Spare Receptors
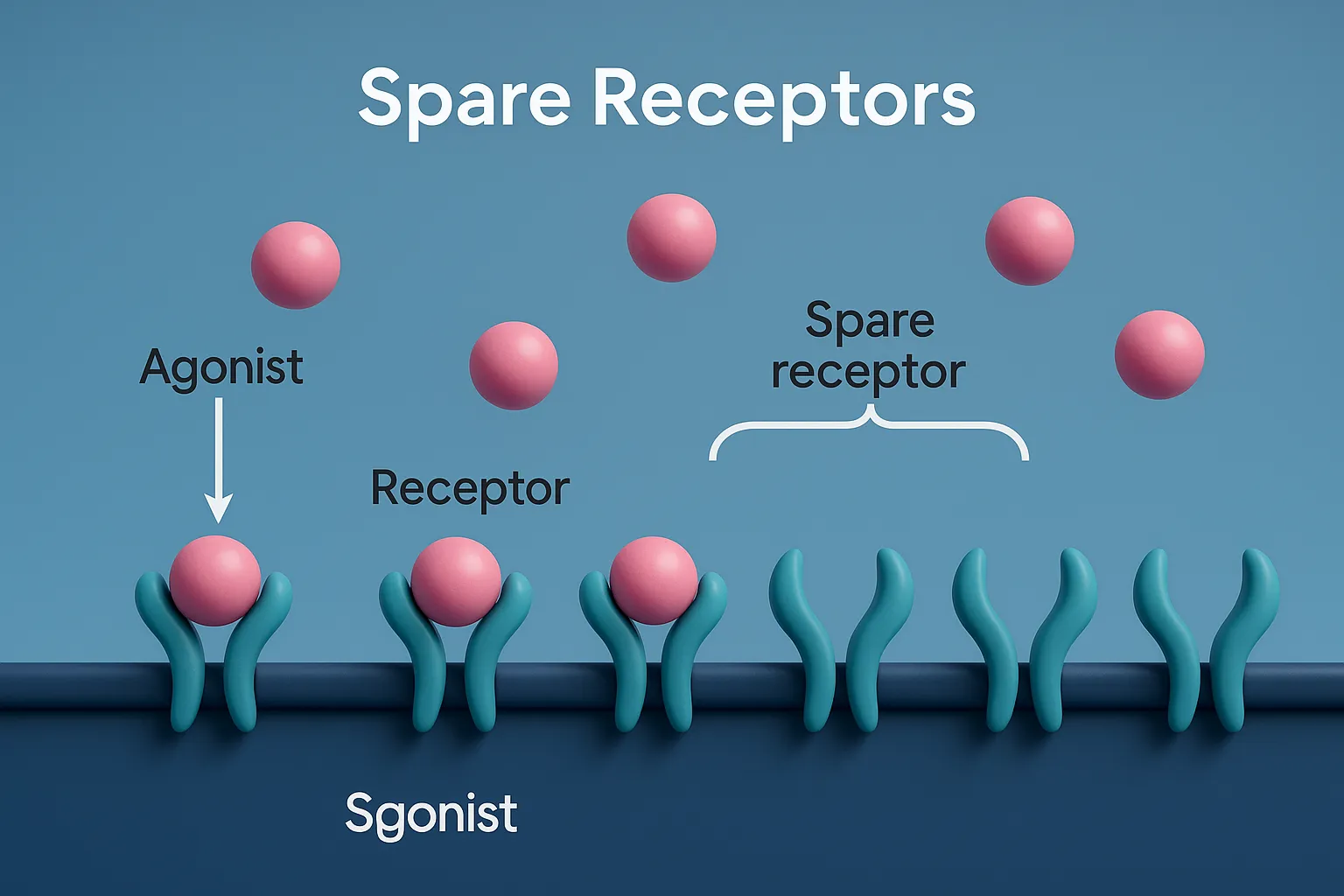
Spare receptors enhance drug response, allowing maximum effect even when not all receptors are occupied. Definition of Spare Receptors: Spare receptors are receptors that are not required to be occupied by a drug to produce the maximum response. Significance: A full response can be achieved even when only a small fraction of total receptors are … Read more