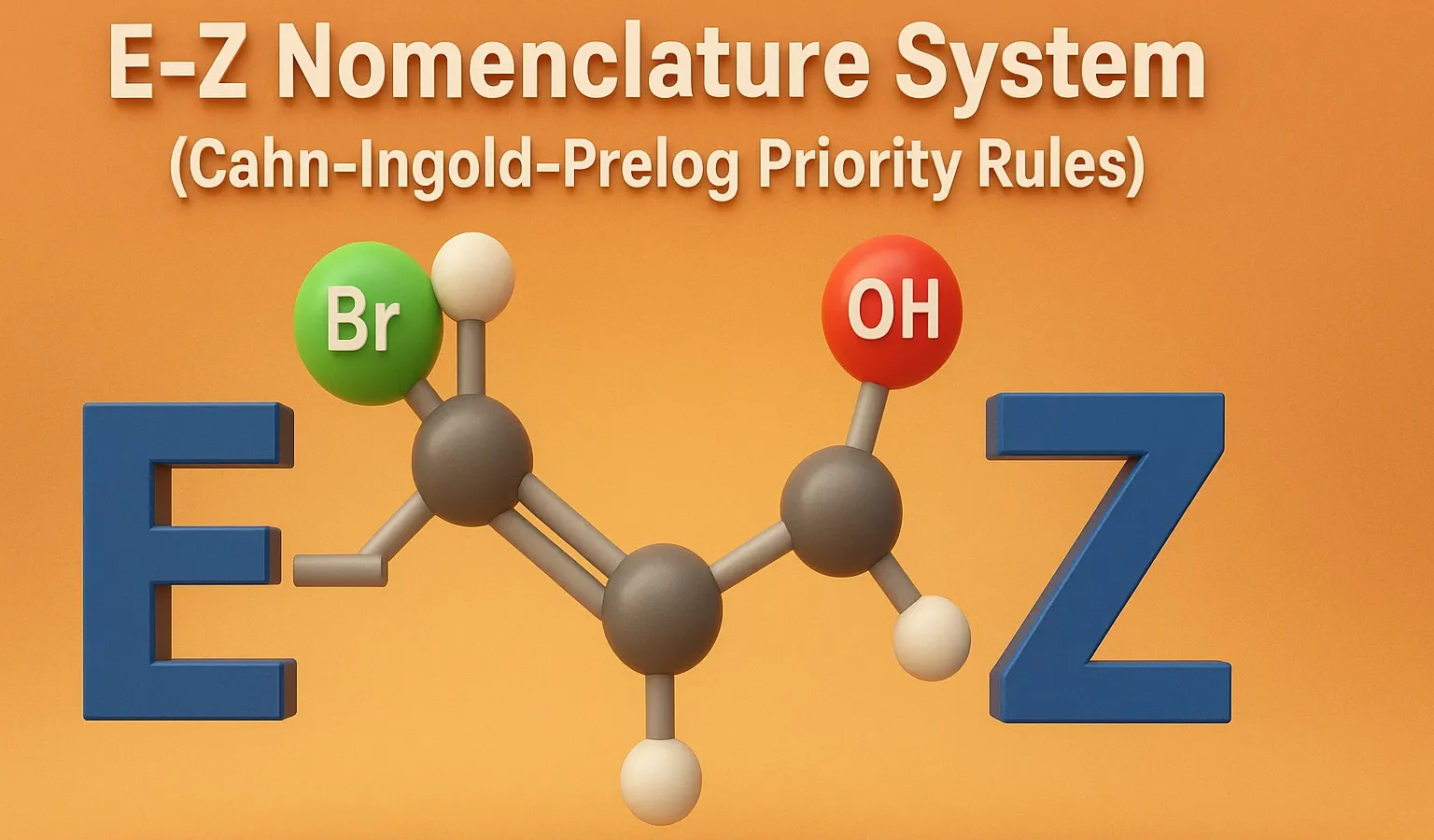
E–Z Nomenclature System (Cahn–Ingold–Prelog Priority Rules)
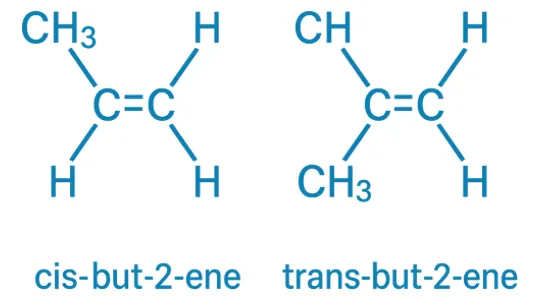
