Metoprolol
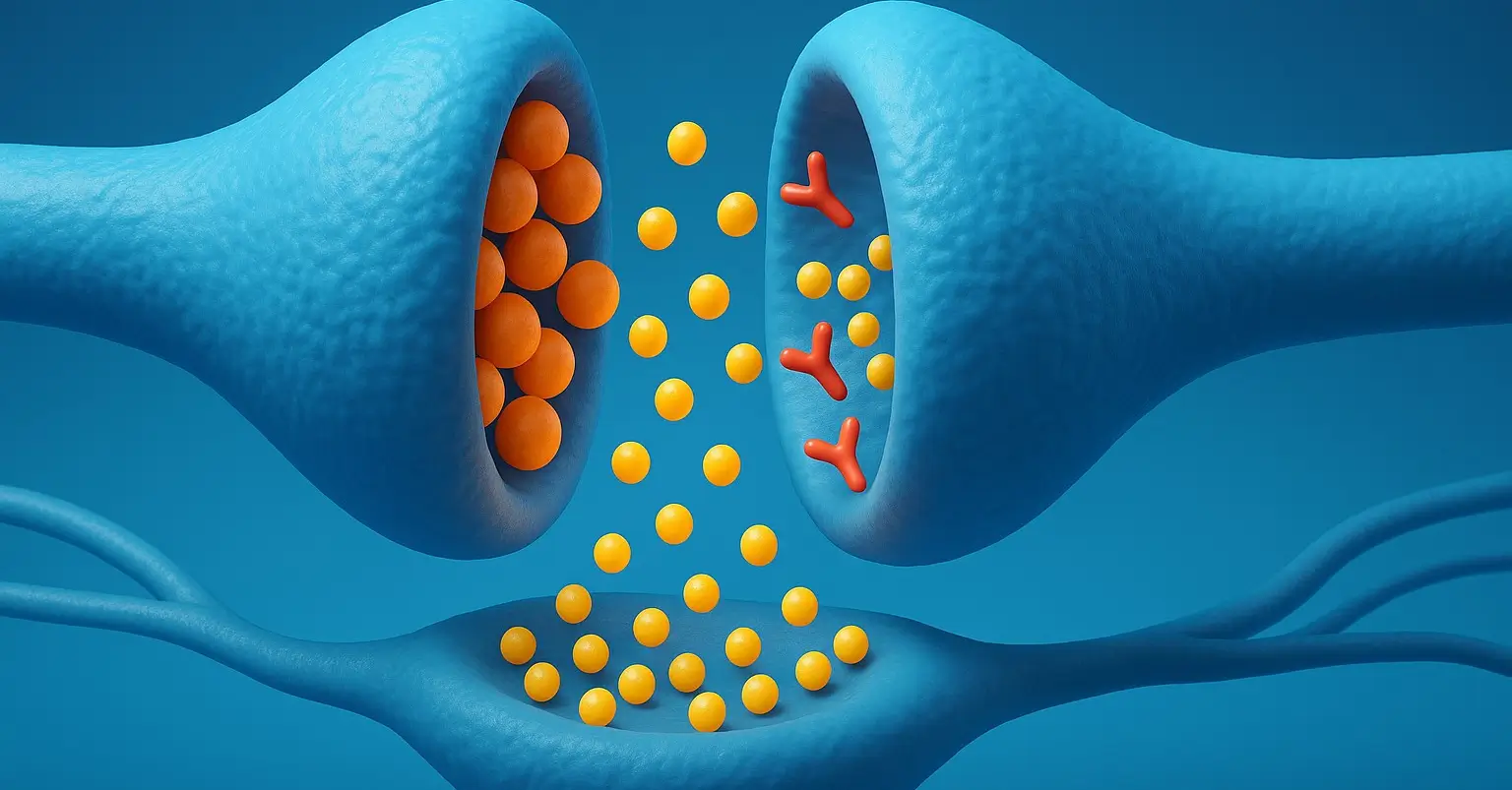
Metoprolol is a selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor blocker (β1-blocker) used primarily to manage cardiovascular conditions. It reduces the effects of adrenaline on the heart, leading to decreased heart rate, cardiac output, and blood pressure. Chemical Structure & Formula: Comprises an aromatic ring joined to an oxypropanolamine chain and is typically used as a racemic mixture … Read more