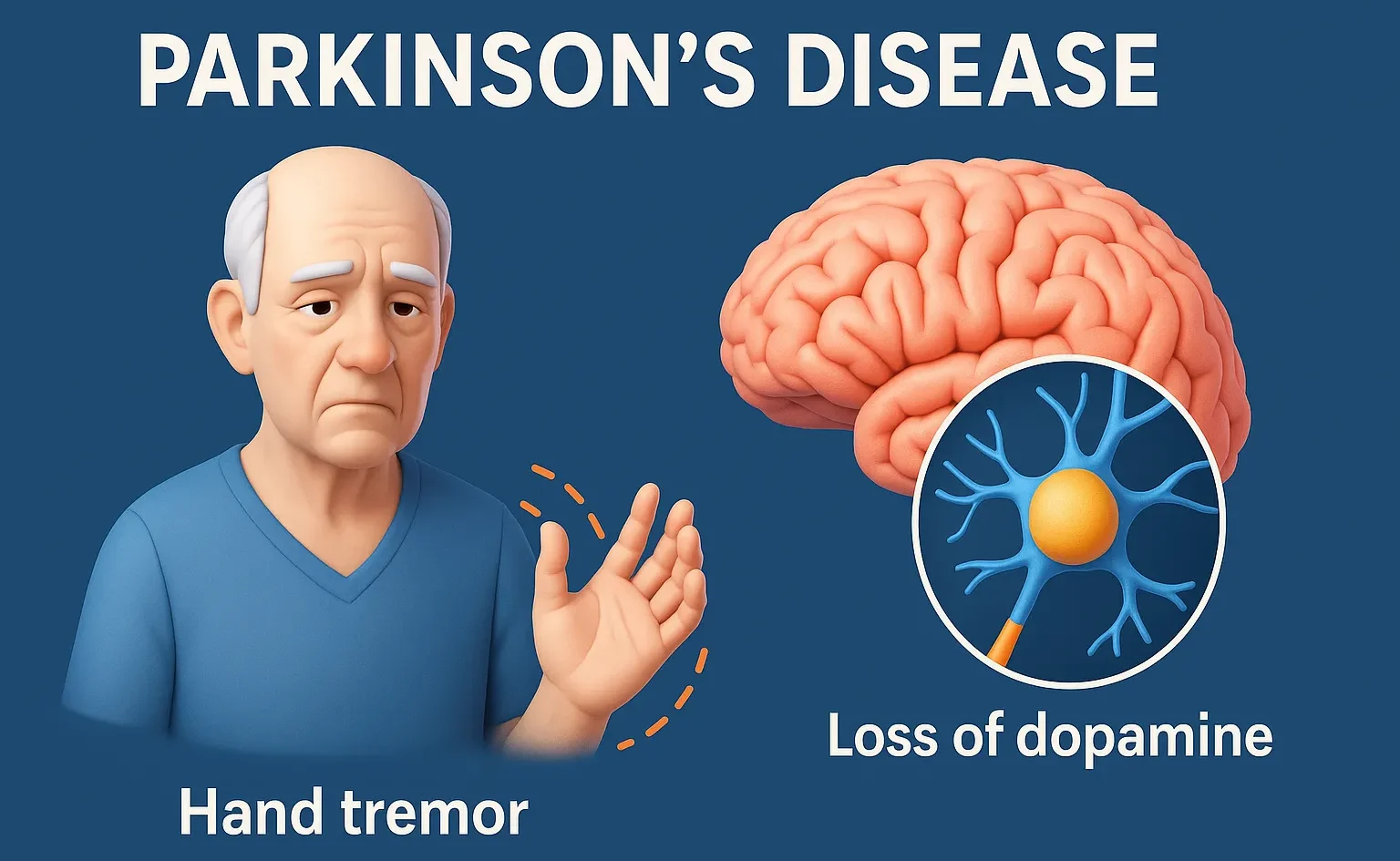
Drugs Used in Parkinson’s Disease
This article explains about the Drugs for Parkinson’s disease improve dopamine levels or reduce symptoms like tremors and stiffness. Dopaminergic Agents Levodopa + Carbidopa Levodopa is a precursor to dopamine that crosses the blood-brain barrier. Carbidopa inhibits peripheral DOPA decarboxylase, preventing conversion of levodopa to dopamine outside the CNS, thus increasing its bioavailability in the … Read more