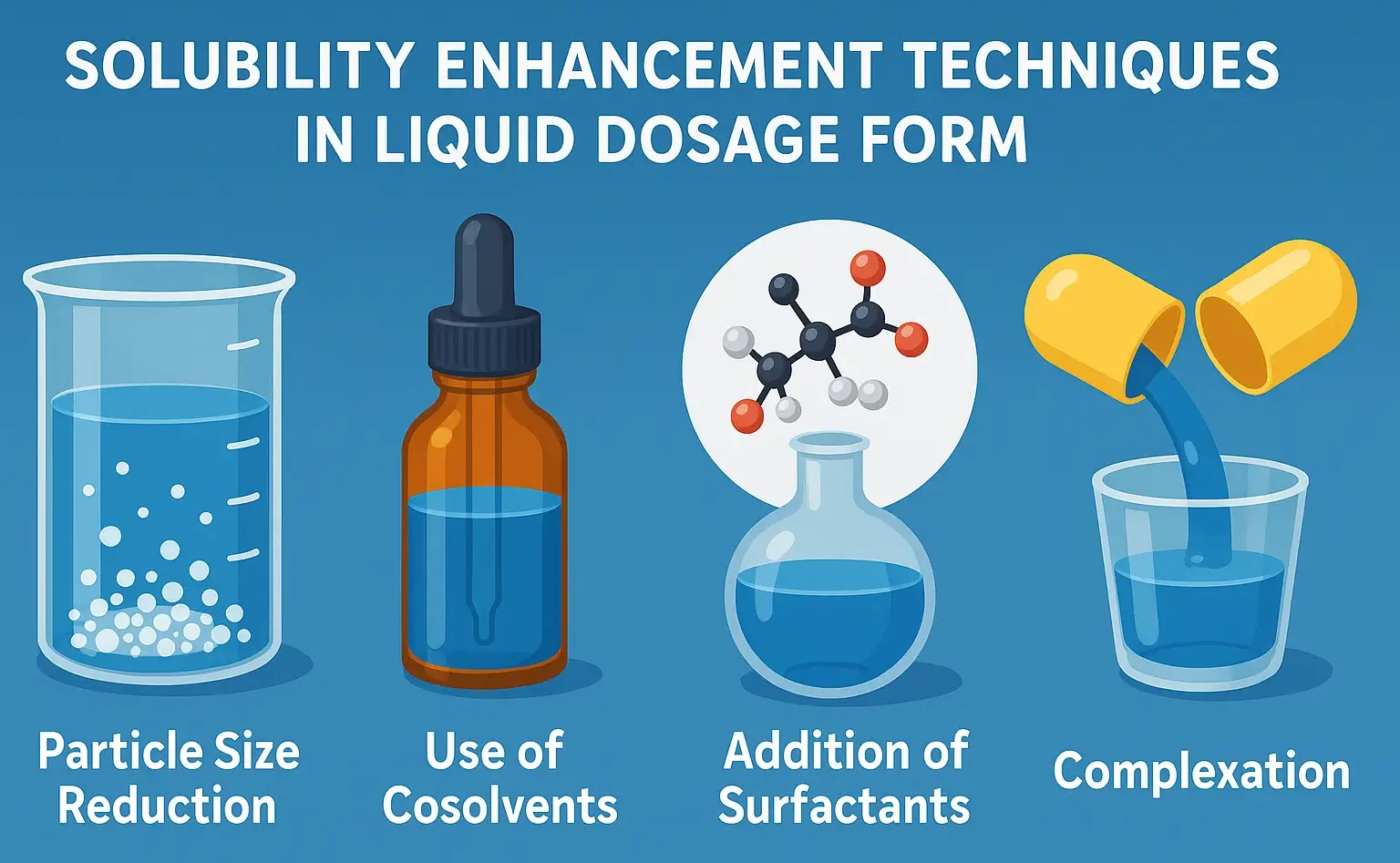
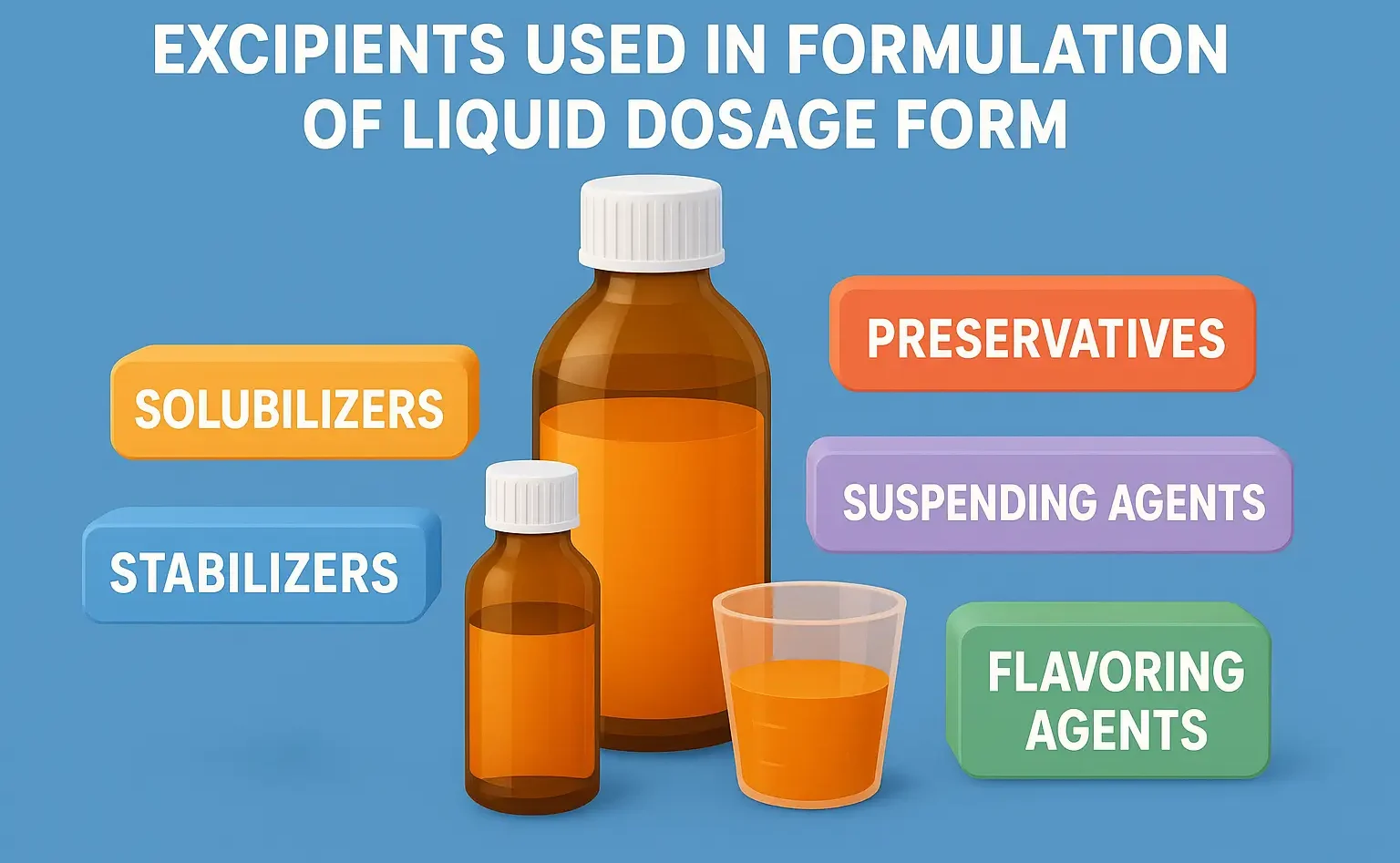
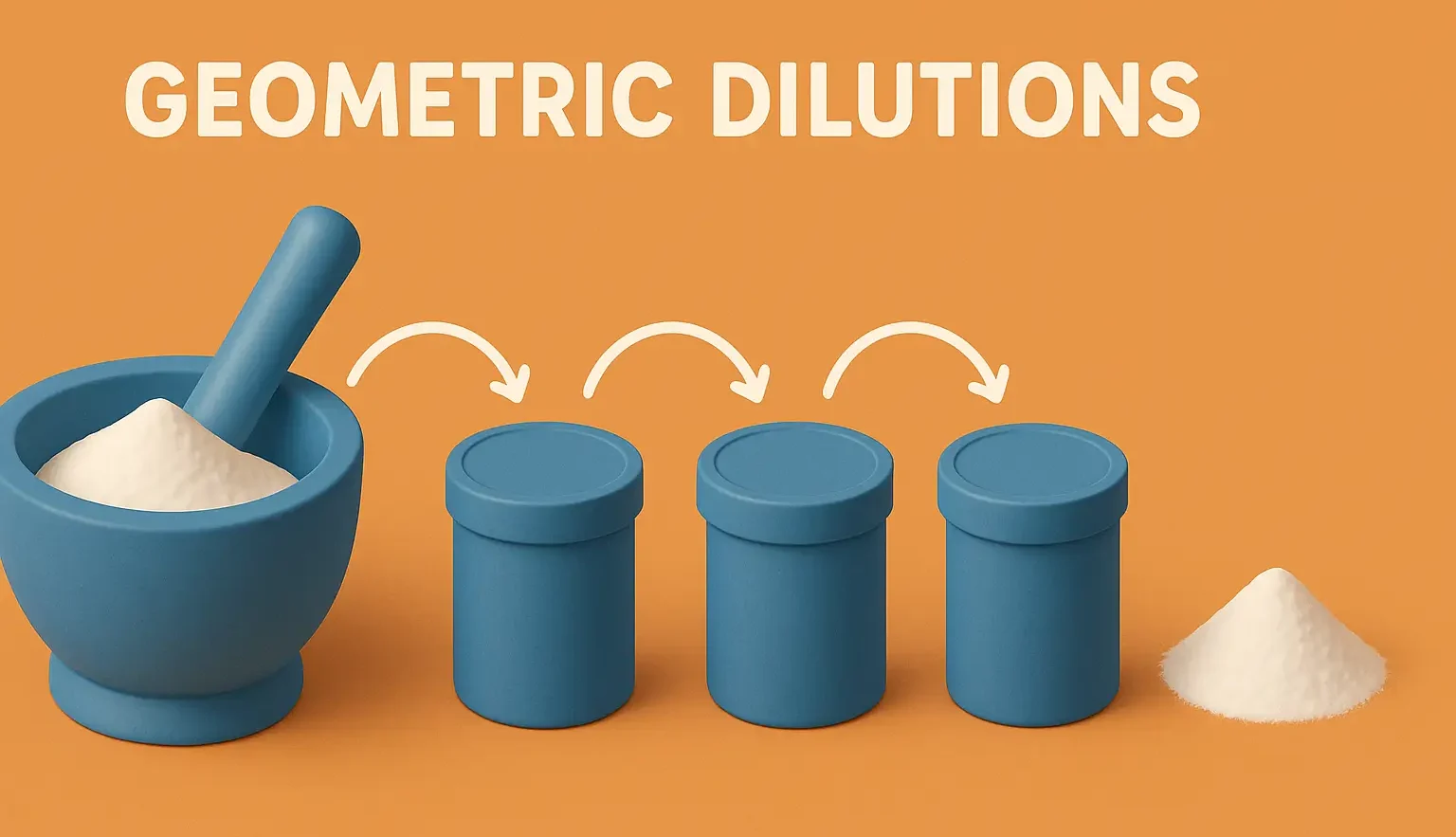
Throat Paint
Throat Paint is a topical medication used to treat sore throats and other throat conditions. It is applied directly to the affected area using a swab or applicator. Throat Paint often contains antiseptic, anesthetic, or anti-inflammatory ingredients to relieve pain and inflammation. Preparation of throat Paints: Step-by-Step Preparation: Prepare Base: Use a viscous base like … Read more