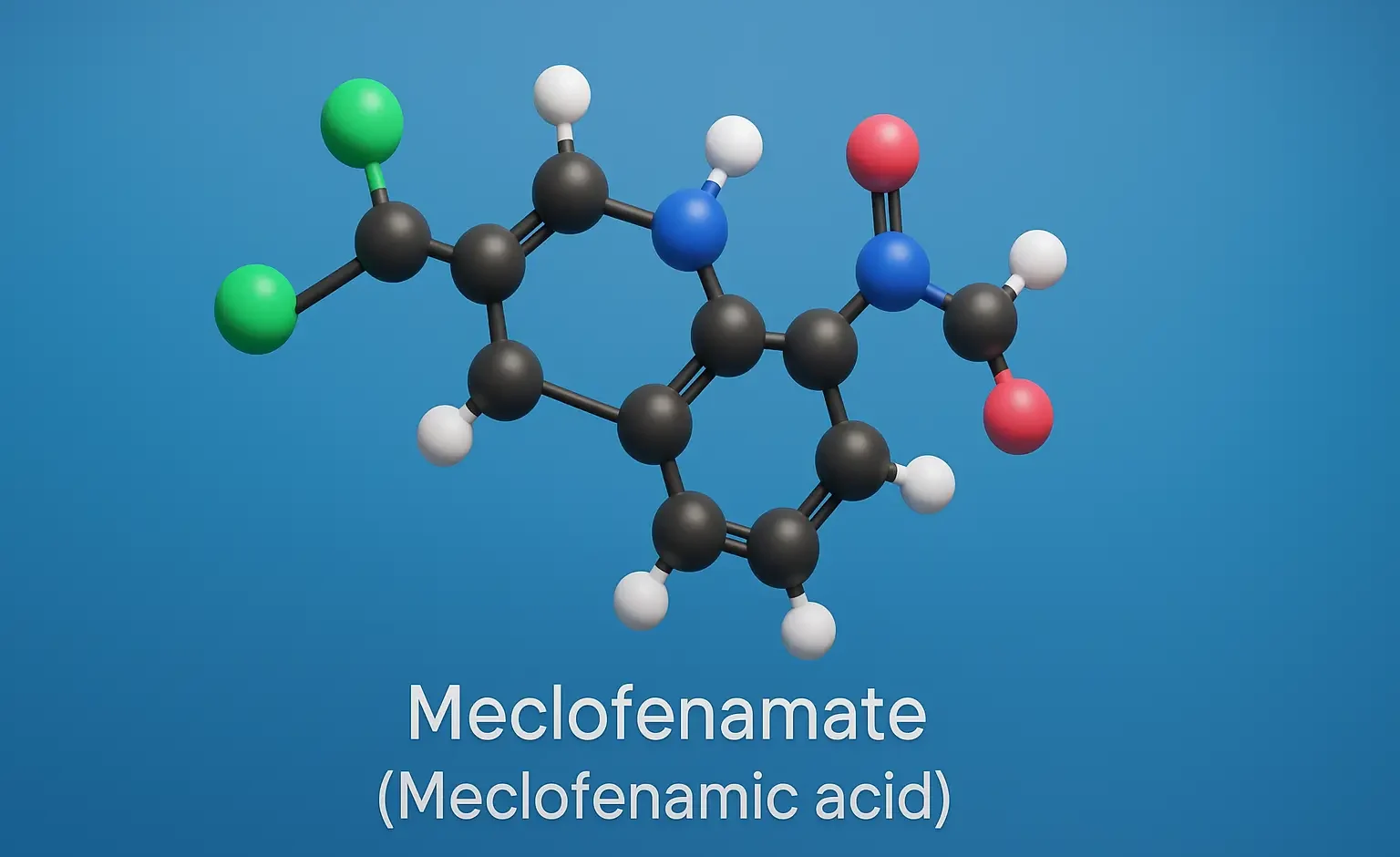
Meclofenamate (Meclofenamic acid)
Meclofenamate (Meclofenamic acid) is an NSAID effective in pain, inflammation, and arthritis relief. It inhibits COX enzymes, reducing prostaglandin synthesis and inflammation. Chemical Formula: C₁₄H₁₁Cl₂NO₂ Mechanism of Action: Reversible, non-selective COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis Uses of Meclofenamate (Meclofenamic acid): Mild to moderate pain Dysmenorrhea Osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis Side Effects of Meclofenamate (Meclofenamic acid): GI … Read more