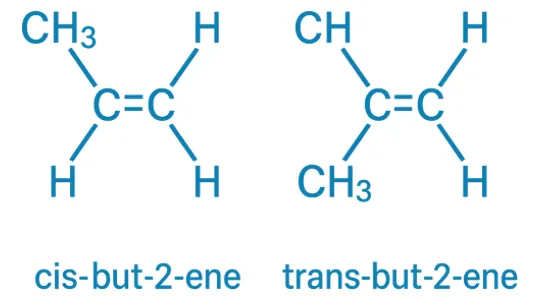
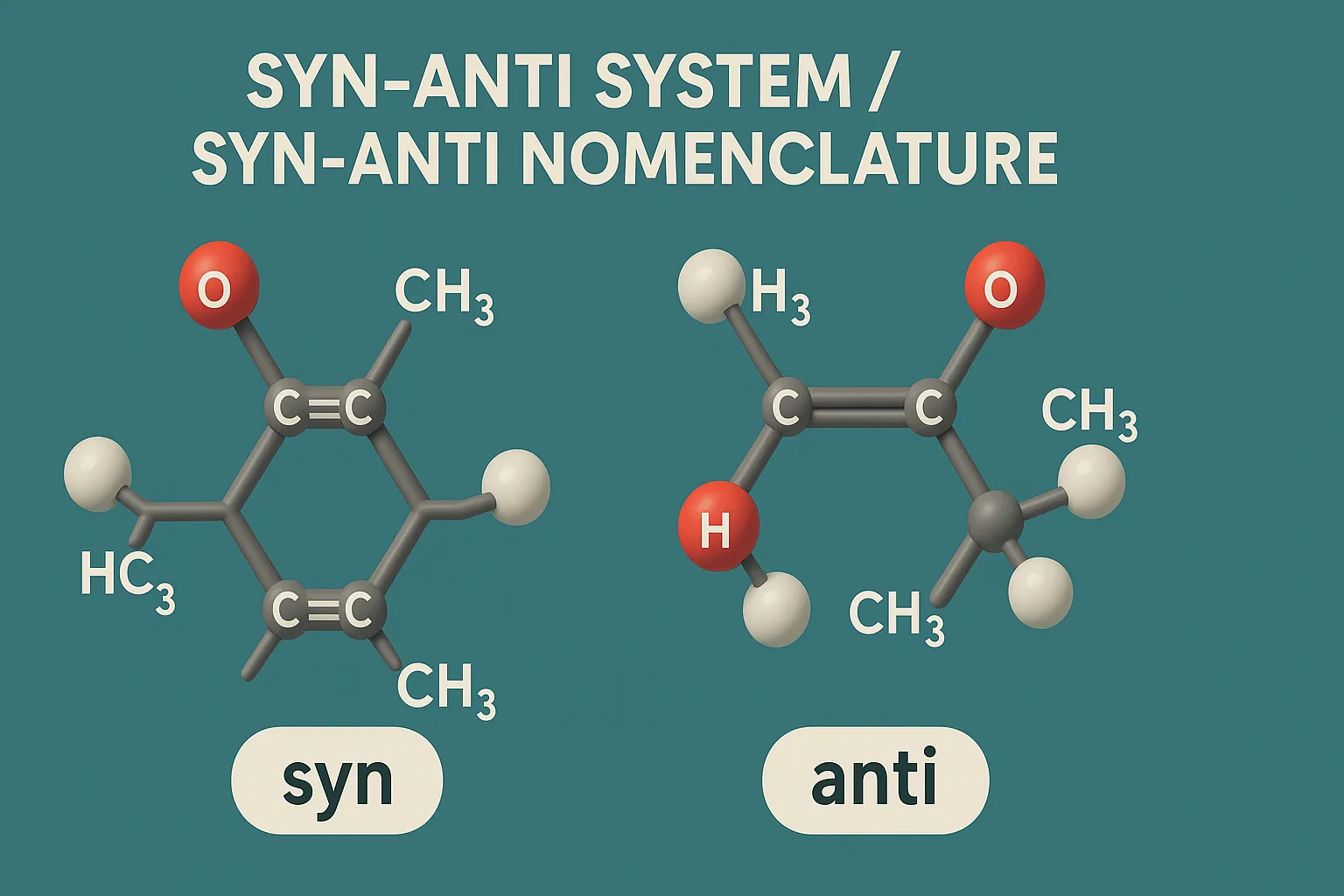
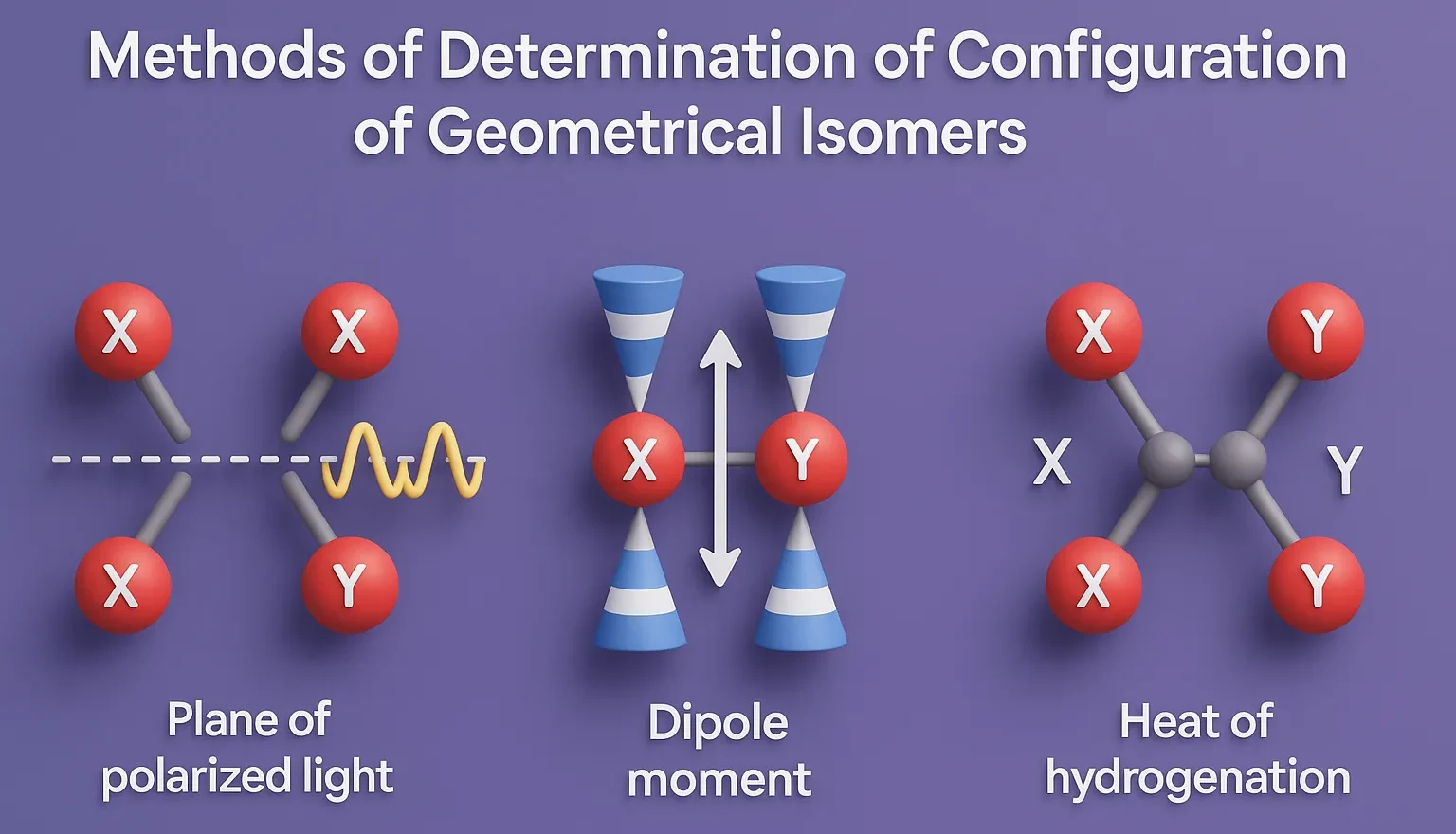
