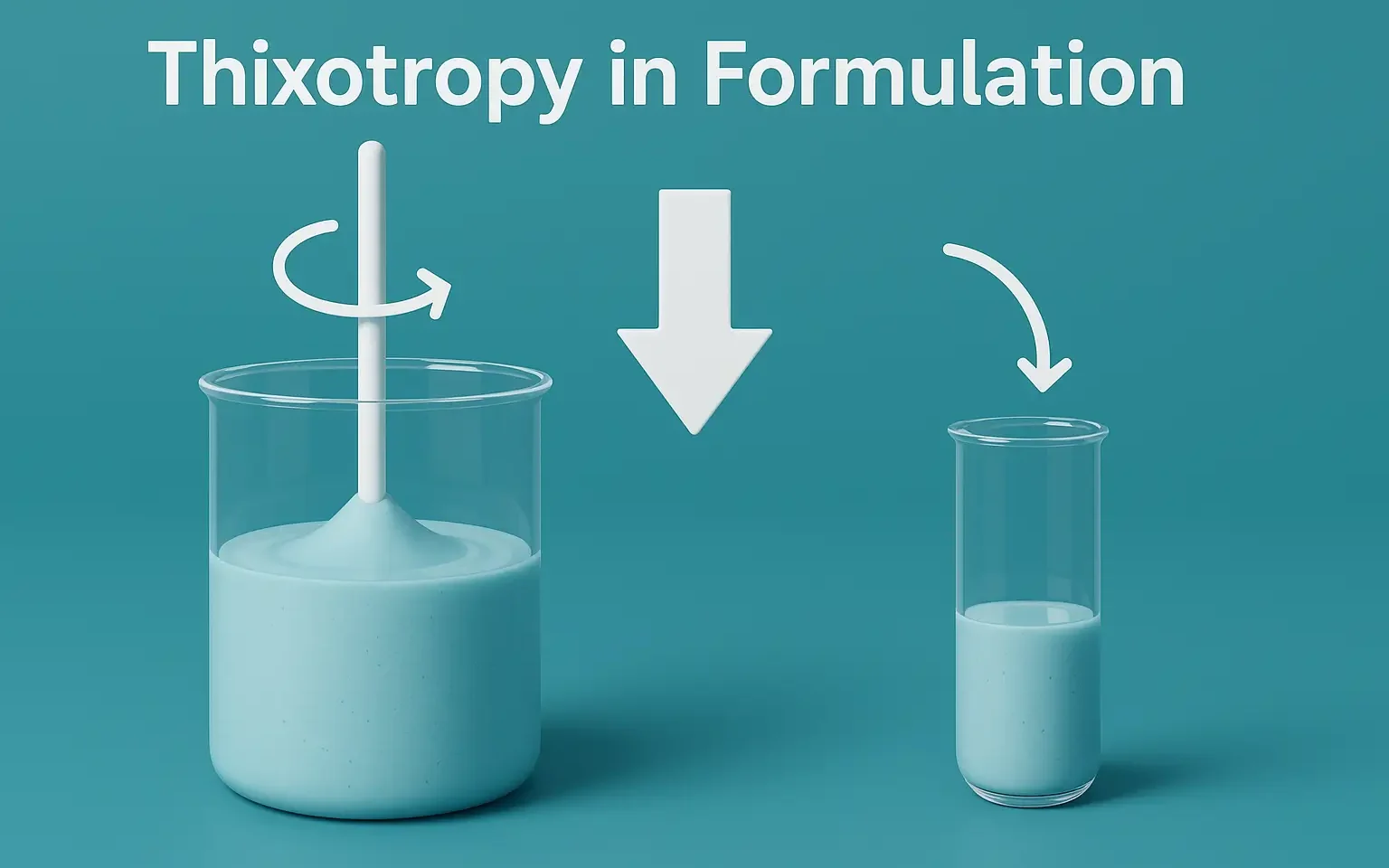
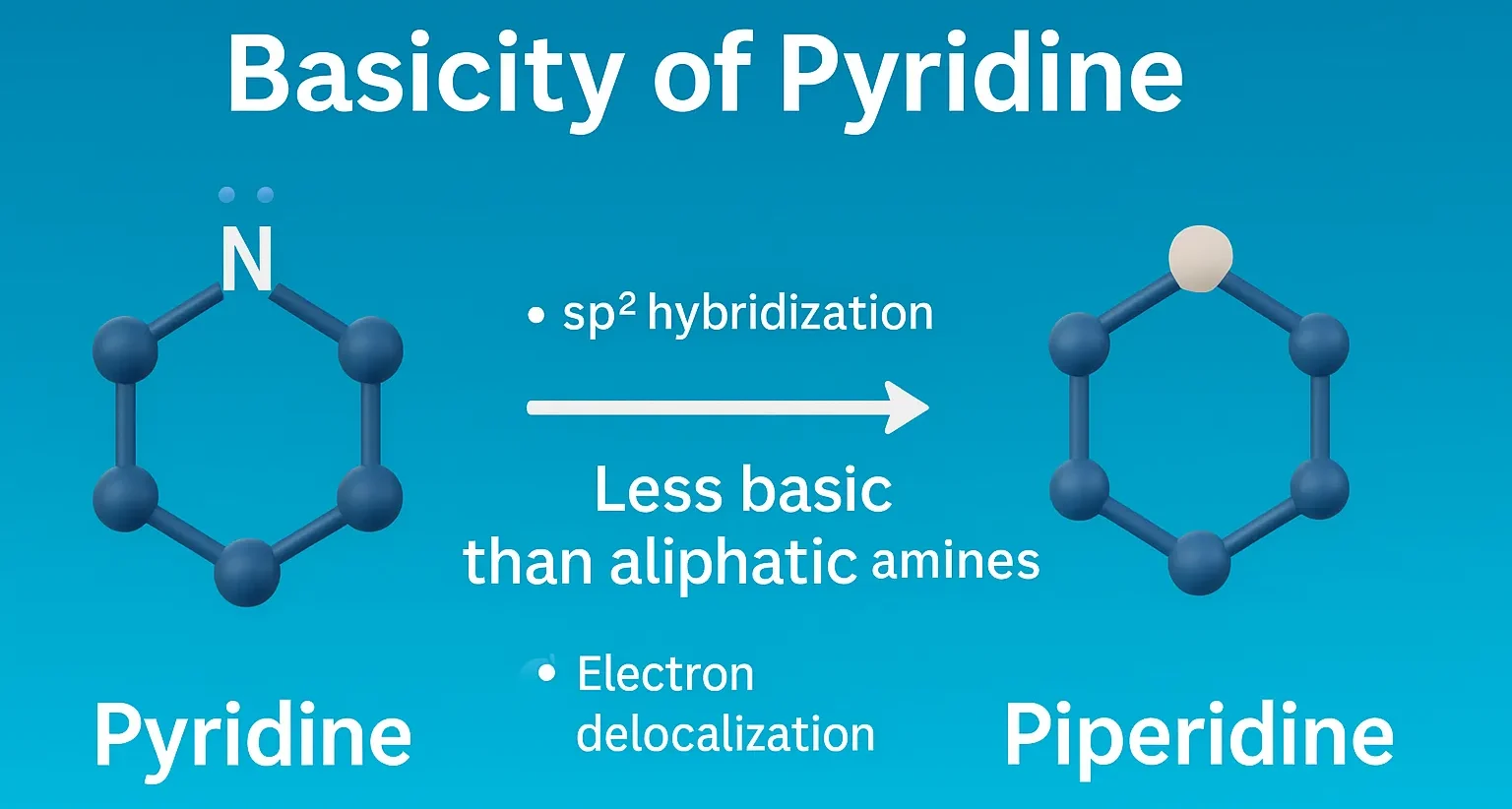
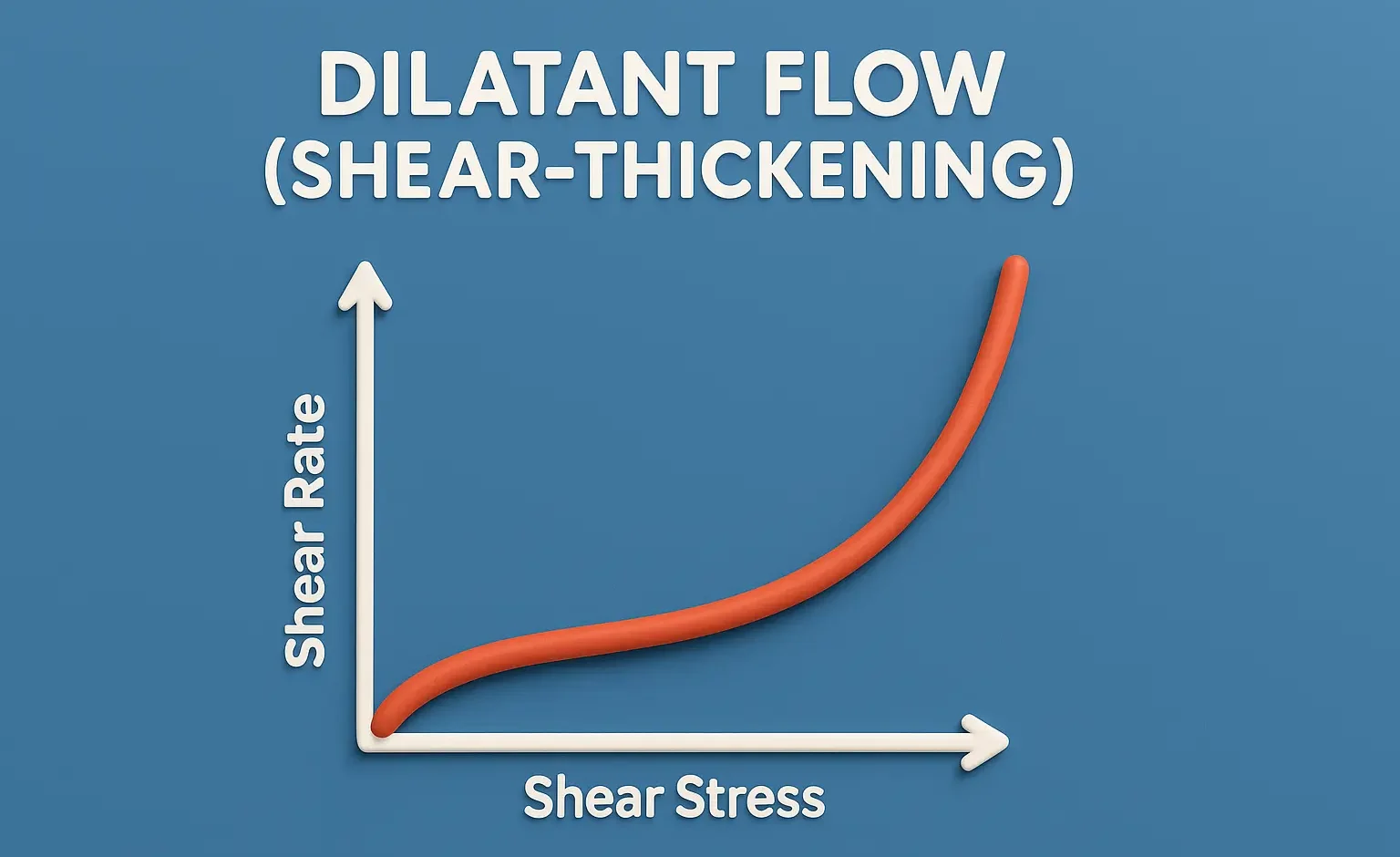
