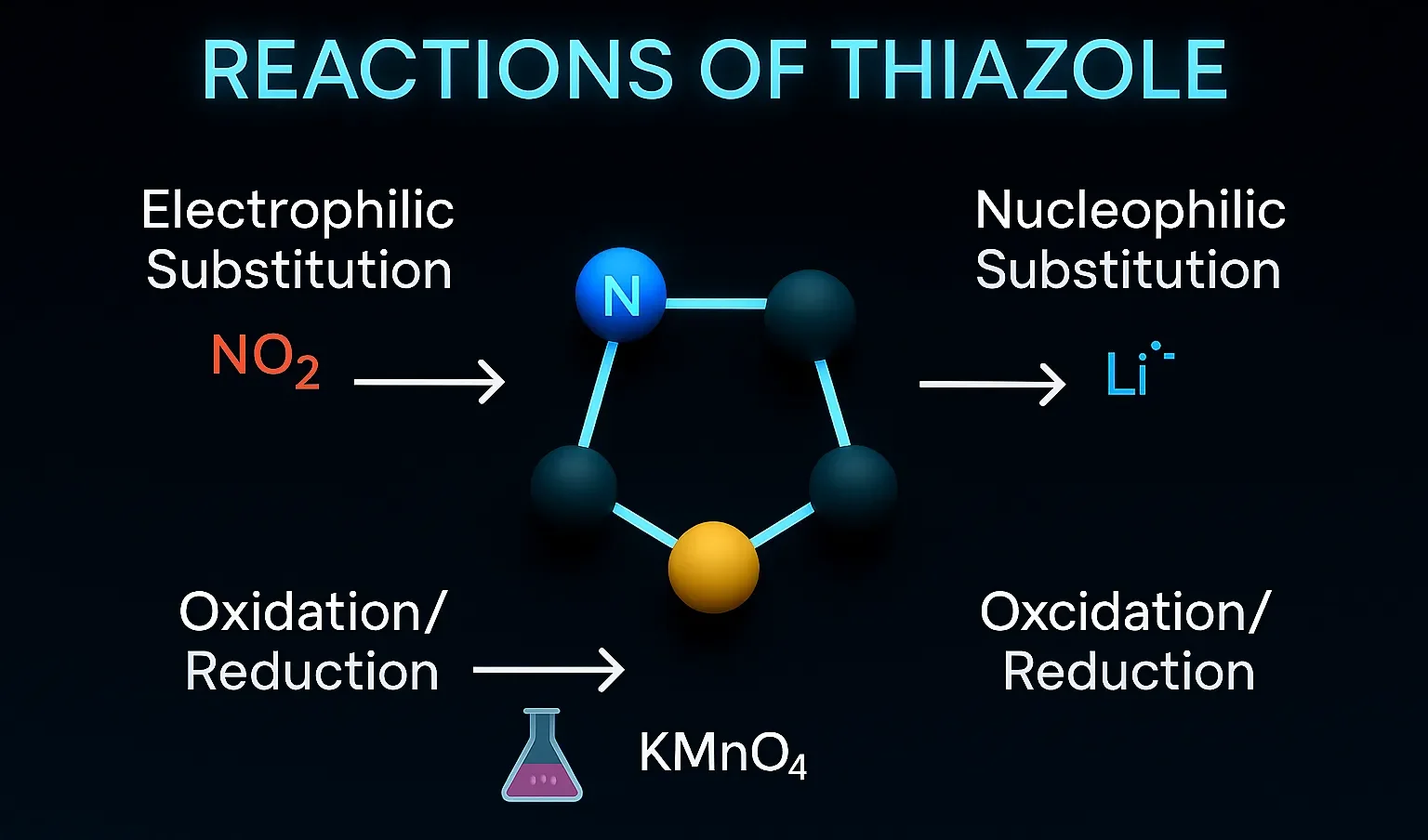
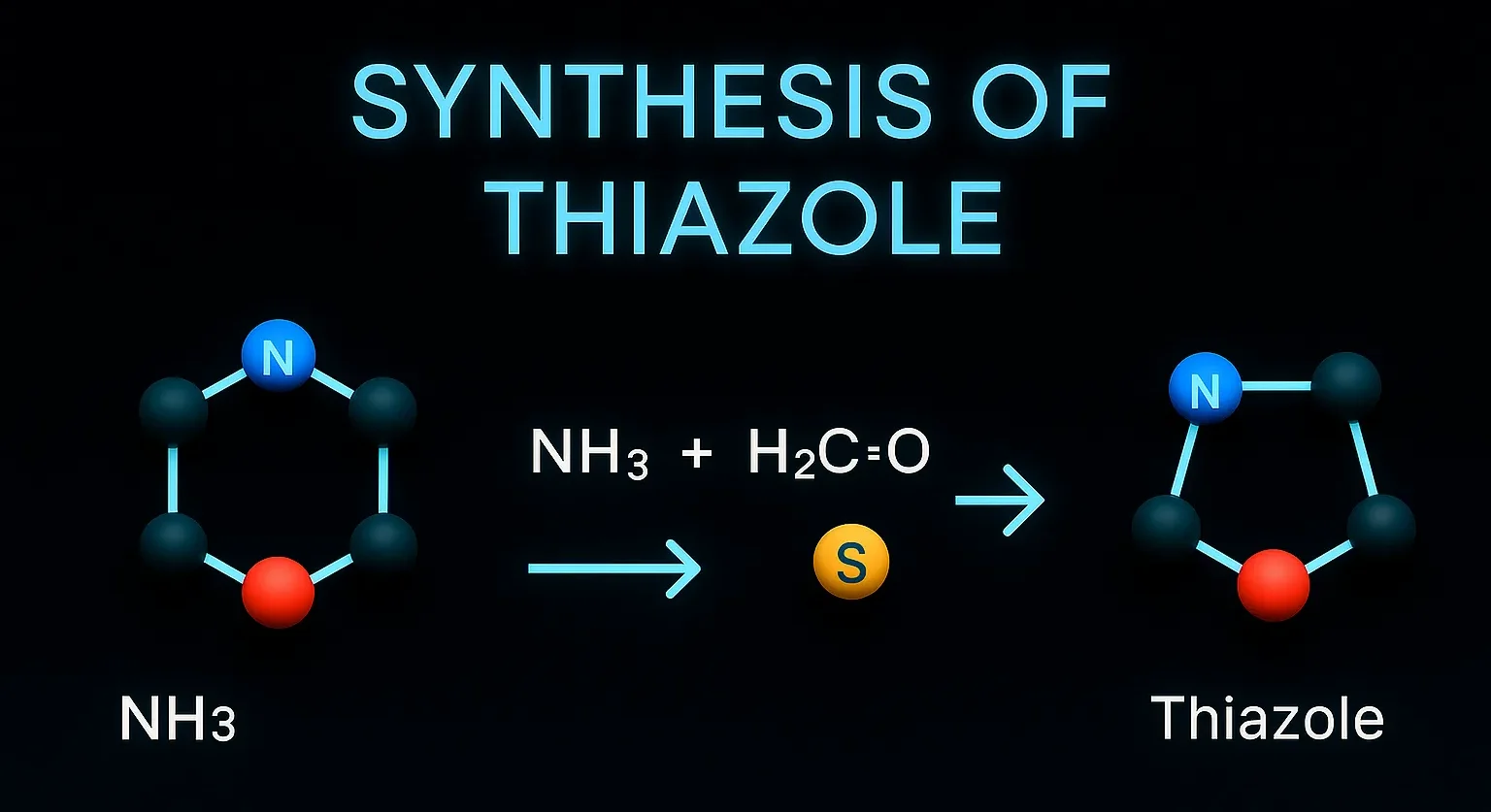
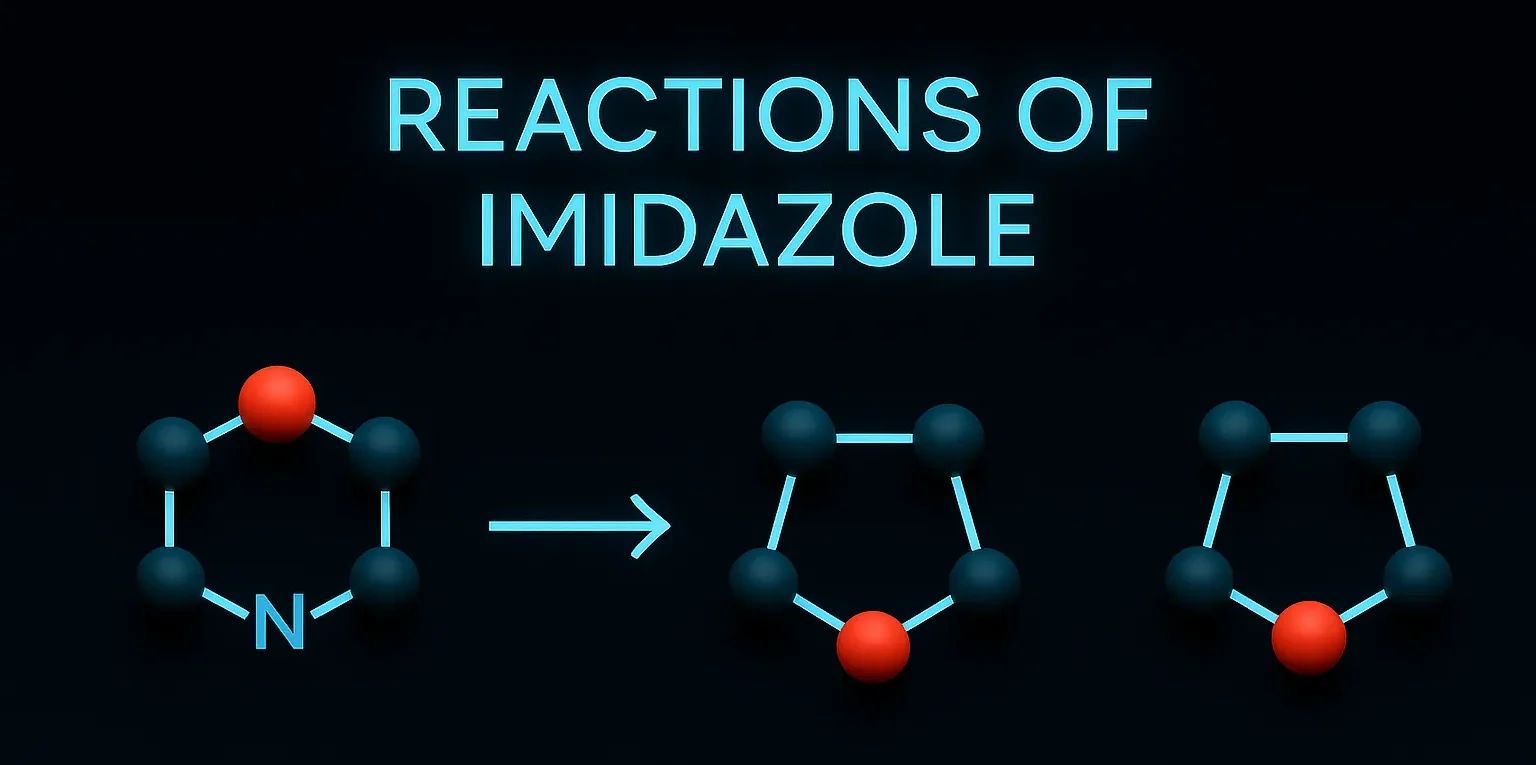
