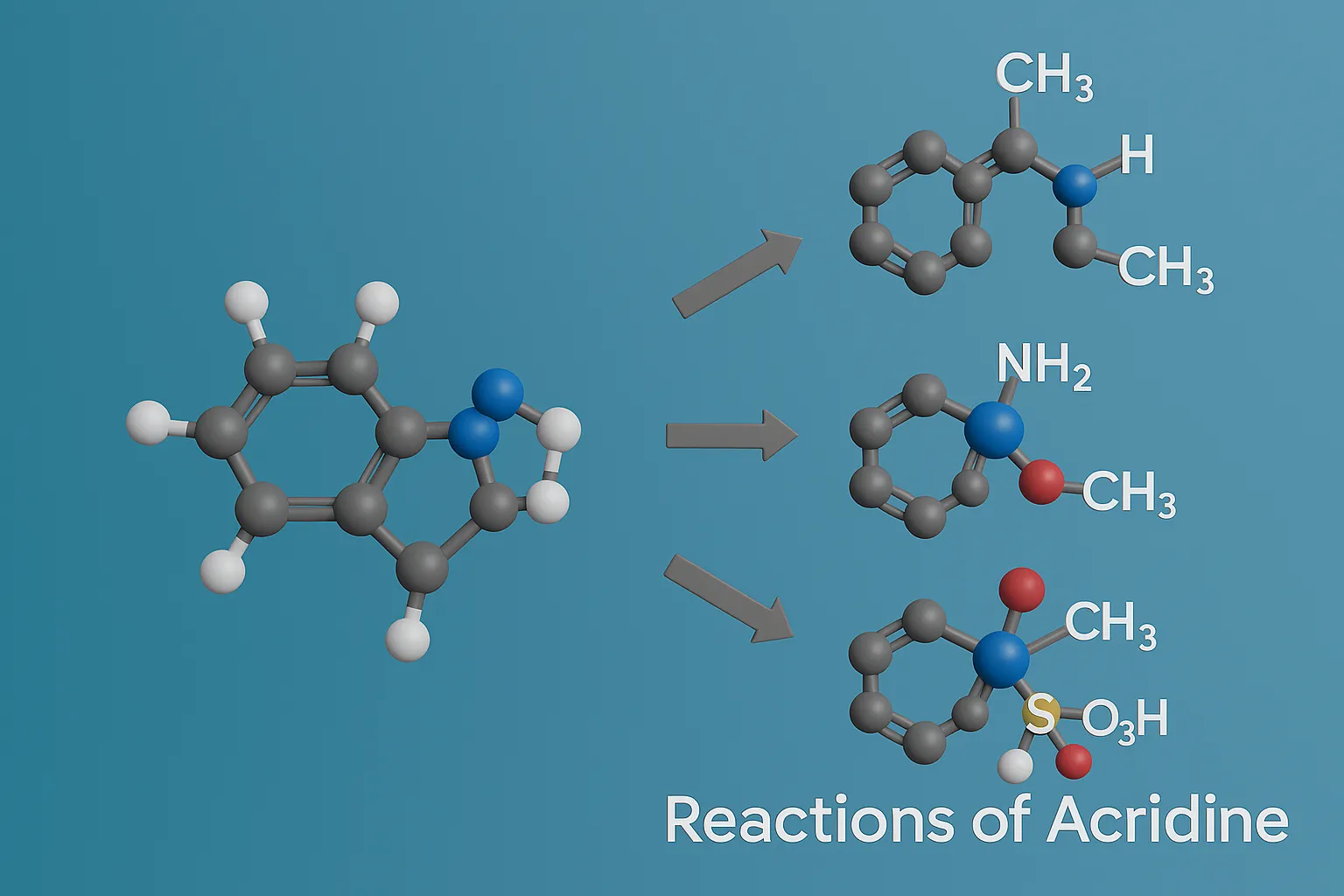
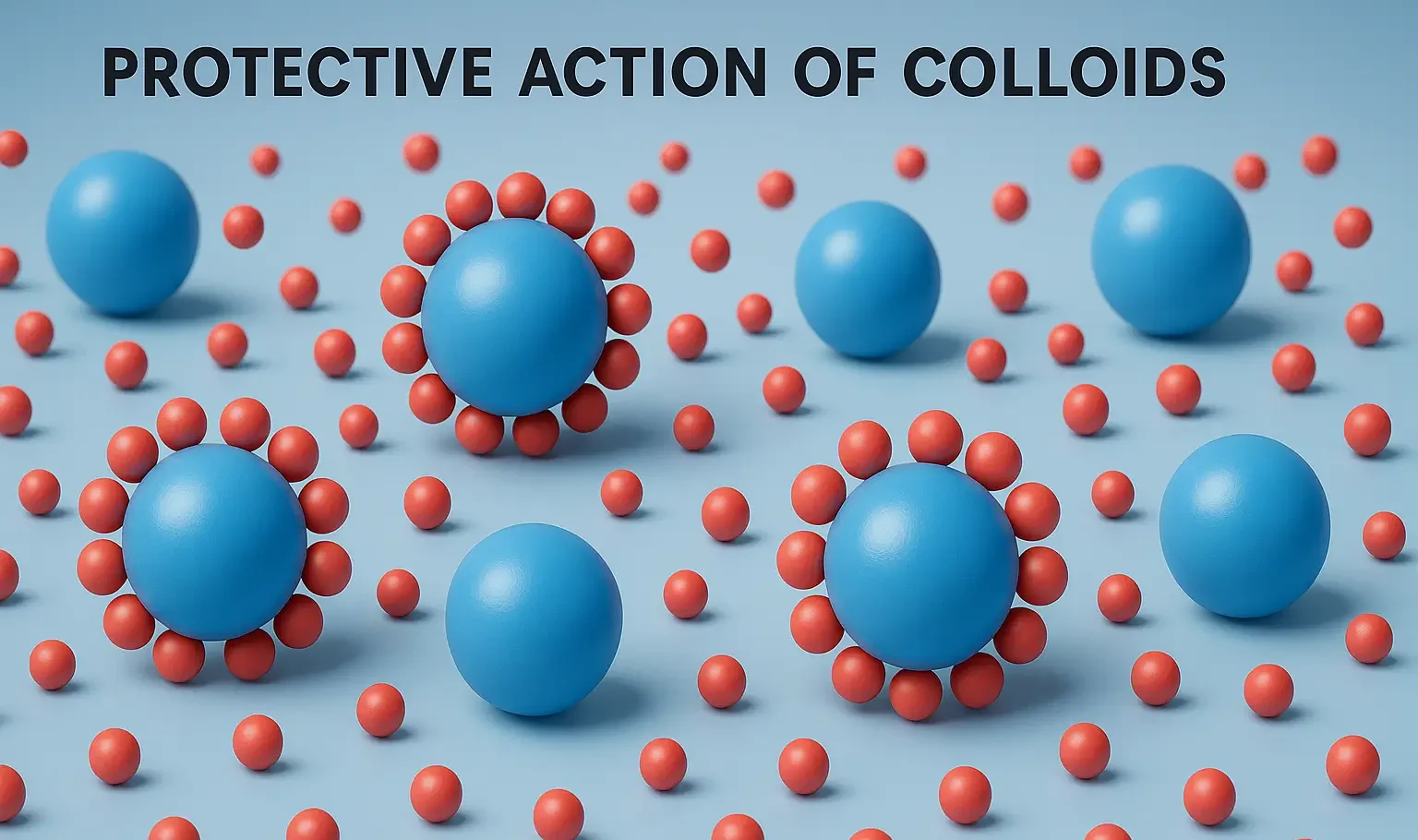
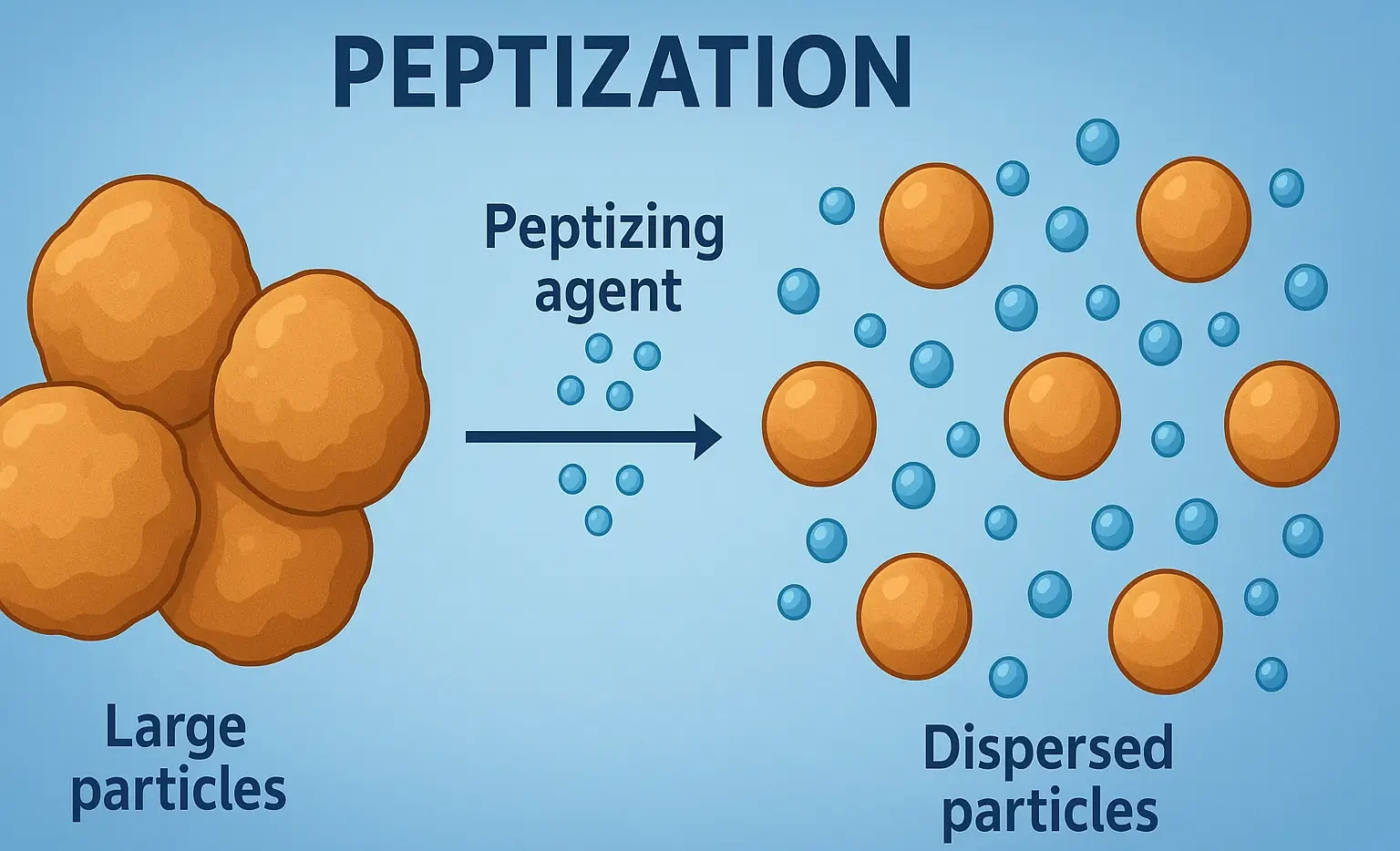
