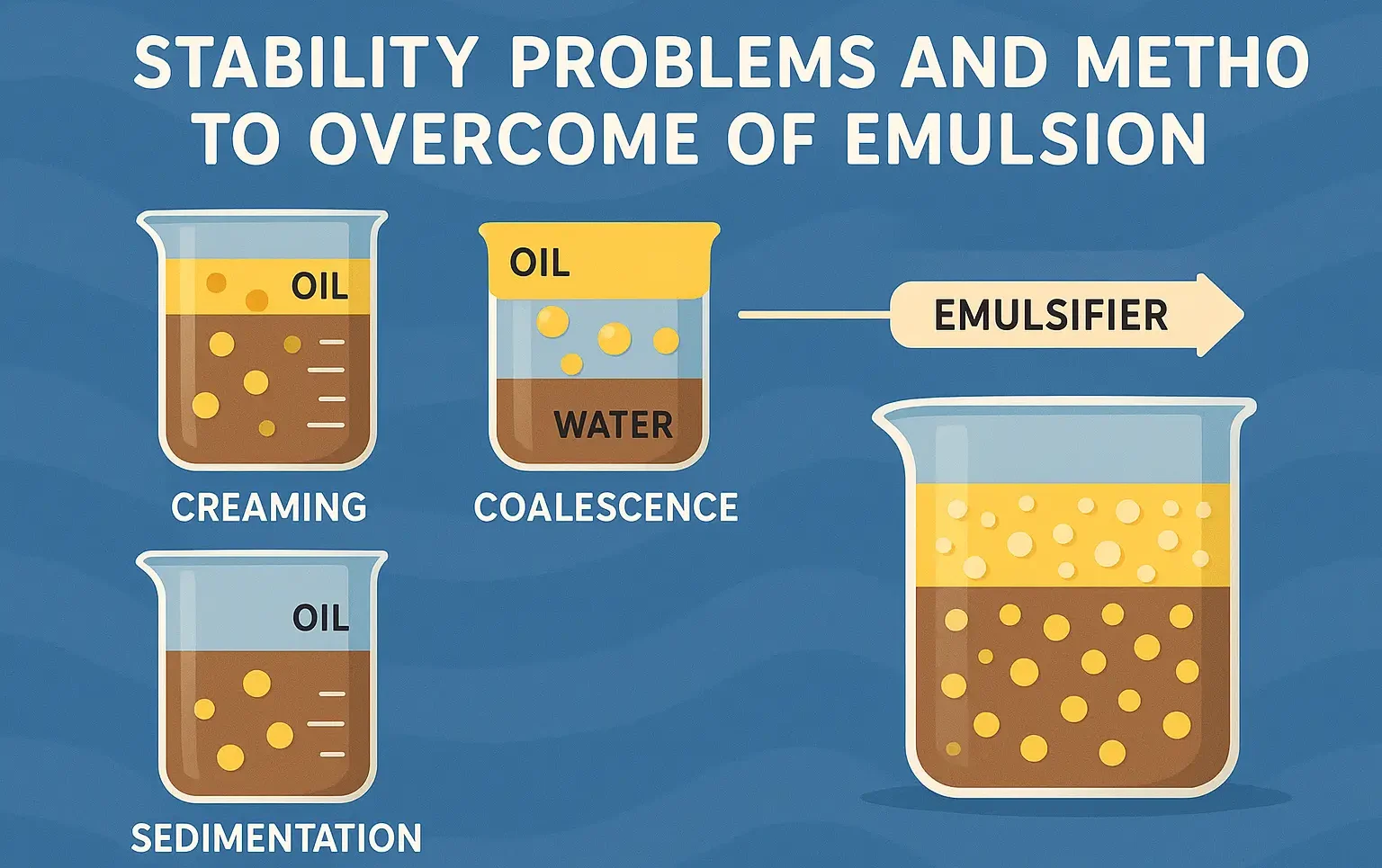
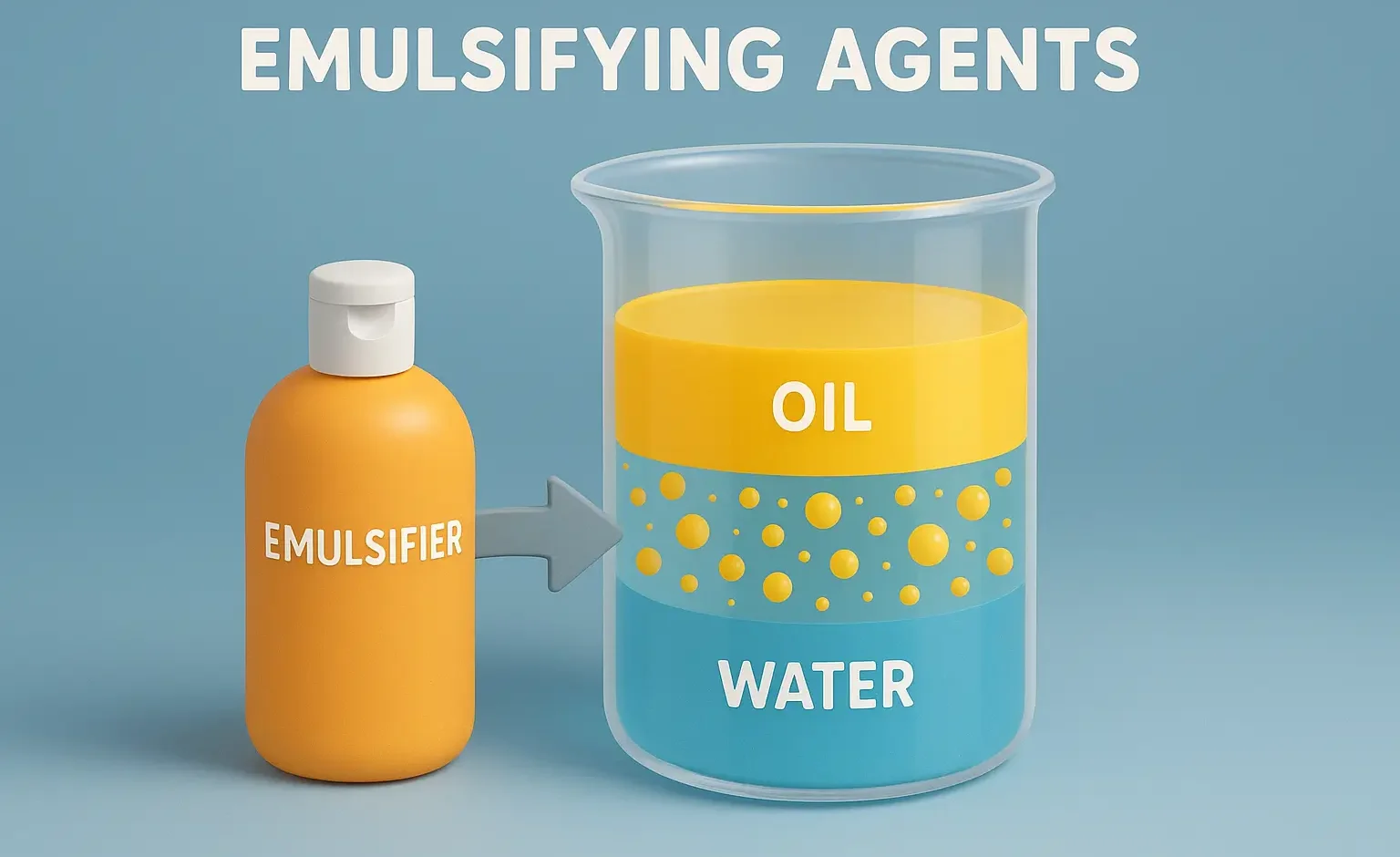
Evaluation of suppositories
The evaluation of suppositories is essential to ensure quality, safety, and efficacy. Key parameters assessed include: Weight Variation Suppositories should have uniform weight for accurate dosing. Individual suppositories are weighed, and the weight variation must fall within pharmacopeial limits. Appearance and Shape Suppositories should have a smooth, uniform appearance without cracks or air bubbles. The … Read more