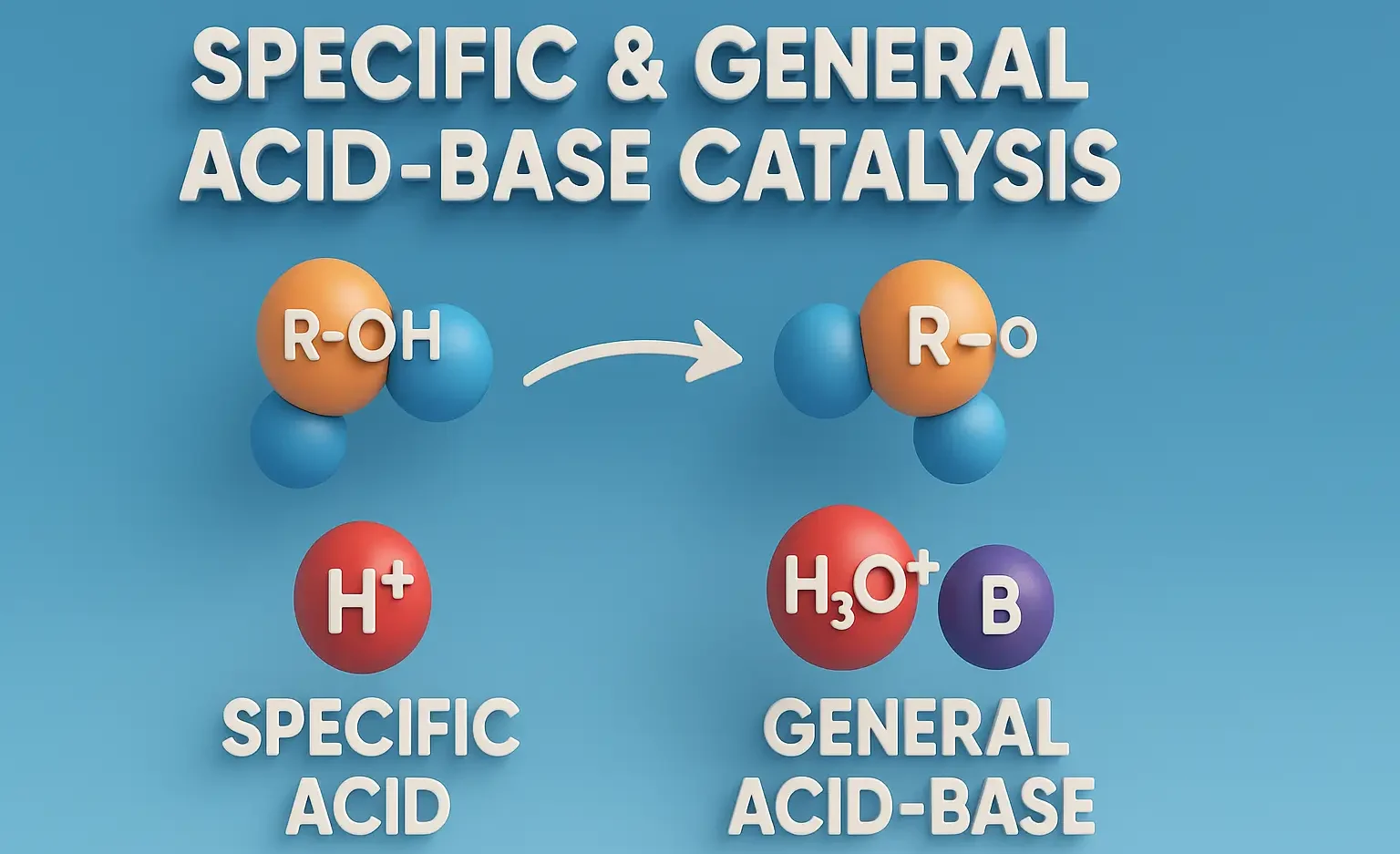
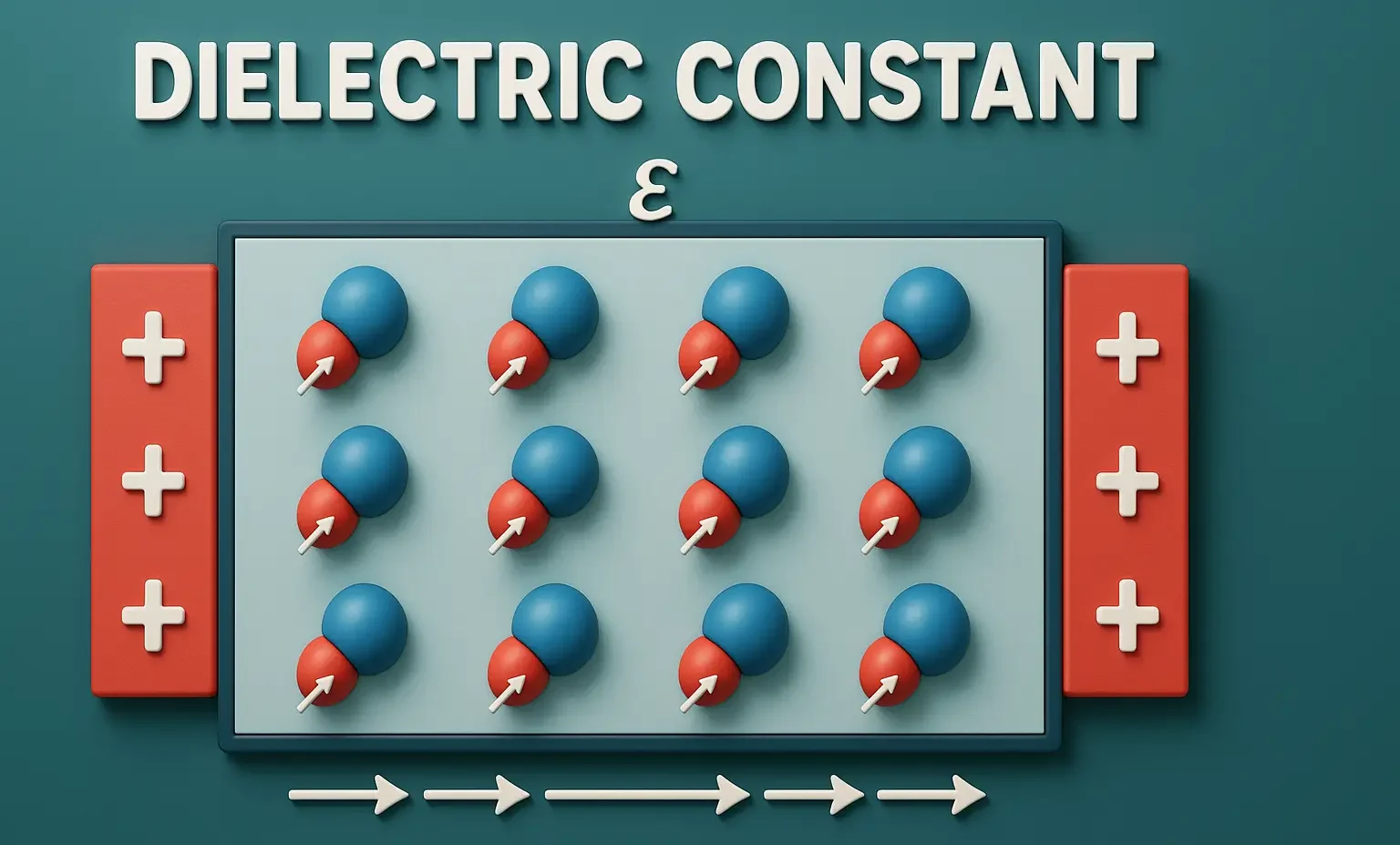
History of Indian pharmacyHistory of Indian pharmacy
Dosage forms are the physical formulations of drugs, prepared to ensure the safe, effective, and accurate administration of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) to patients. They are designed to account for various factors, including the drug’s properties, pharmacokinetics (how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted), pharmacodynamics (the effects of the drug on the … Read more