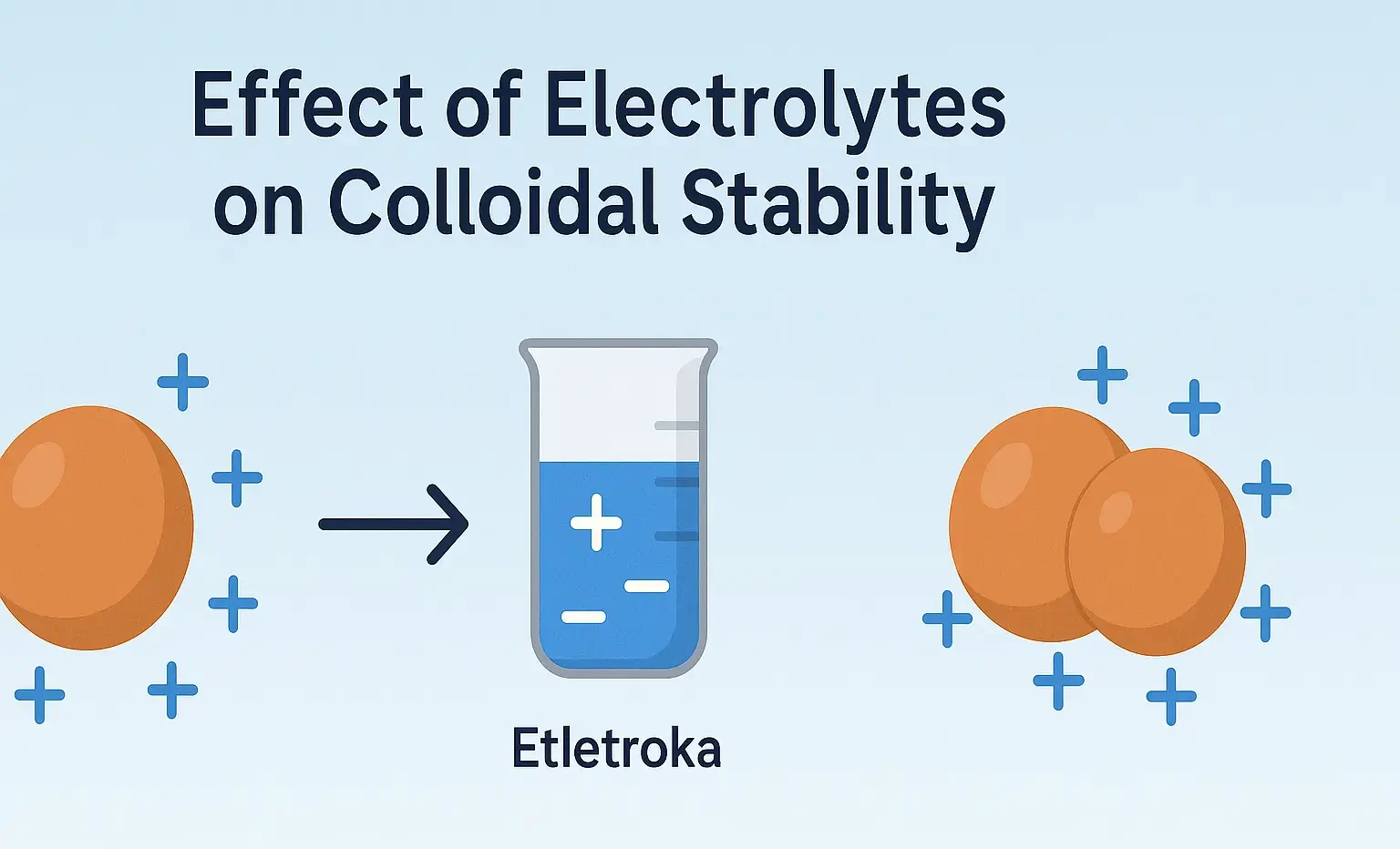
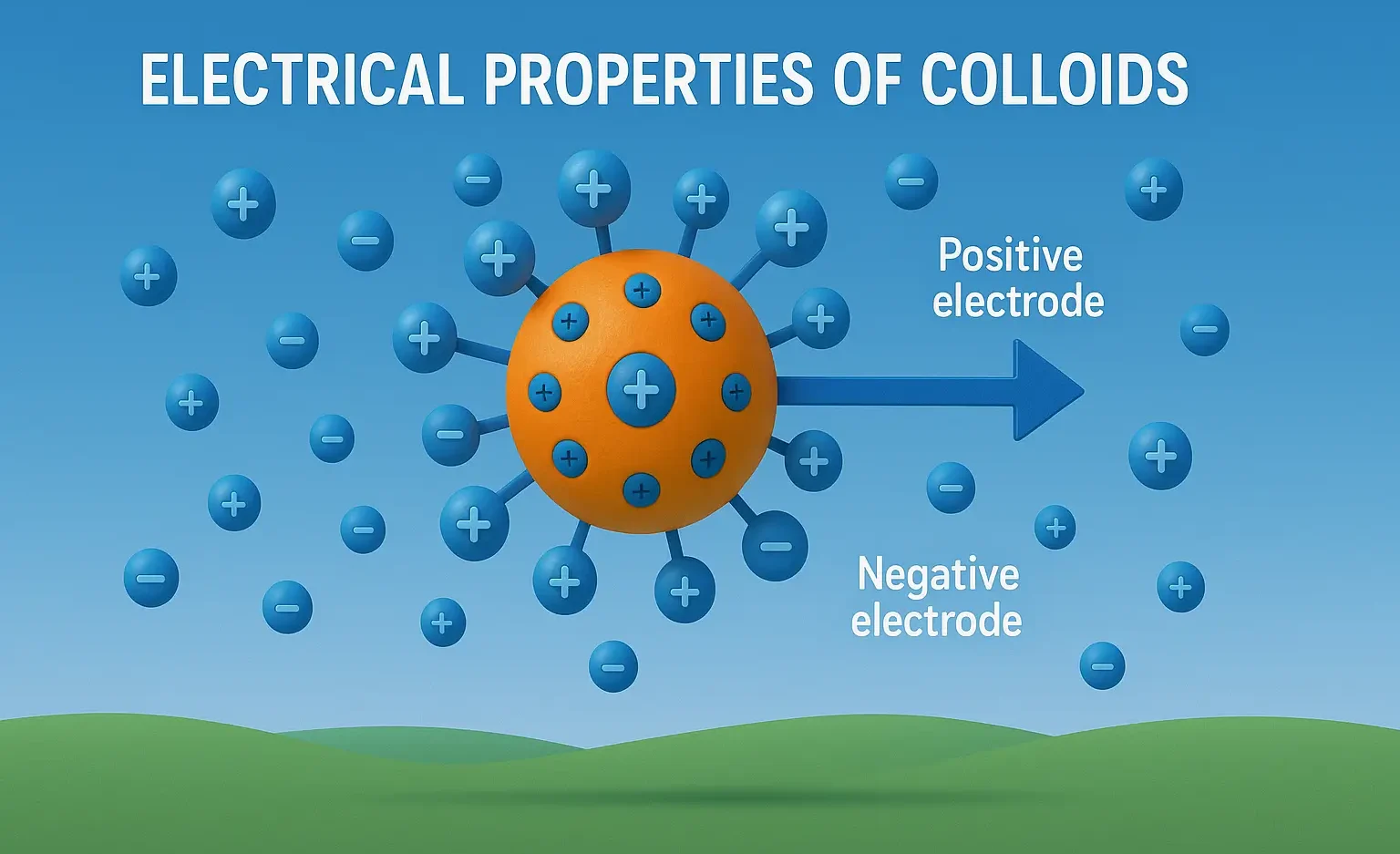
Reactions of Acridine
Reactions of Acridine involve electrophilic substitution, oxidation, and reduction processes important in pharmaceuticals and dyes. Reactions of Acridine Electrophilic Substitution (EAS) Preferred at positions 2 and 7 (central ring). Examples: Nitration: 2-nitroacridine (HNO₃ + H₂SO₄) Halogenation: Br₂ → 2-bromoacridine Nucleophilic Substitution (NAS) C-9 and neighboring positions can undergo substitution when activated (e.g., by halogen + … Read more