Introduction to Conductometry in Pharmaceutical Analysis
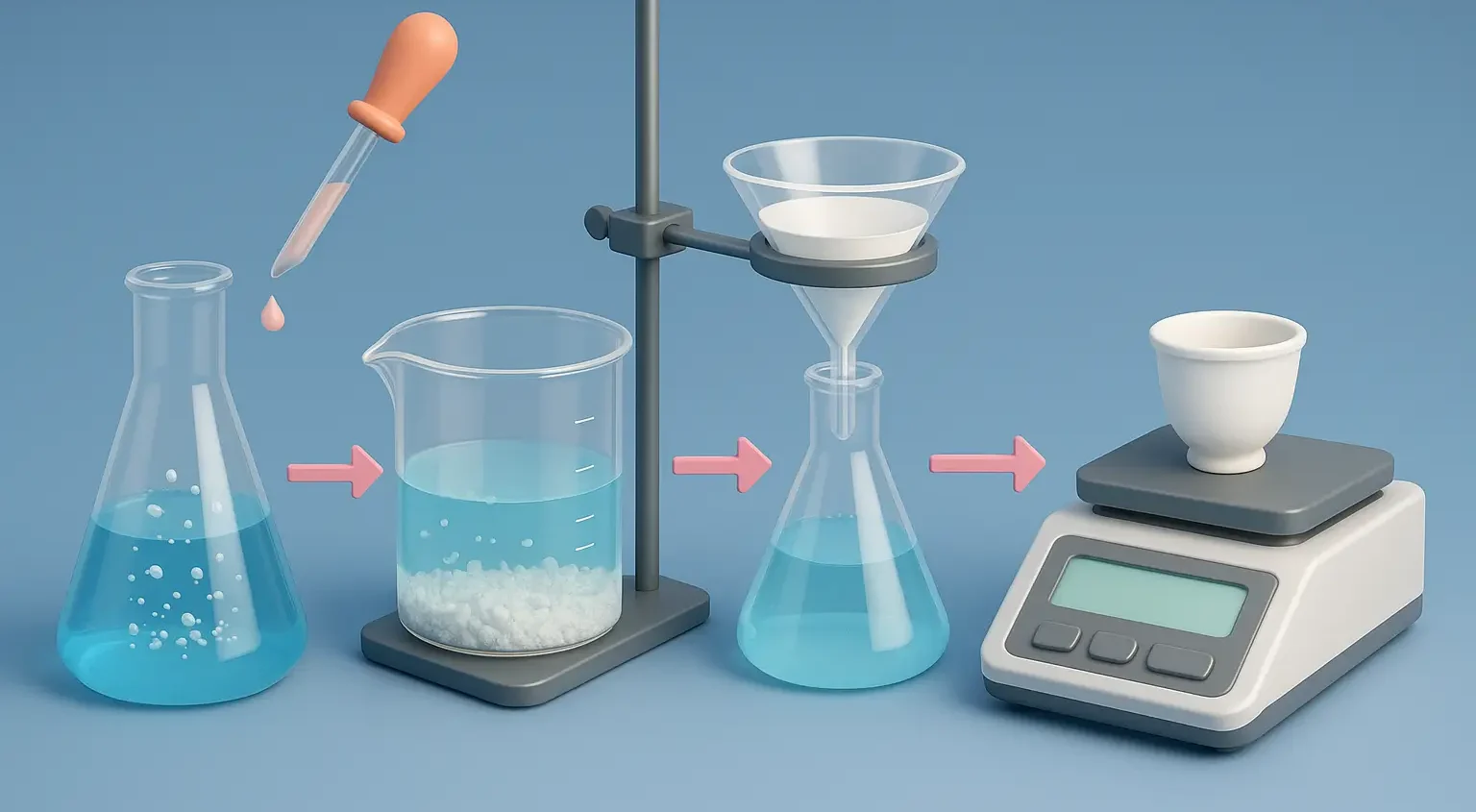
Introduction to Conductometry in Pharmaceutical Analysis is a significant analytical technique used in various fields, including pharmaceutical analysis, to measure the electrical conductivity of a solution. This measurement is indicative of the presence and concentration of ions in the solution, which is essential for understanding many aspects of a solution’s composition and properties. Here’s an … Read more