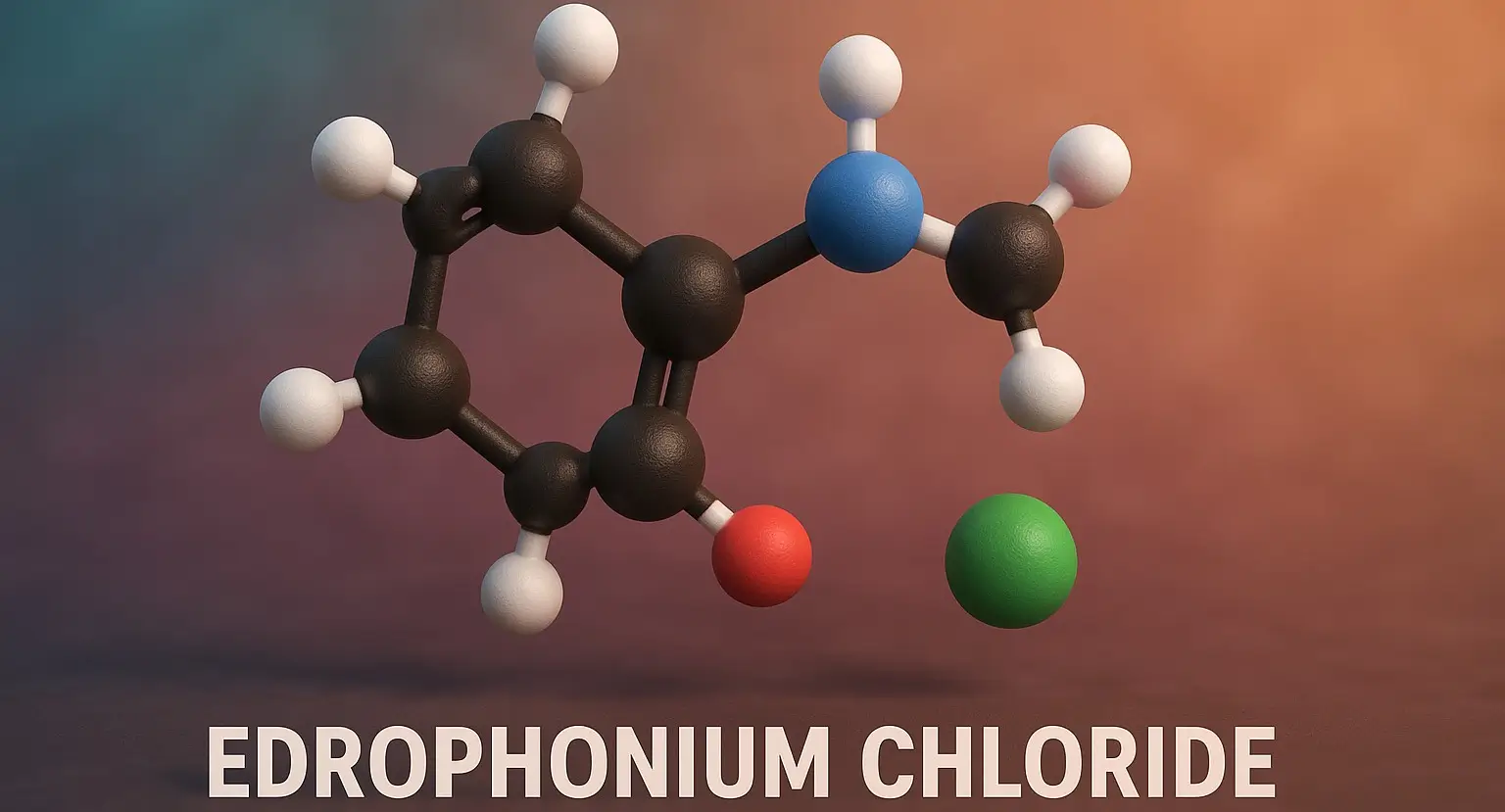
Edrophonium Chloride
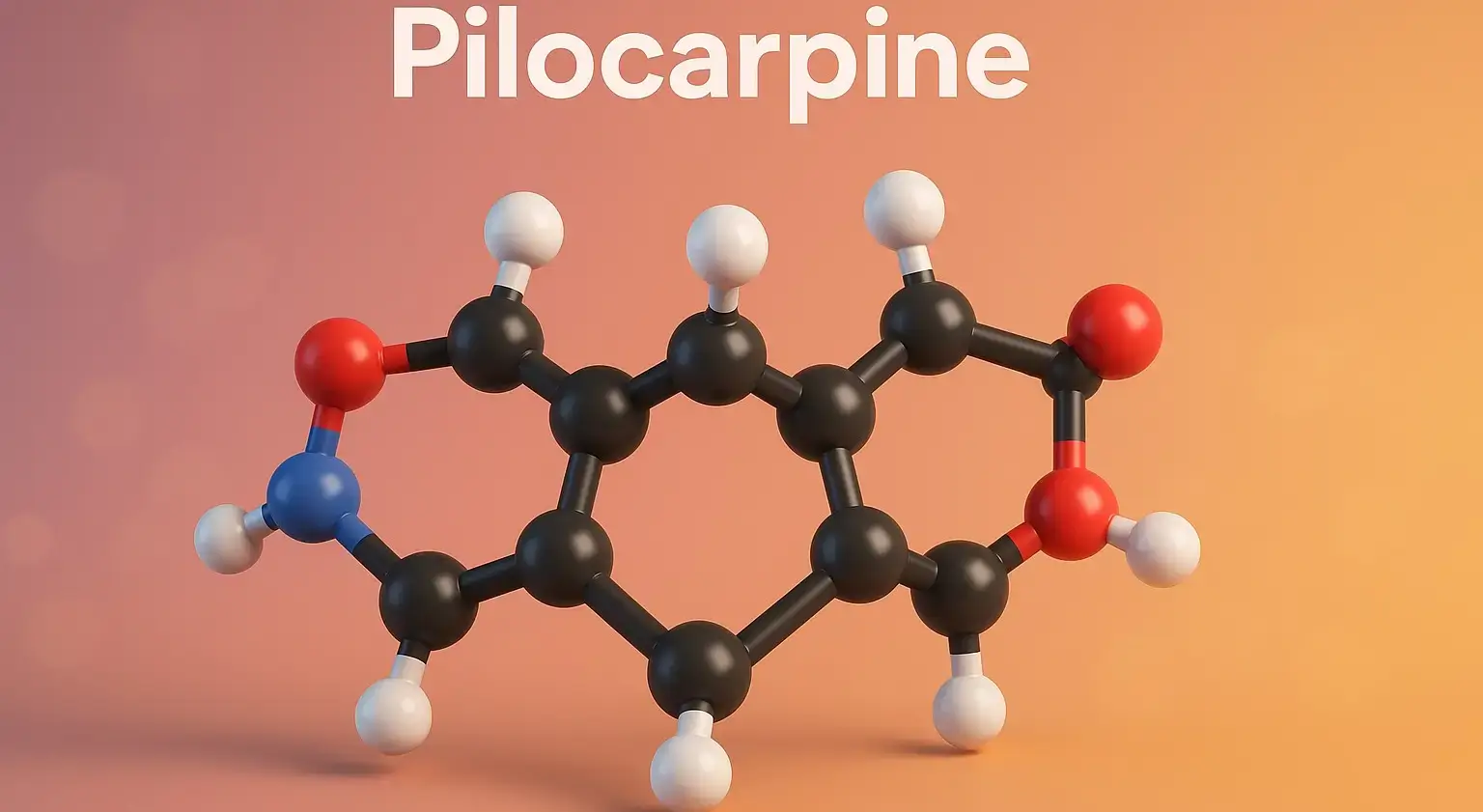
Edrophonium Chloride is a short-acting, quaternary ammonium compound classified as a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It temporarily increases acetylcholine levels at neuromuscular junctions by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₁₆ClNO Mechanism of Action: Short-acting reversible AChE inhibitor. Binds via electrostatic + hydrogen bonding, not covalent. Uses of Edrophonium Chloride: Diagnosis of myasthenia gravis (Tensilon test) … Read more