Stability of Emulsions
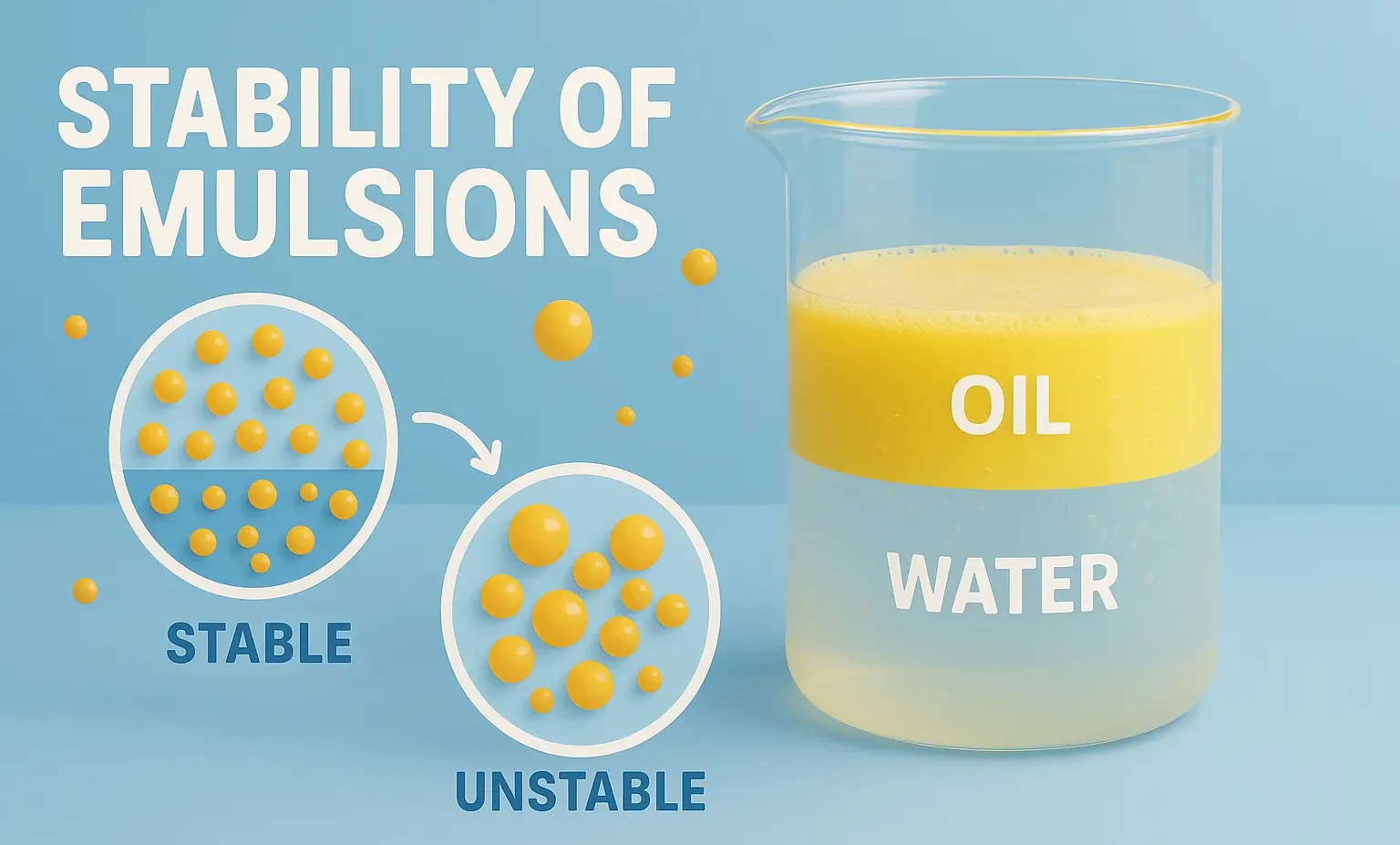
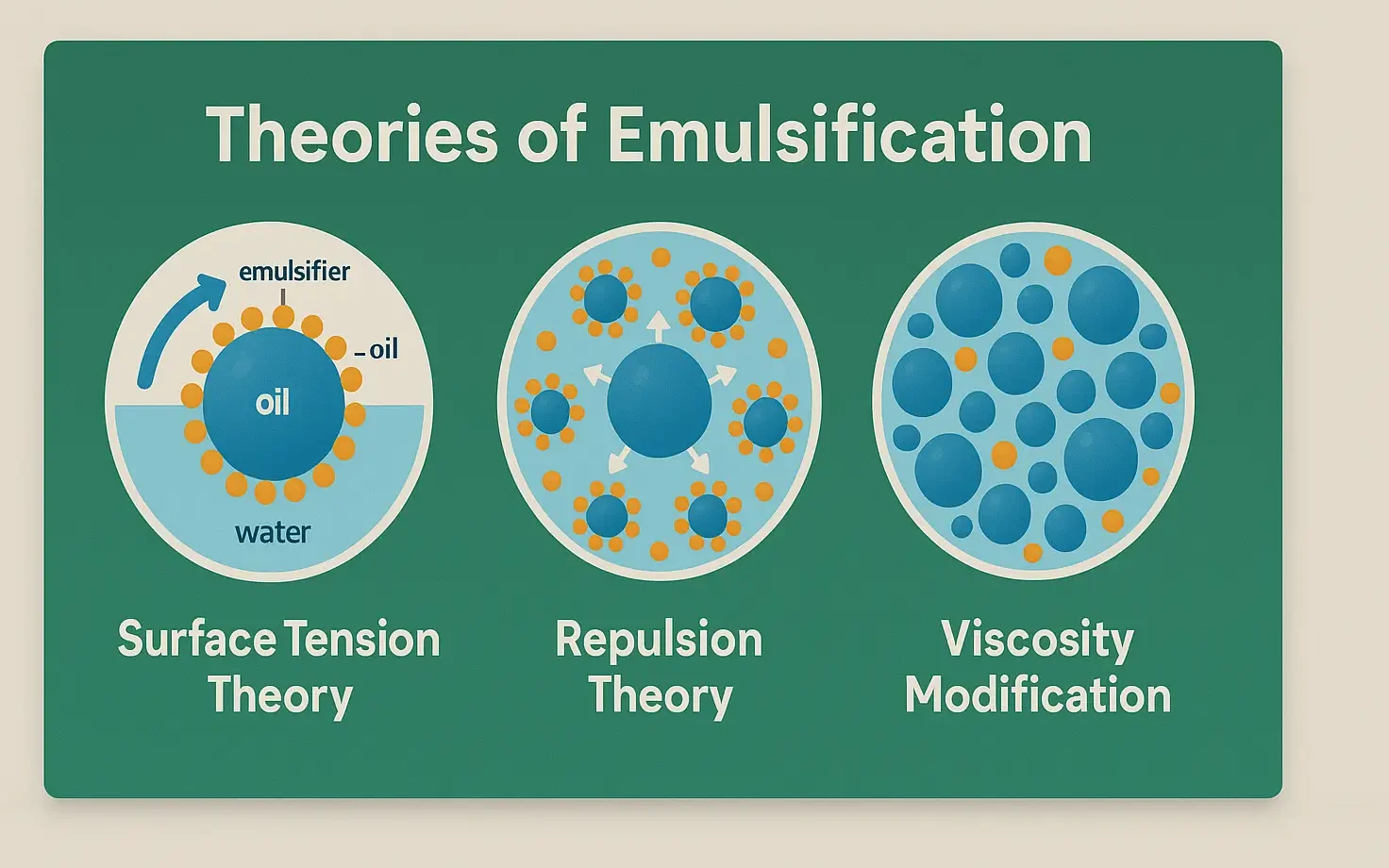
Stability of Emulsions refers to the ability of dispersed droplets to resist coalescence and phase separation. It is vital in pharmaceuticals, foods, and cosmetics for product effectiveness. Stability refers to the ability of an emulsion to resist changes such as separation, creaming, cracking, or phase inversion over time. Types of Instability in Emulsions Instability may … Read more