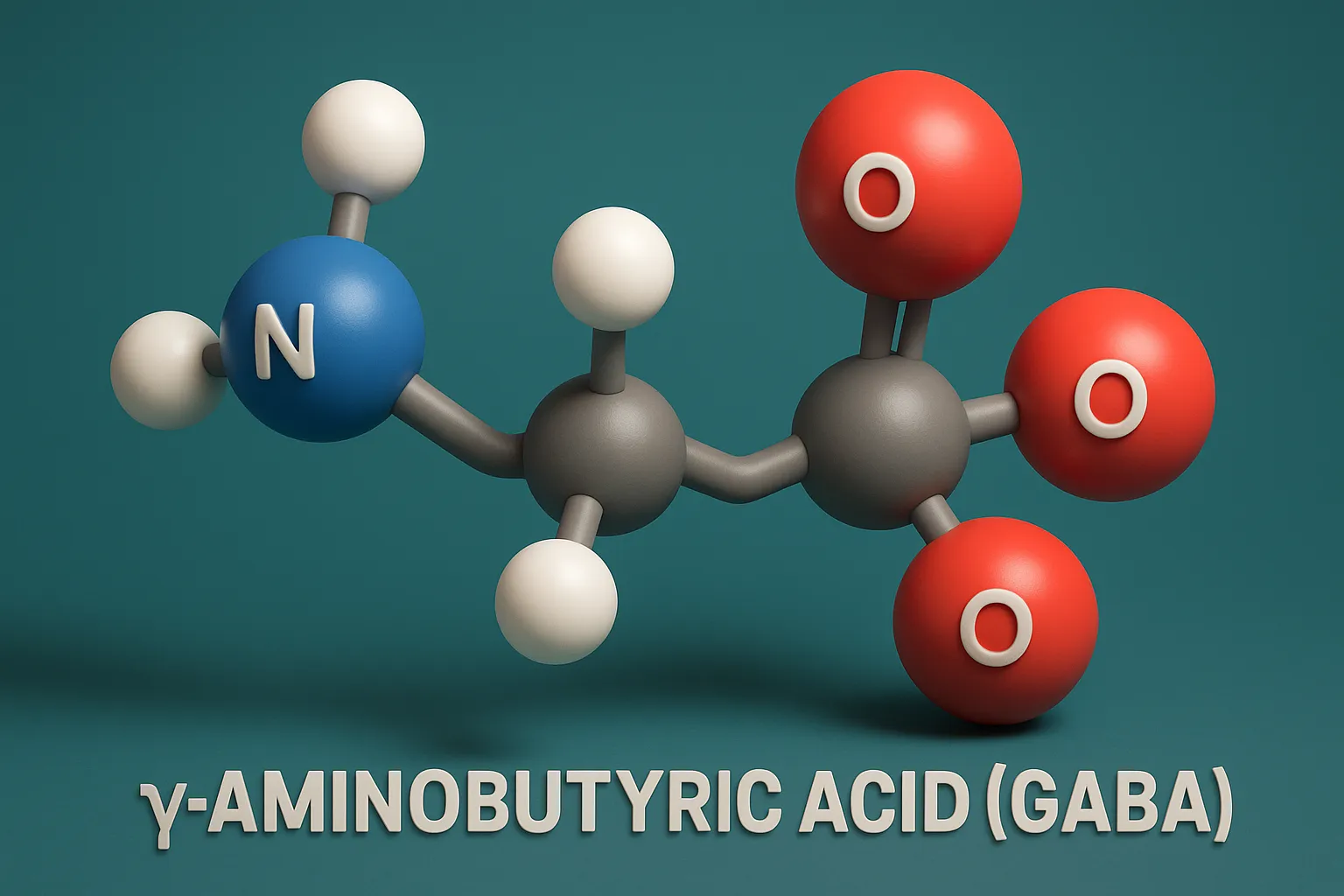