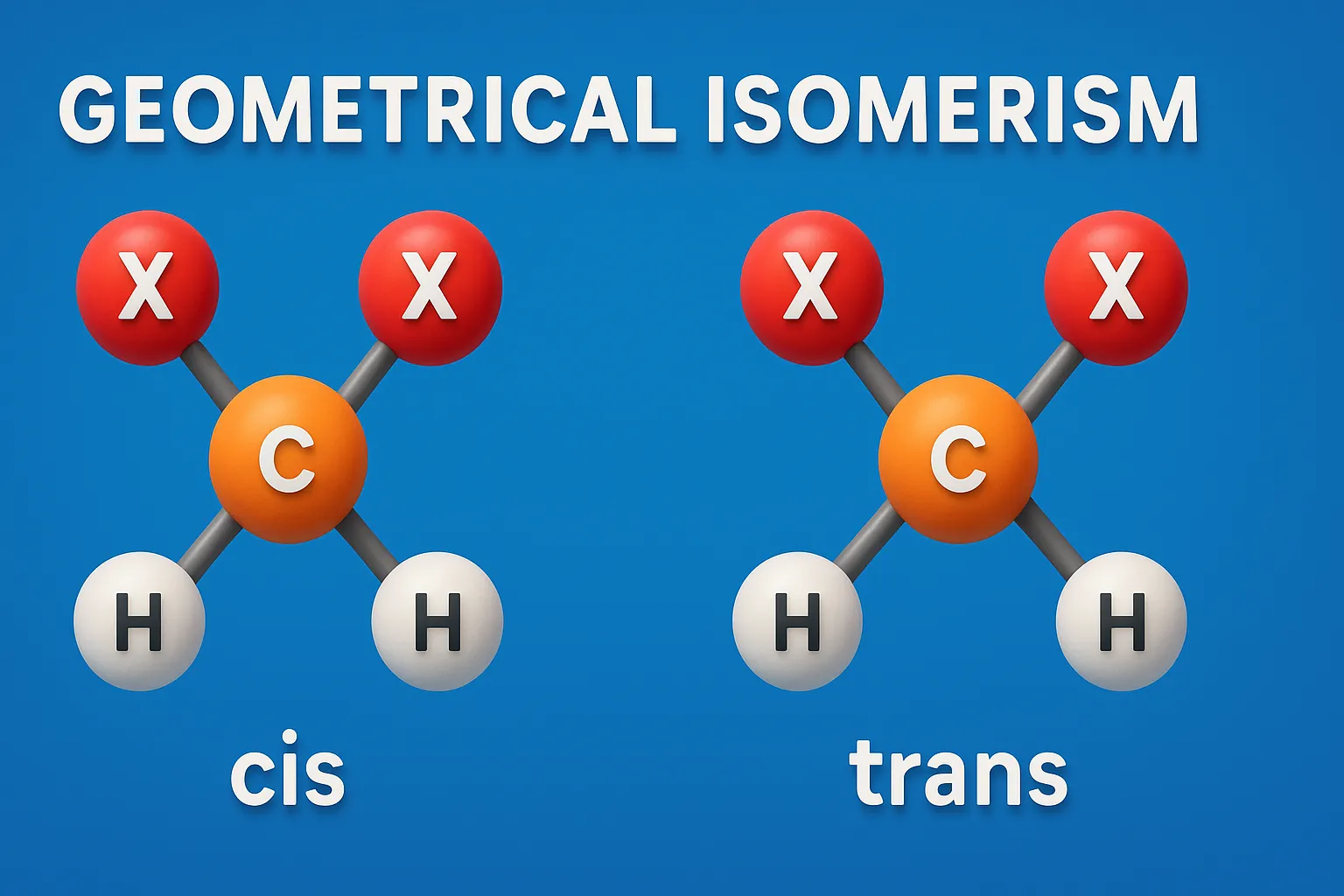
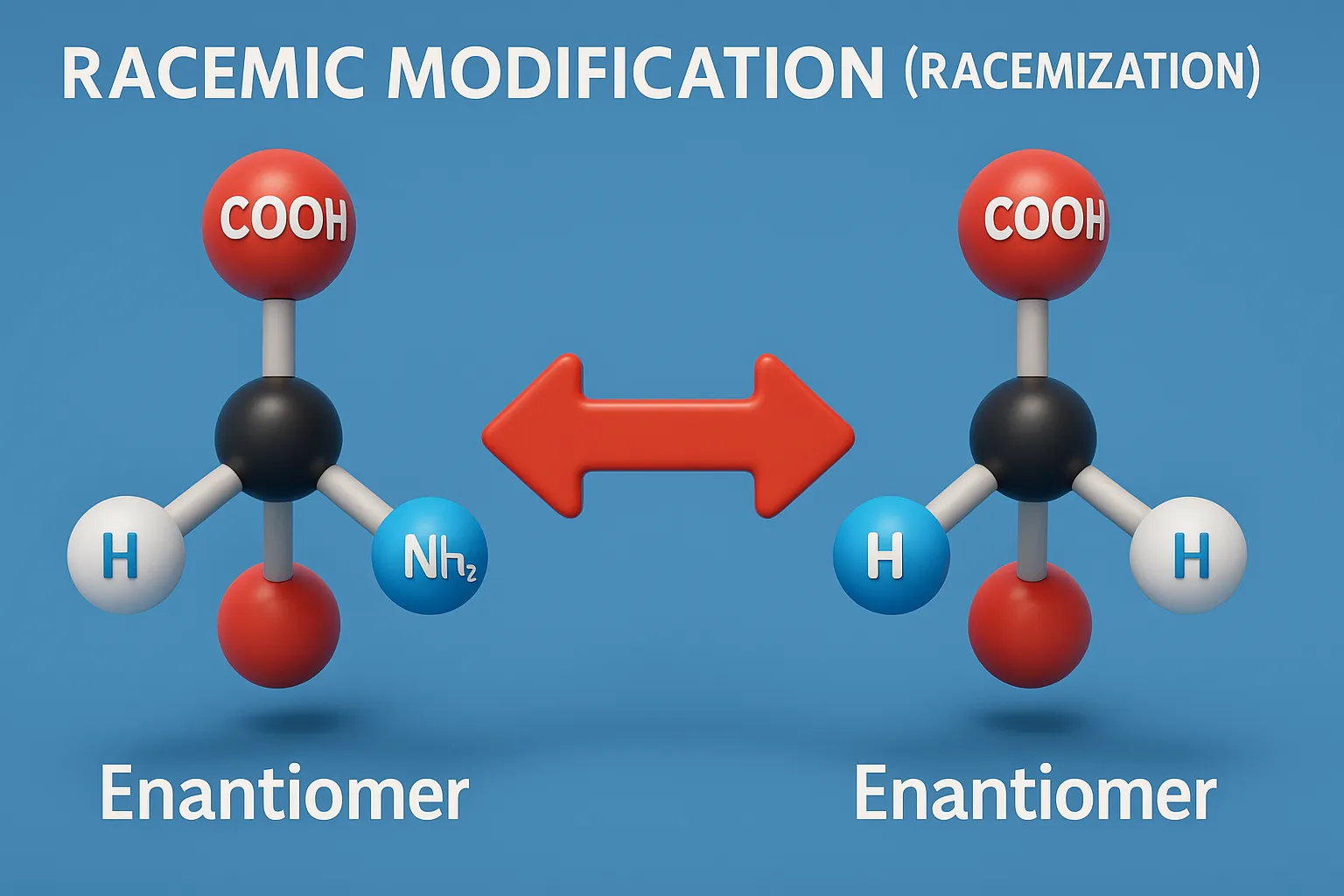
