Kinetics of Protein Binding
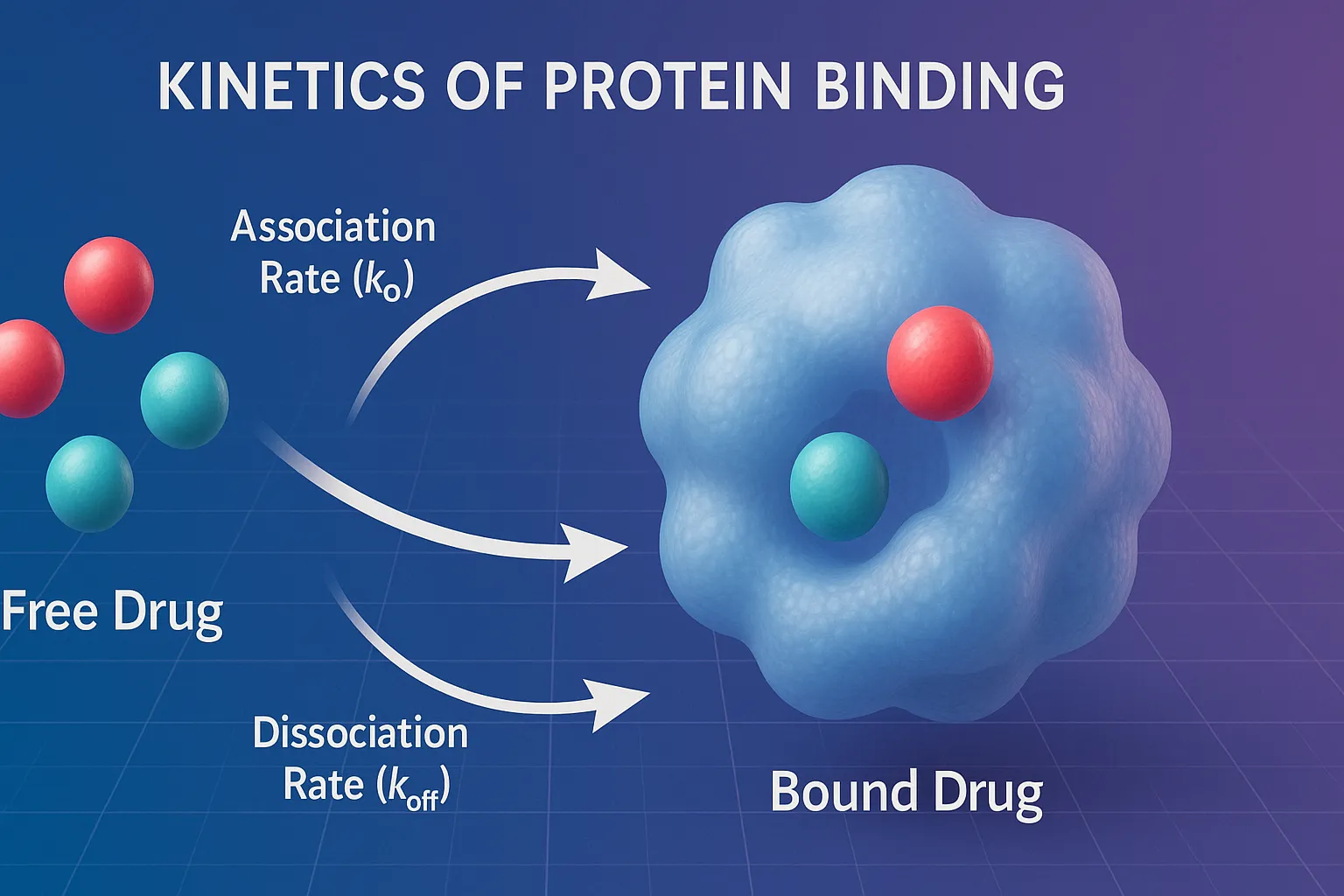
Kinetics of Protein Binding describes drug–protein association and dissociation rates impacting pharmacokinetics and dynamics. Protein binding kinetics describes the interaction between a drug (D) and a protein (P) to form a drug-protein complex (DP). This process follows a reversible equilibrium: $D + P \;\rightleftharpoons\; DP$ Rate of Drug-Protein Binding The association and dissociation of drug-protein … Read more