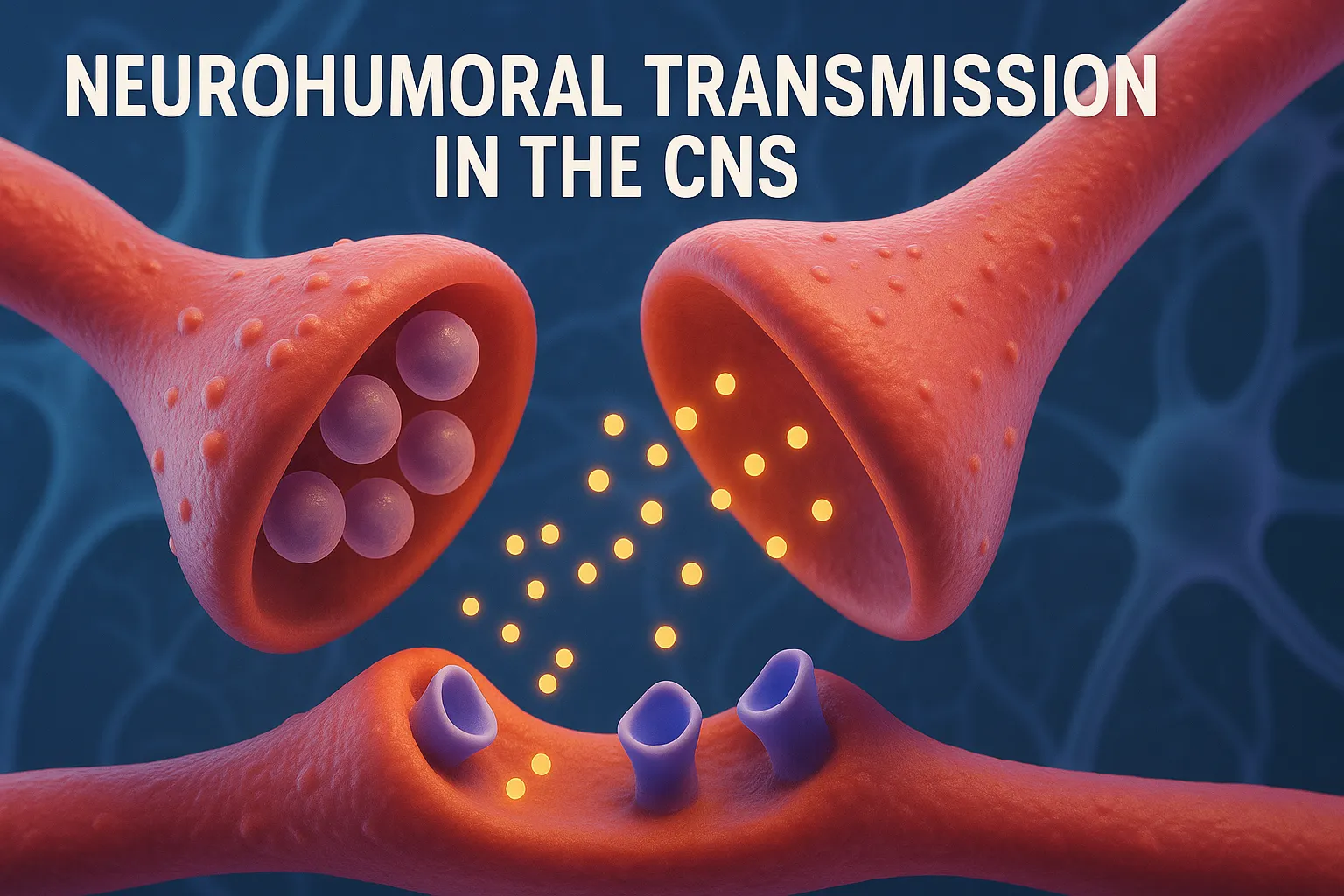
