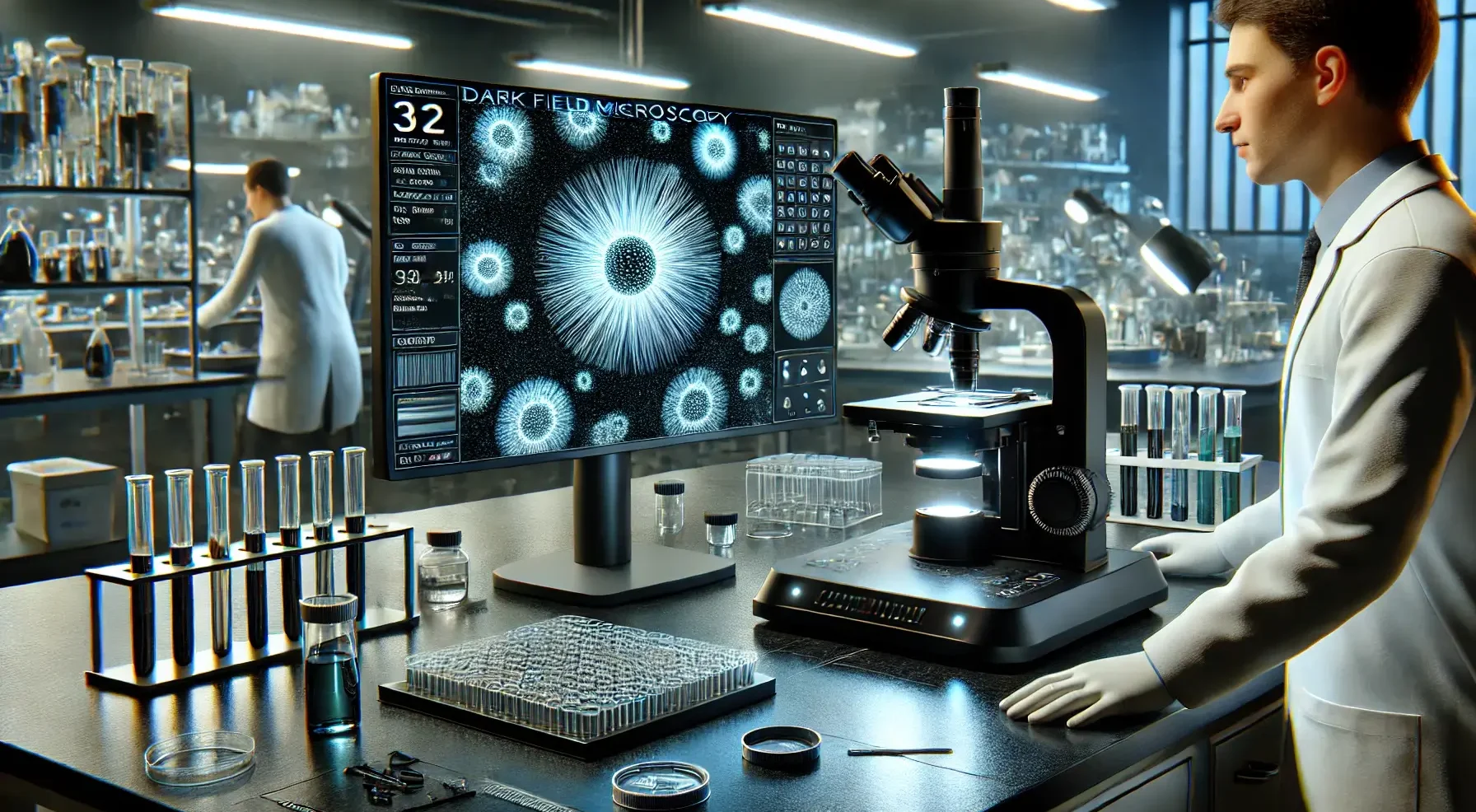
Dark Field Microscopy
Dark field microscopy enhances the contrast of transparent and unstained specimens by illuminating them with light that does not enter the objective lens unless it is scattered by the specimen. This creates a bright image of the specimen against a dark background, making normally invisible structures visible. Procedure for Dark Field Microscopy Preparation of the … Read more