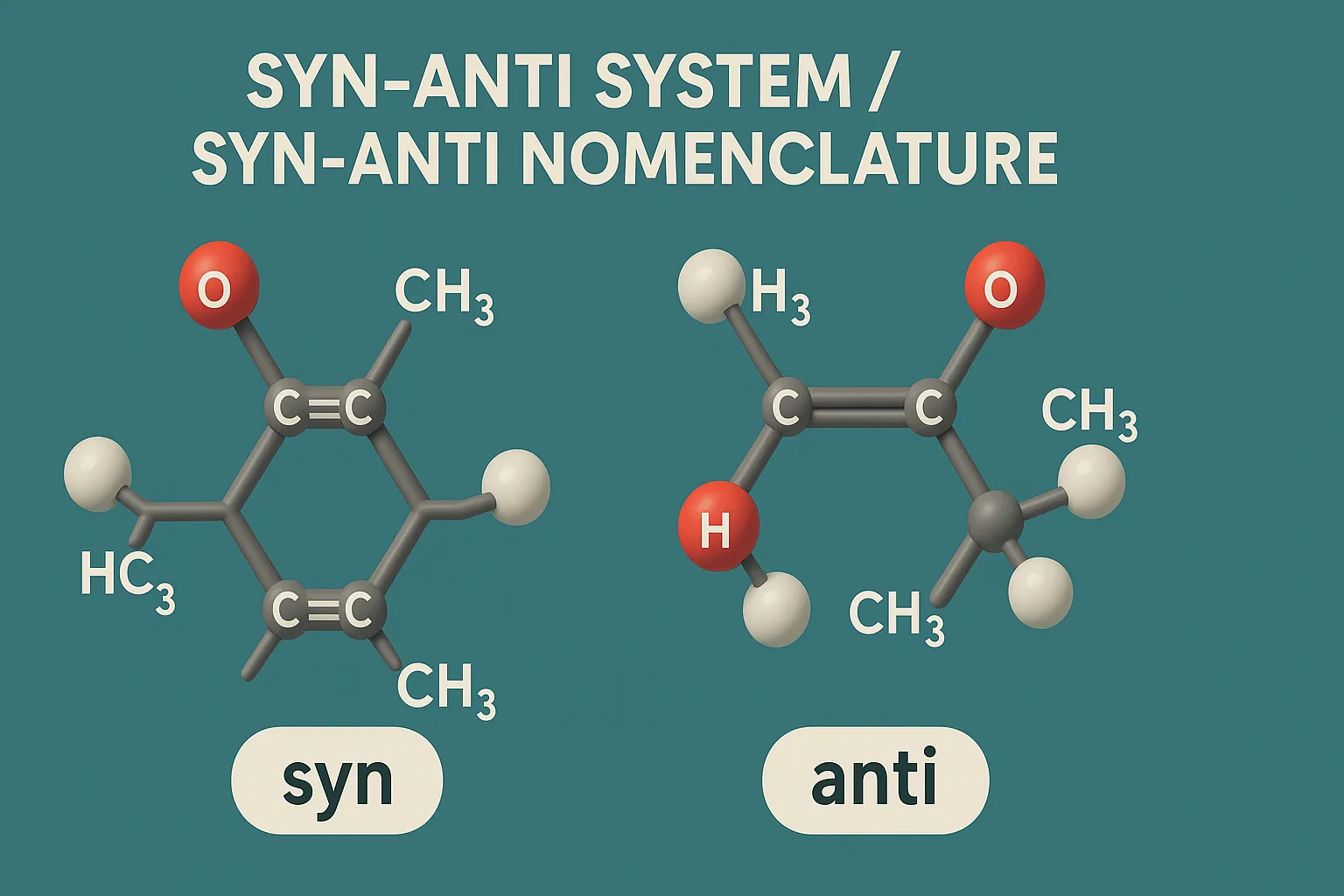
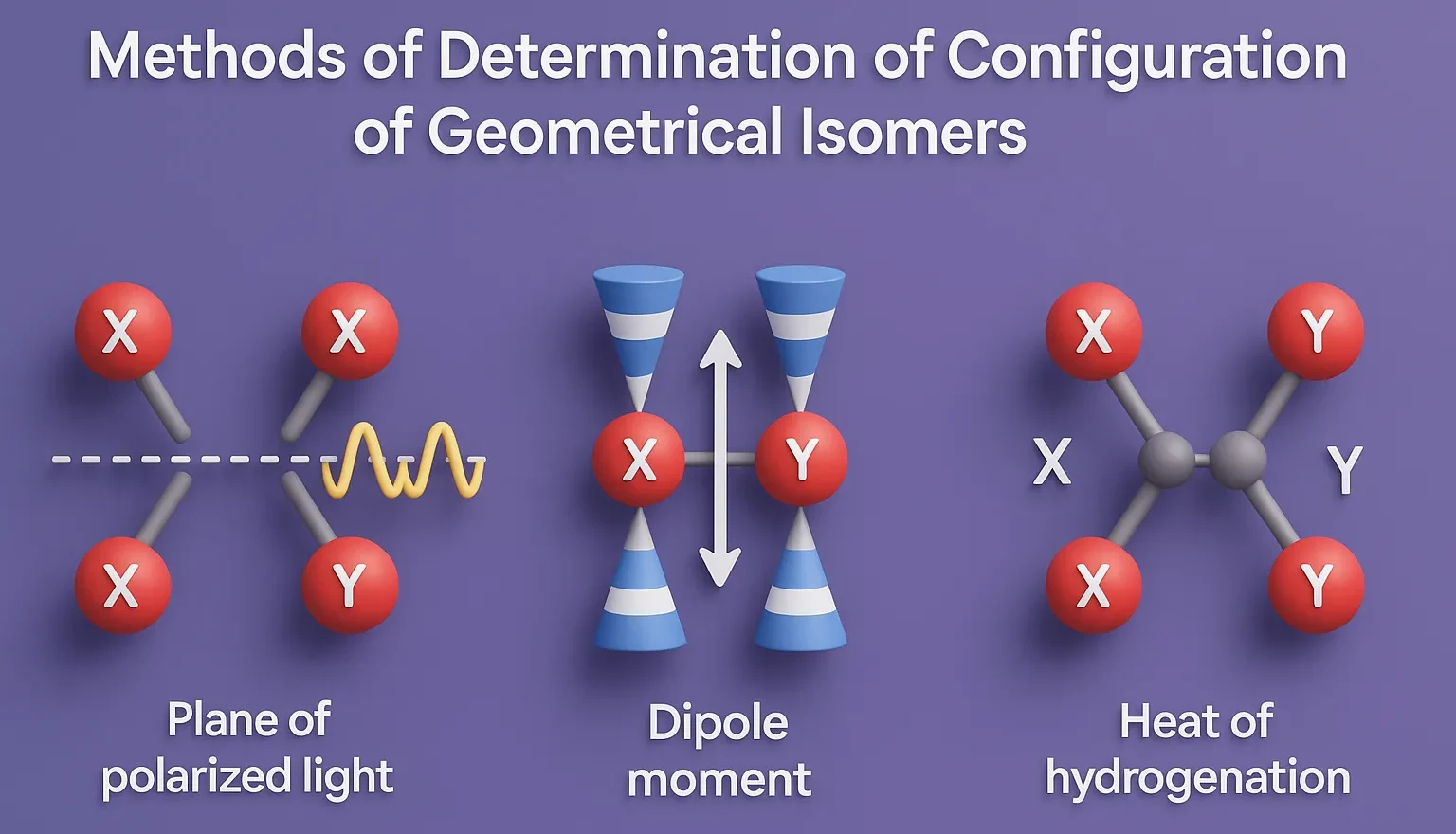
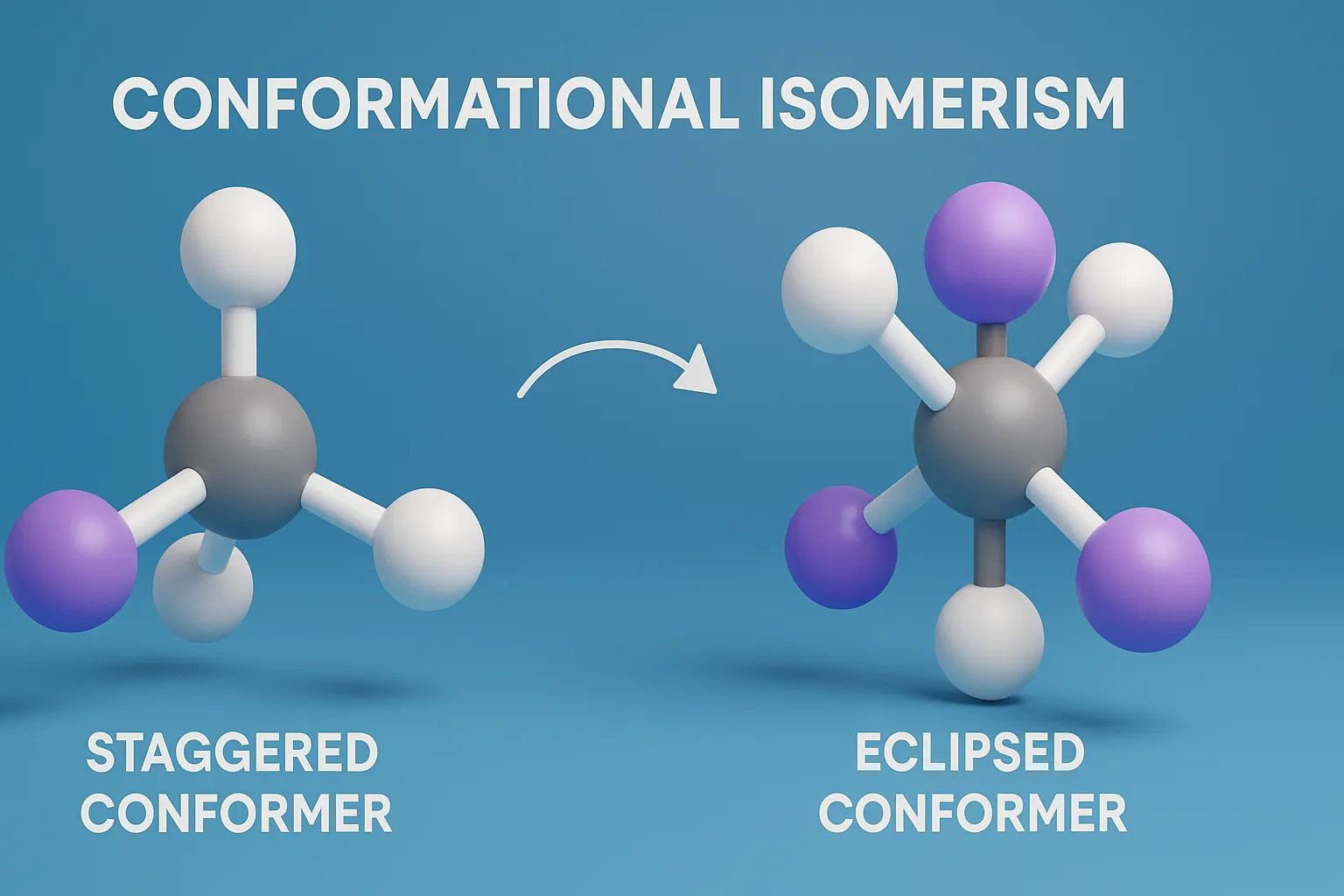
