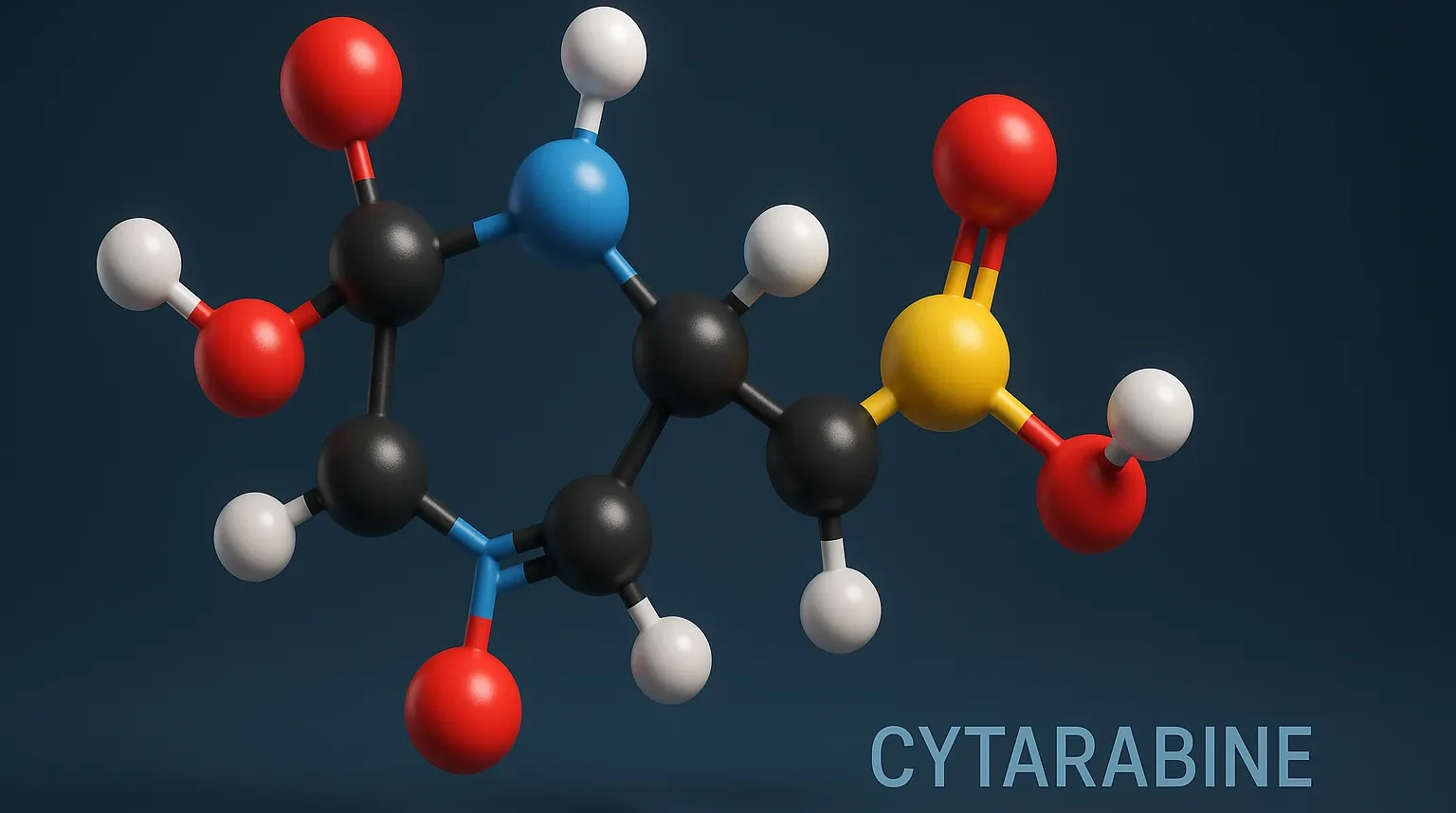
Cytarabine
Cytarabine is an anti-neoplastic antimetabolite used in leukemia treatment by inhibiting DNA synthesis in rapidly dividing cancer cells. Structure of Cytarabine It is also known as Ara-C, is a pyrimidine analog with the following structural features: Cytosine Base: Similar to the natural nucleobase cytosine. Ribose Sugar: Modified with an arabinose moiety. Chemical Formula: C₄H₇N₃O₅ Mode … Read more