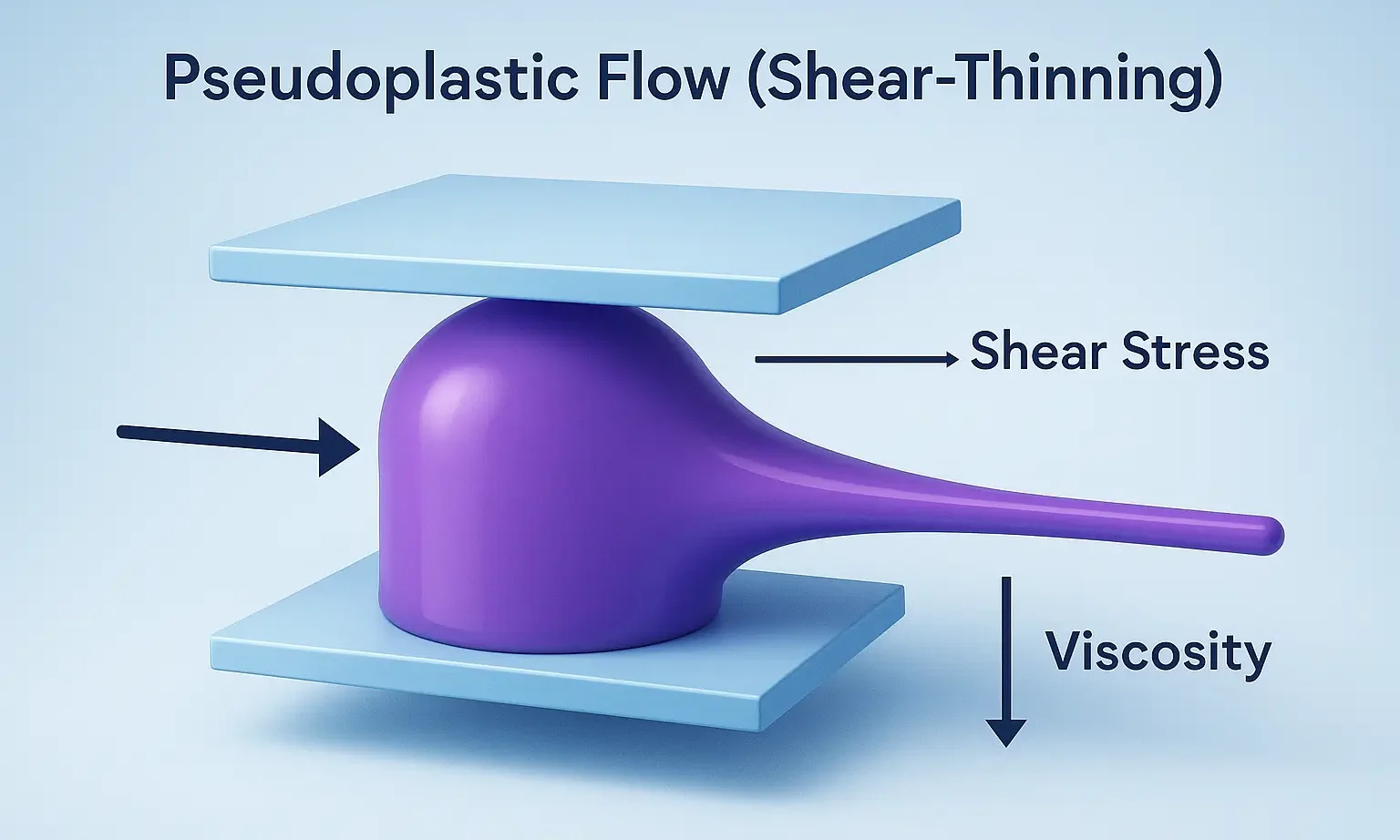
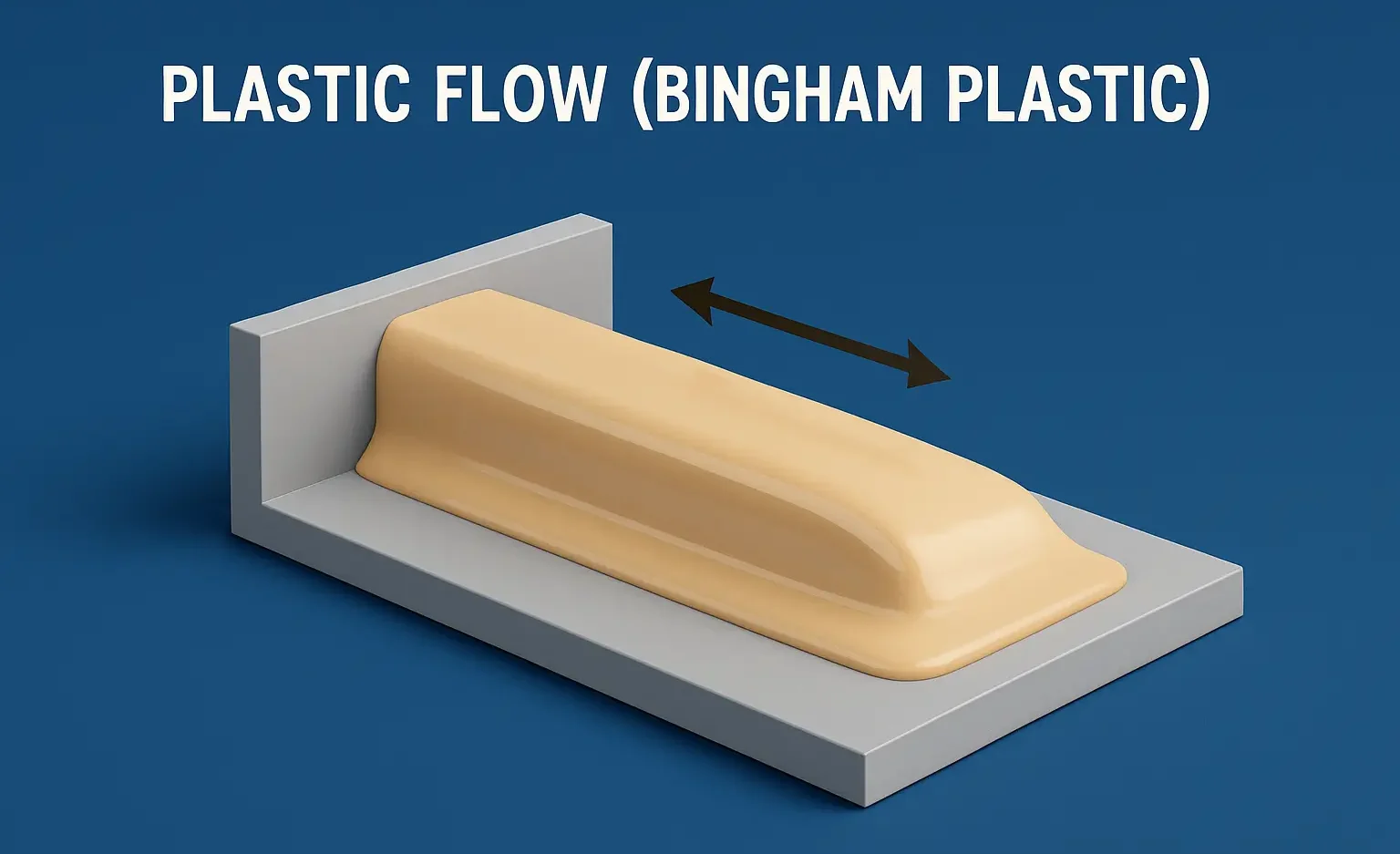
Thixotropy In Formulation
Thixotropy in Formulation describes reversible gel-to-sol transitions under shear, improving dosage form handling. Thixotropy In Formulation is a desirable property in liquid pharmaceutical systems, which should have: High consistency in the container. Yet pour or spread easily upon use. Procaine benzyl penicillin (procaine penicillin) combines benzyl penicillin with the local anaesthetic procaine. Thixotropy enhances suspension … Read more