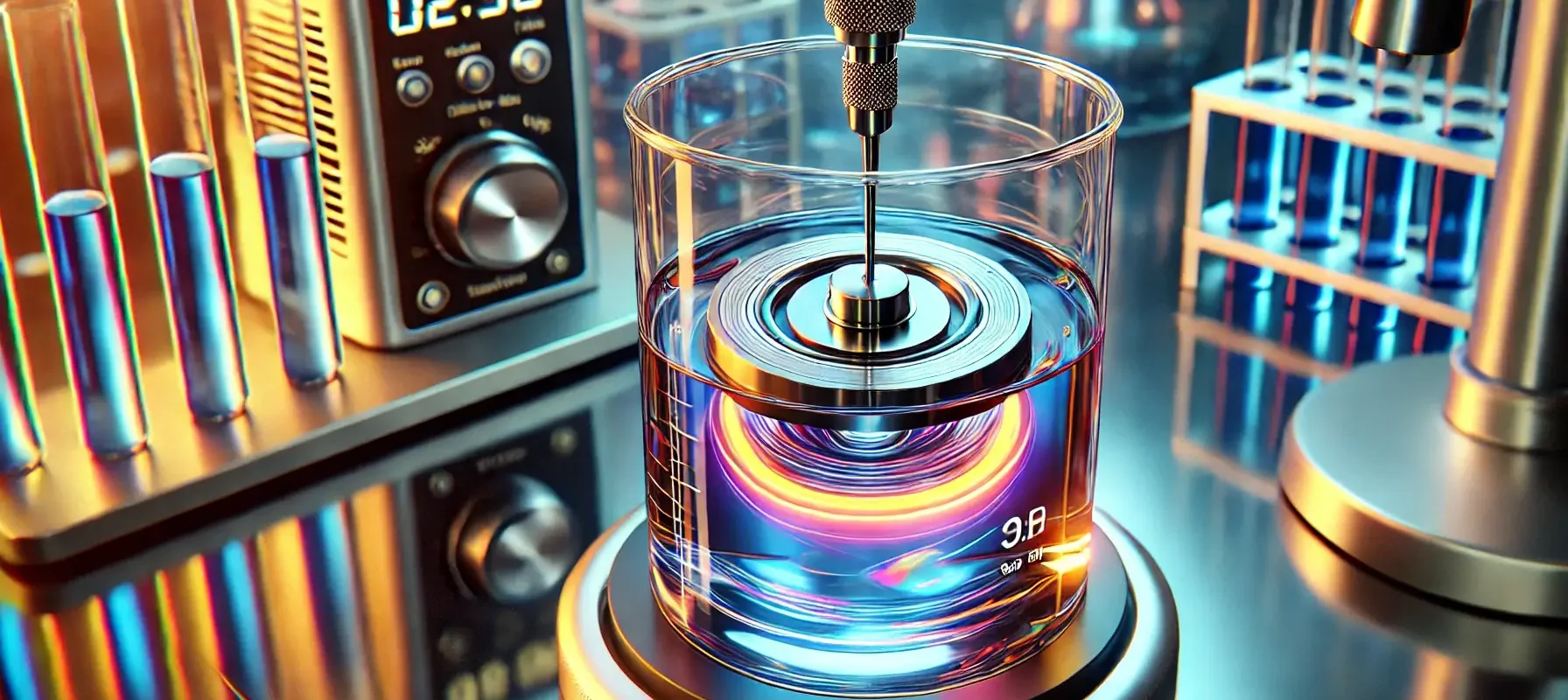
Rotating Platinum Electrode (RPE)
The Rotating Platinum Electrode (RPE) is used in electrochemical experiments, especially in rotating disk electrode (RDE) and rotating ring-disk electrode (RRDE) configurations. It provides enhanced mass transport for studying redox reactions, kinetics, and mass transfer. Construction of Rotating Platinum Electrode: Platinum Disk: A flat, polished platinum disk (1-10 mm in diameter) mounted on insulating material … Read more