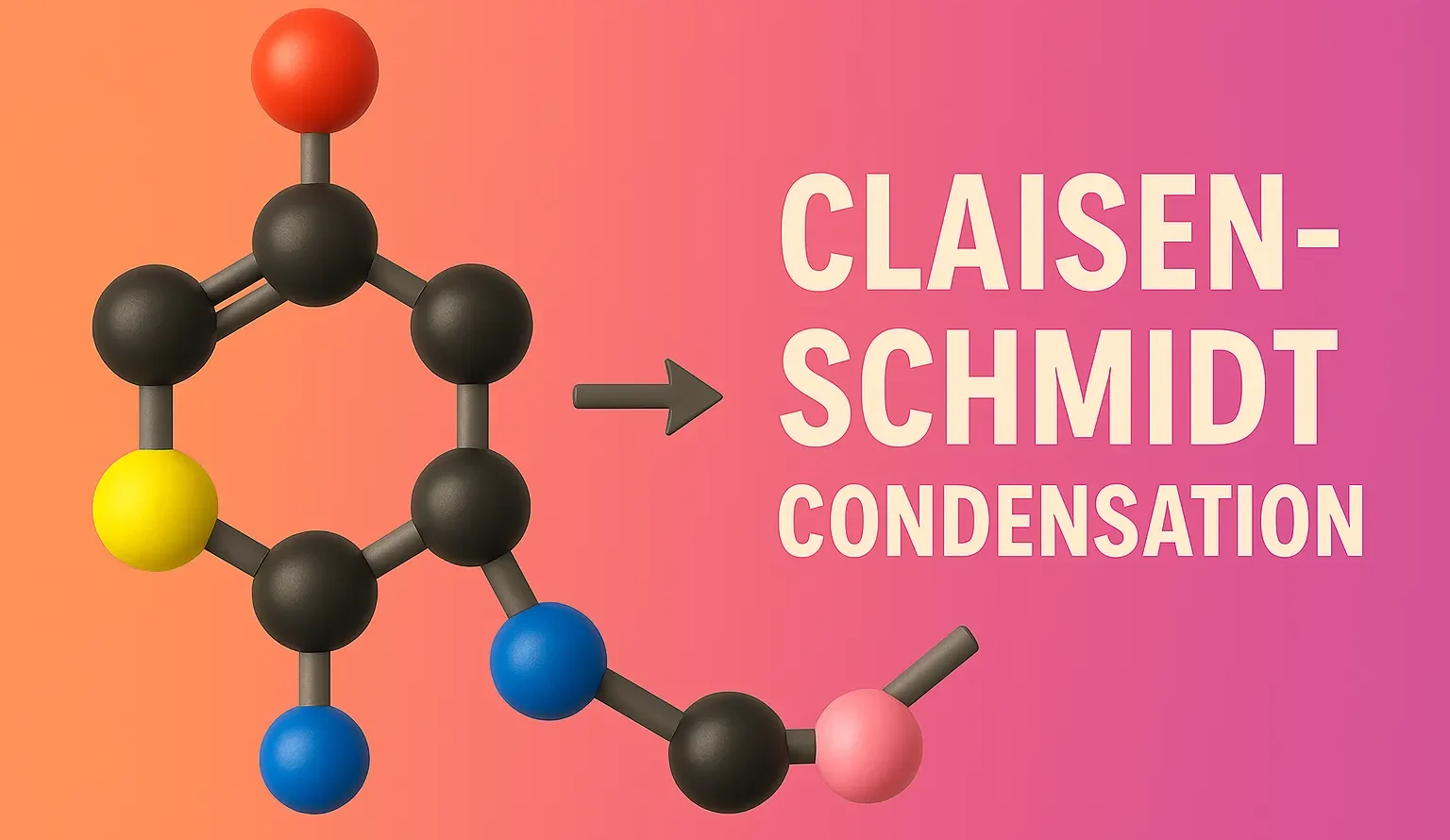
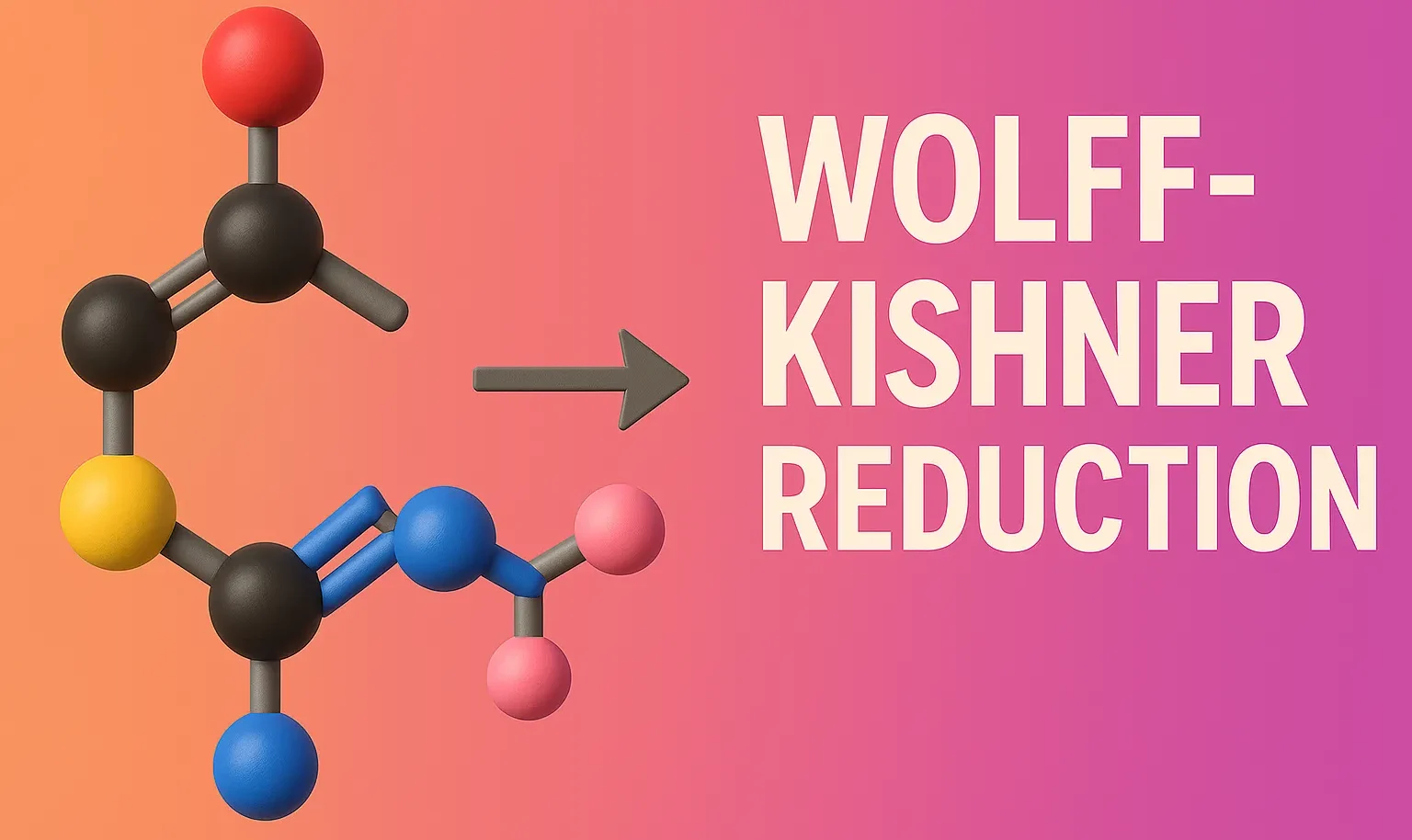
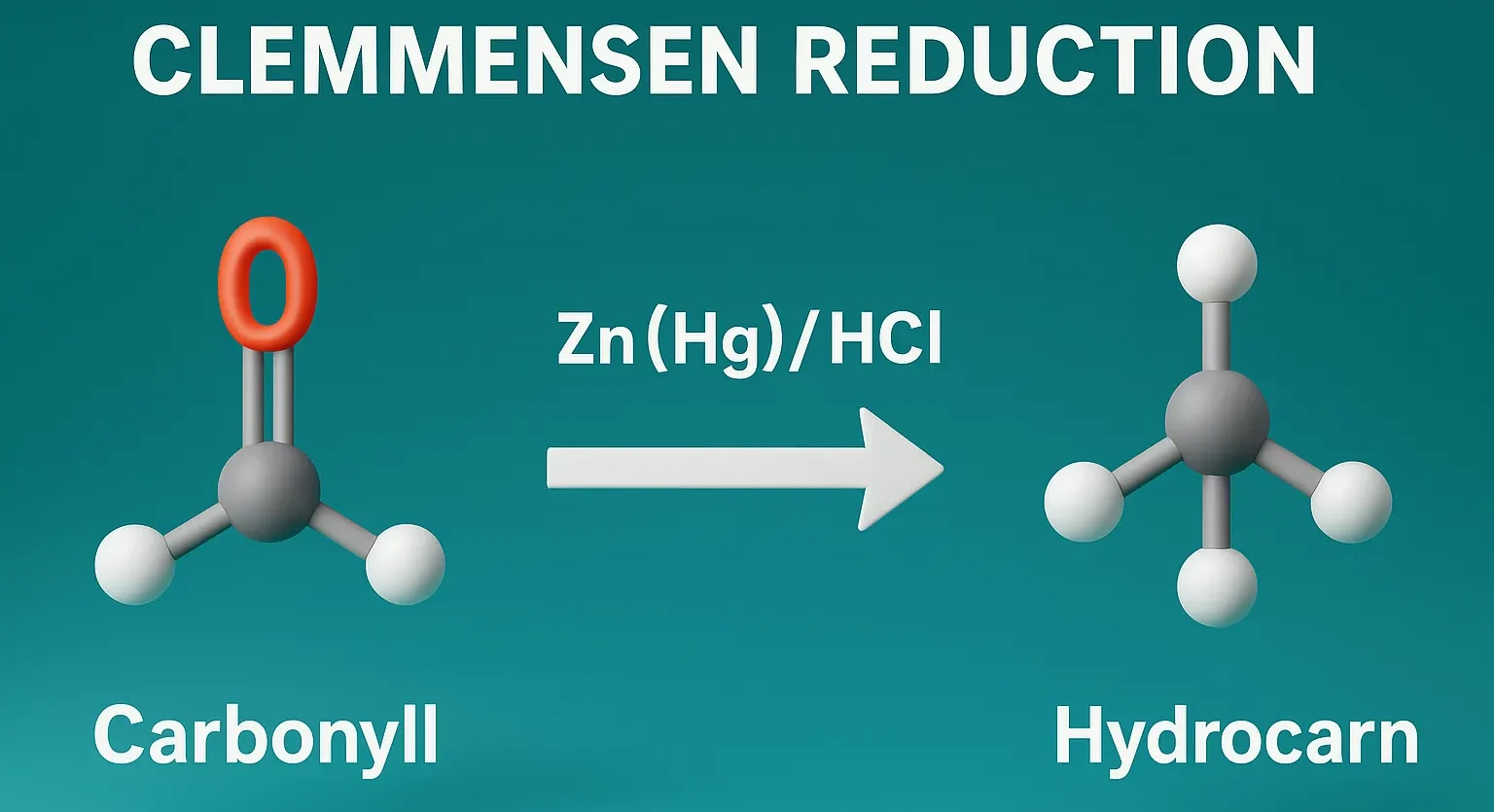
Claisen-Schmidt Condensation
Claisen-Schmidt Condensation forms α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds by reacting aromatic aldehydes with ketones in base. The Claisen–Schmidt condensation is a base-catalyzed aldol condensation between an aromatic aldehyde and a ketone (or sometimes another aldehyde) with α-hydrogens, typically resulting in an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound. General Reaction: Aromatic aldehyde + Aliphatic ketone —(Base/heat) → α,β-unsaturated ketone + H₂O … Read more