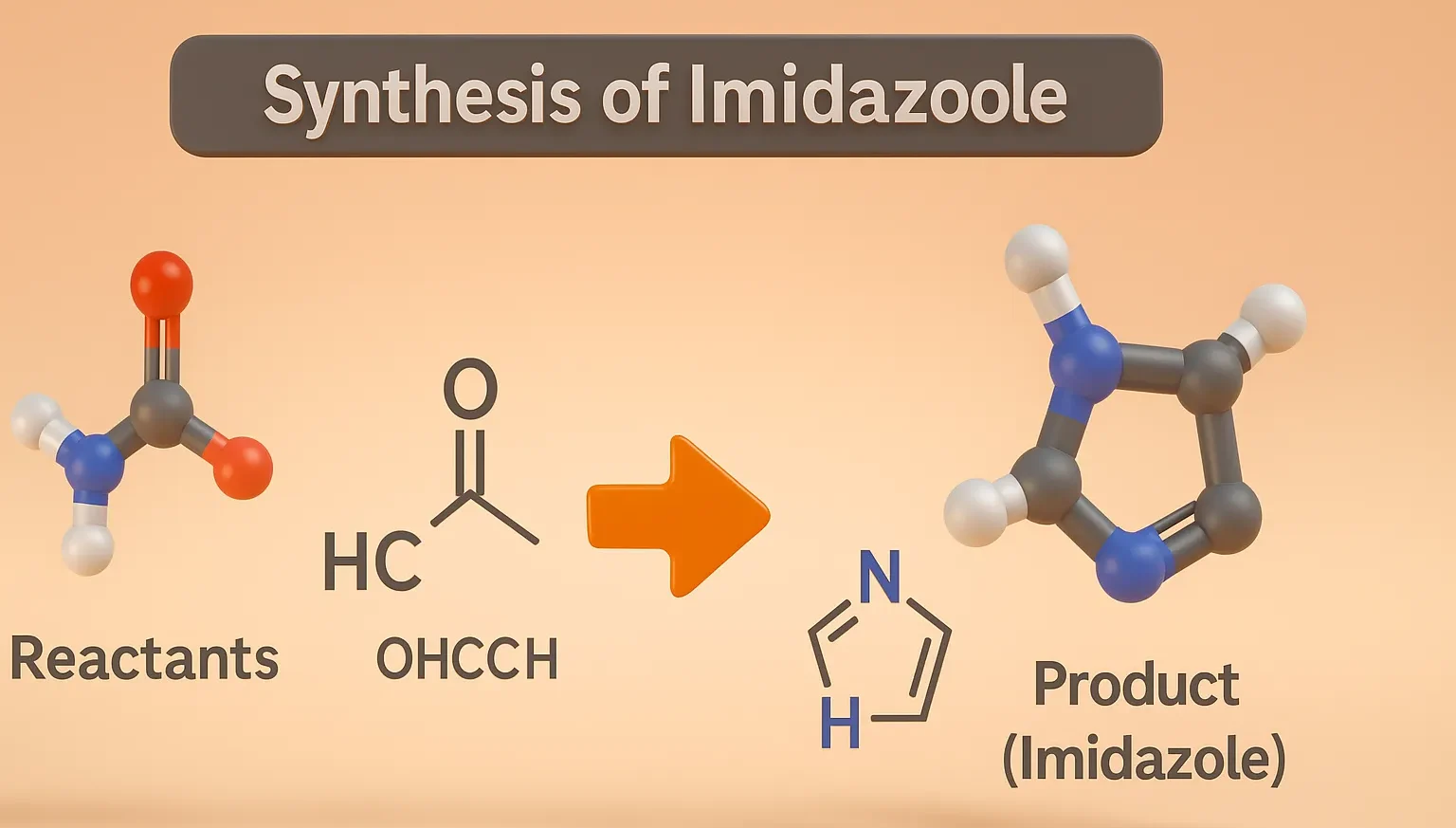
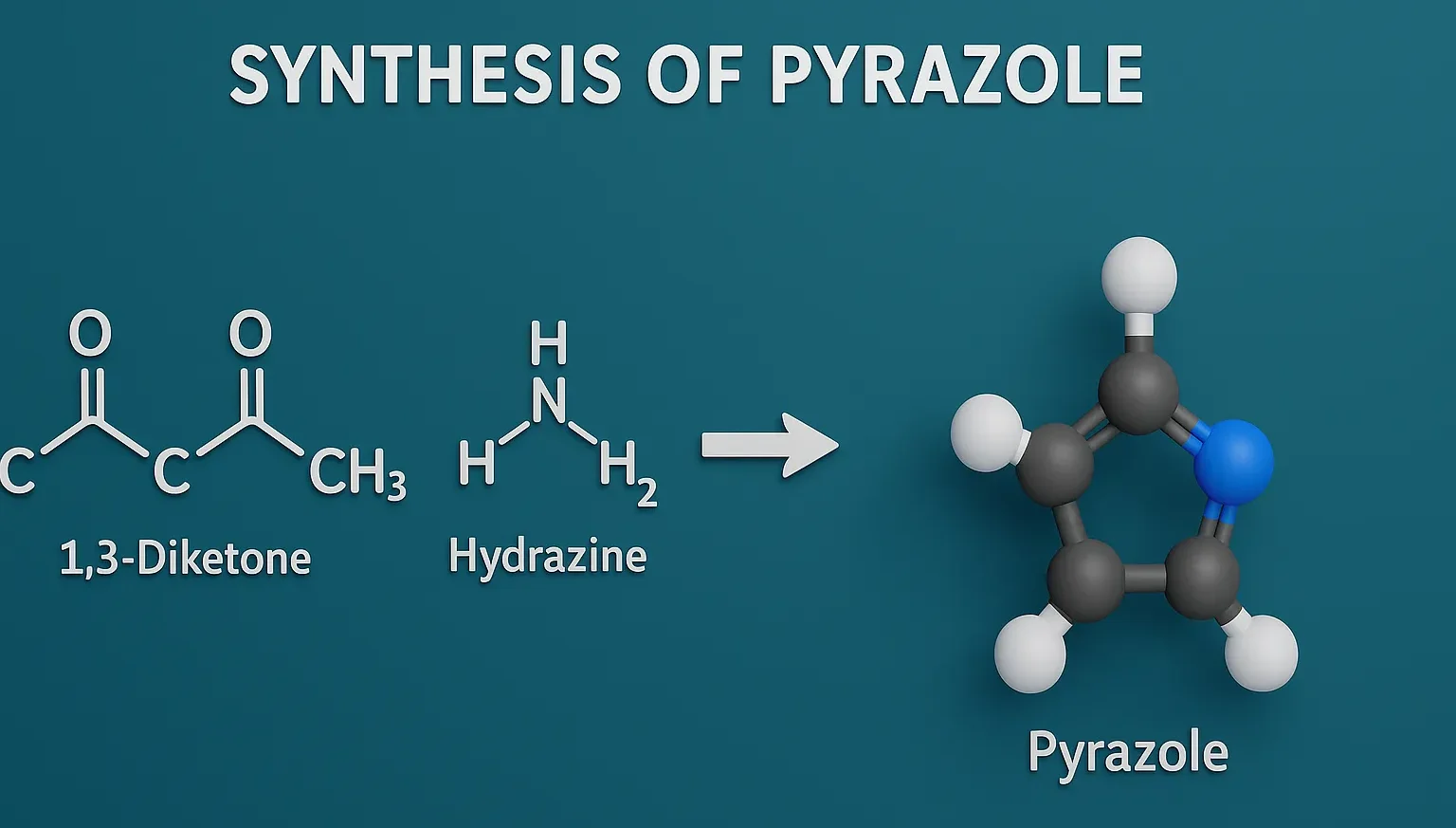
Pyridine
Pyridine is a nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound essential in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and organic synthesis. Chemical Formula of Pyridine: C₅H₅N Physical Properties of Pyridine: Property Value Appearance Colorless liquid Odor Fish-like, unpleasant Boiling Point ~115 °C Melting Point ~-41 °C Solubility Miscible with water and organics Basicity (pKa of conjugate acid) ~5.2 (moderately basic) Medicinal Uses: Pyridine … Read more