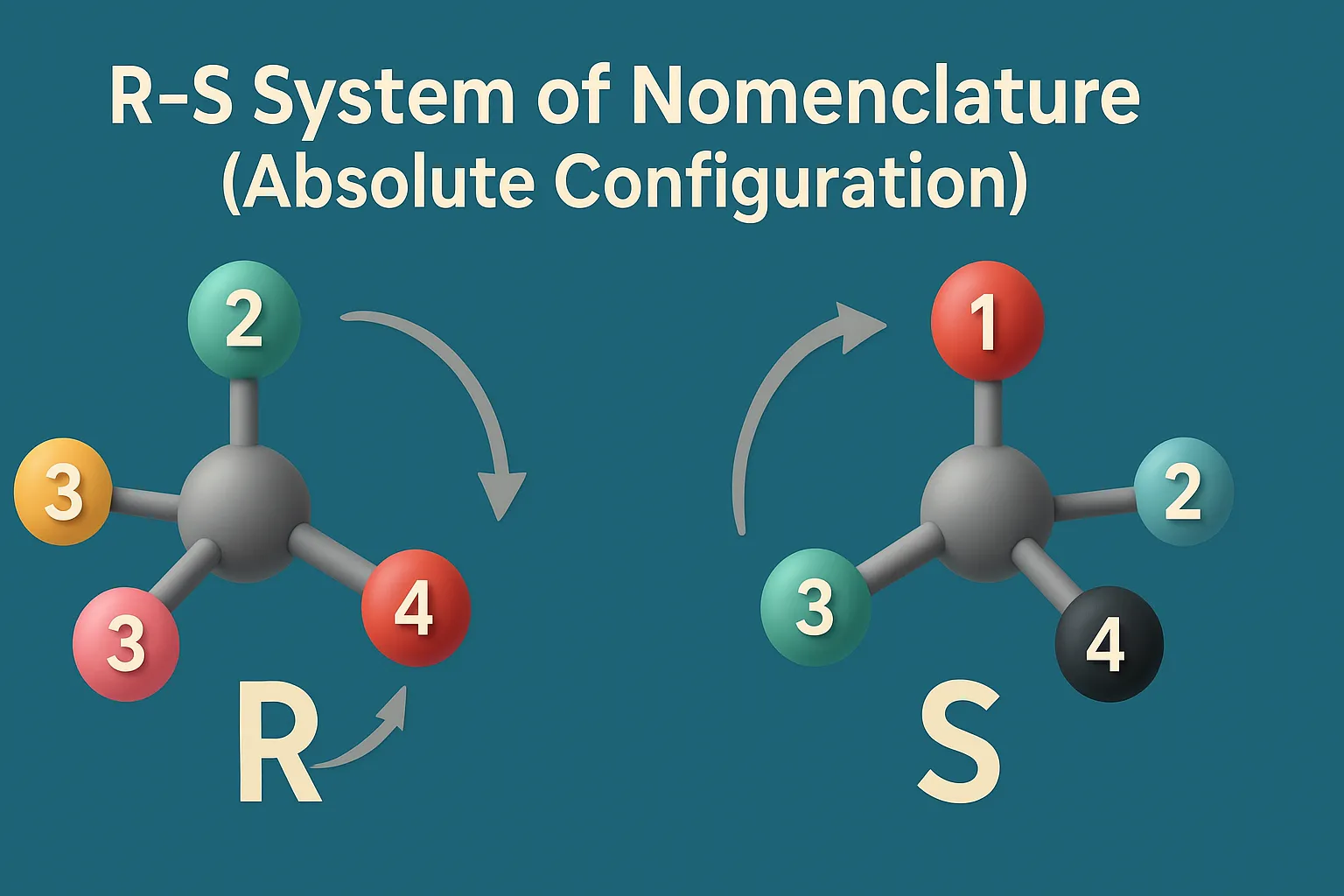
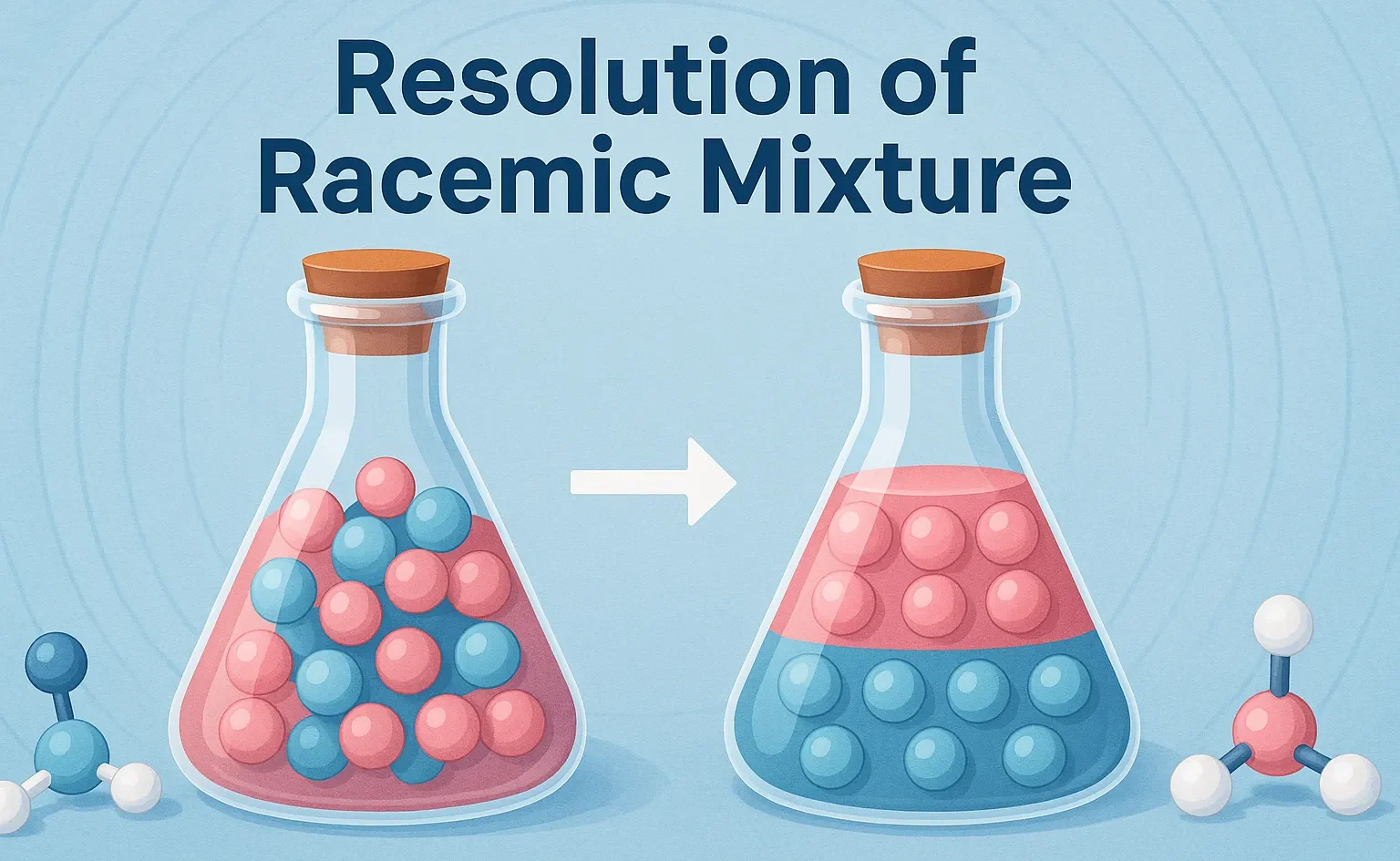
Cis-Trans Nomenclature
Cis-Trans Nomenclature names geometrical isomers by positioning similar groups on the same side (cis) or opposite sides (trans) of a double bond or ring. When to Use: Use the Cis-Trans system when each carbon in the double bond has one identical group. It is suitable for: Simple alkenes with symmetrical groups, Cycloalkanes, where two substituents … Read more