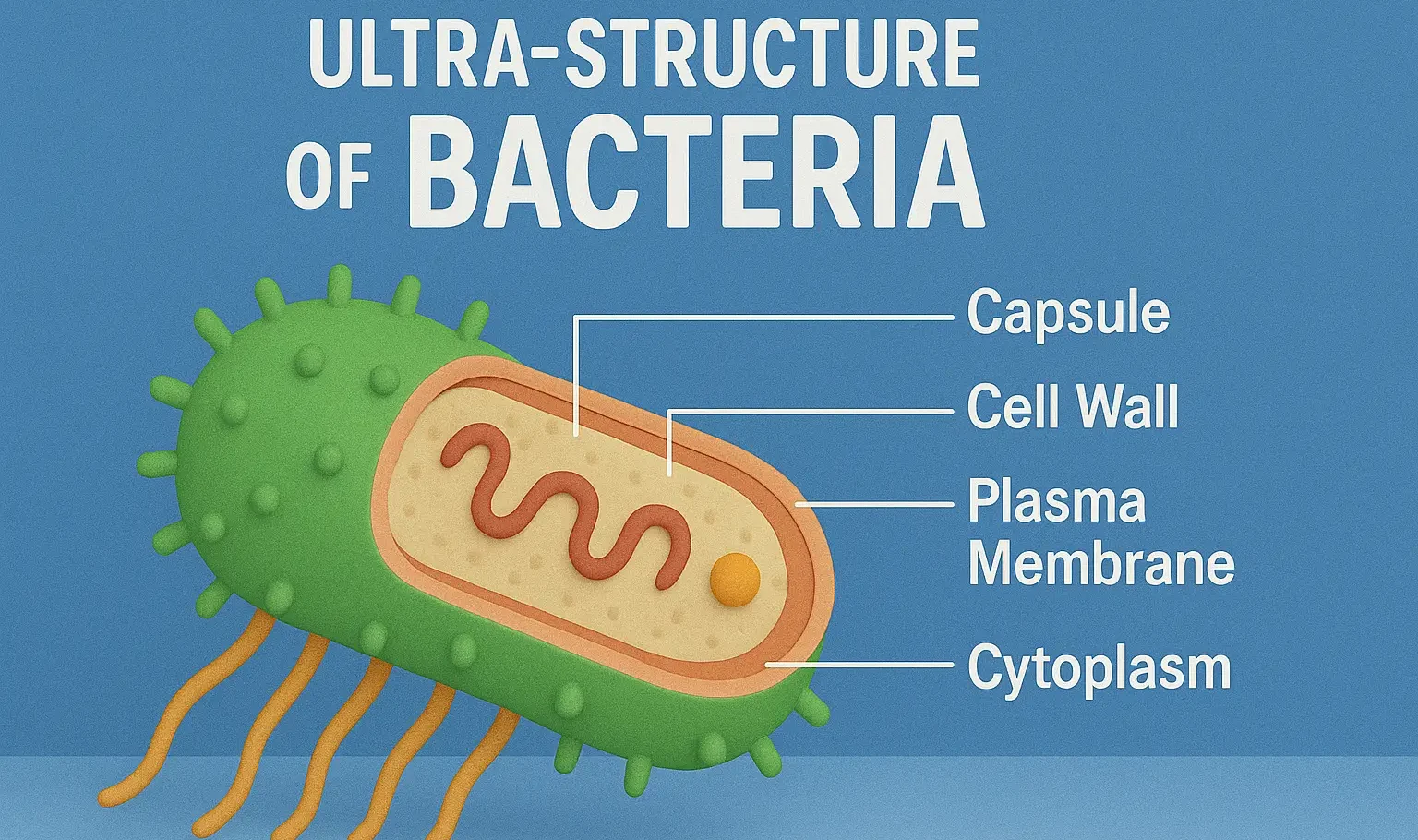
Ultra-structure of Bacteria
Ultra-structure of Bacteria Bacteria are single-celled, prokaryotic microorganisms that are found in virtually every environment on Earth. They belong to the domain Bacteria, one of the two domains of prokaryotes, the other being Archaea. Bacteria are among the earliest forms of life, appearing about 3.5 billion years ago. The ultra-structure of bacteria refers to the … Read more