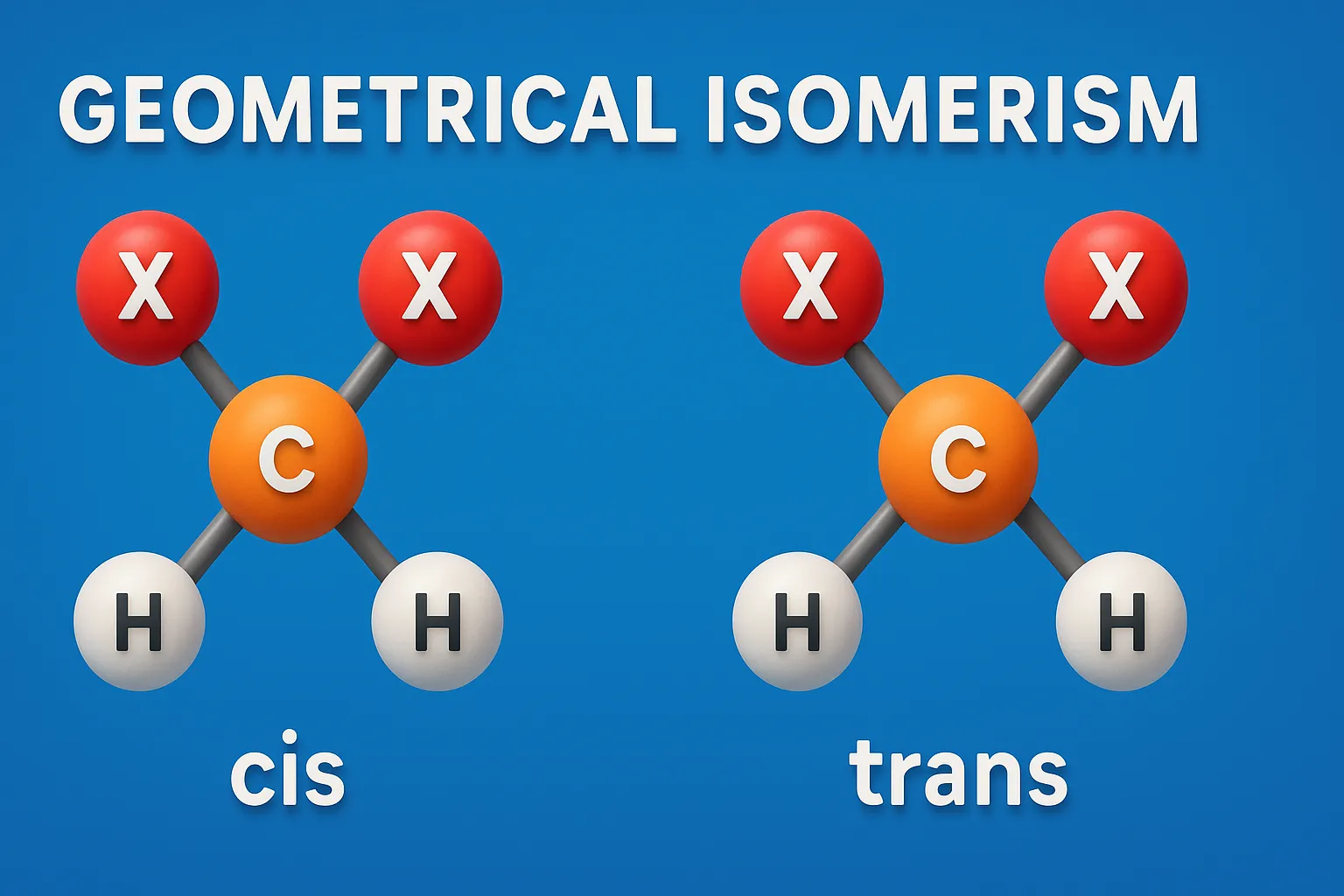
E–Z Nomenclature System uses Cahn–Ingold–Prelog rules to name isomers based on priority groups around a double bond (E = opposite, Z = same side). Why Use E-Z Nomenclature System? When each carbon in the double bond has two different substituents, the cis-trans system is not sufficient. In such cases, the E-Z system provides a consistent … Read more