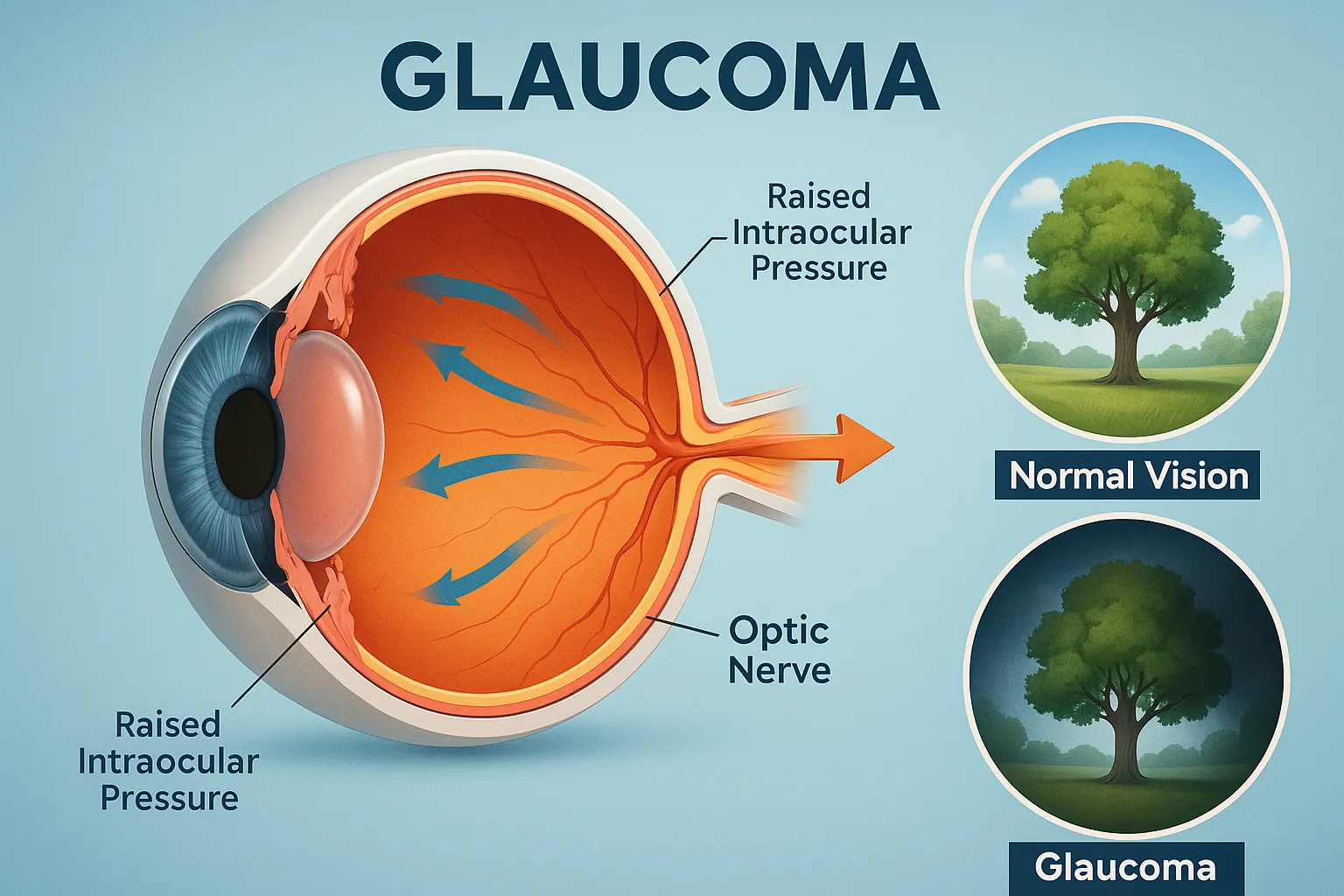
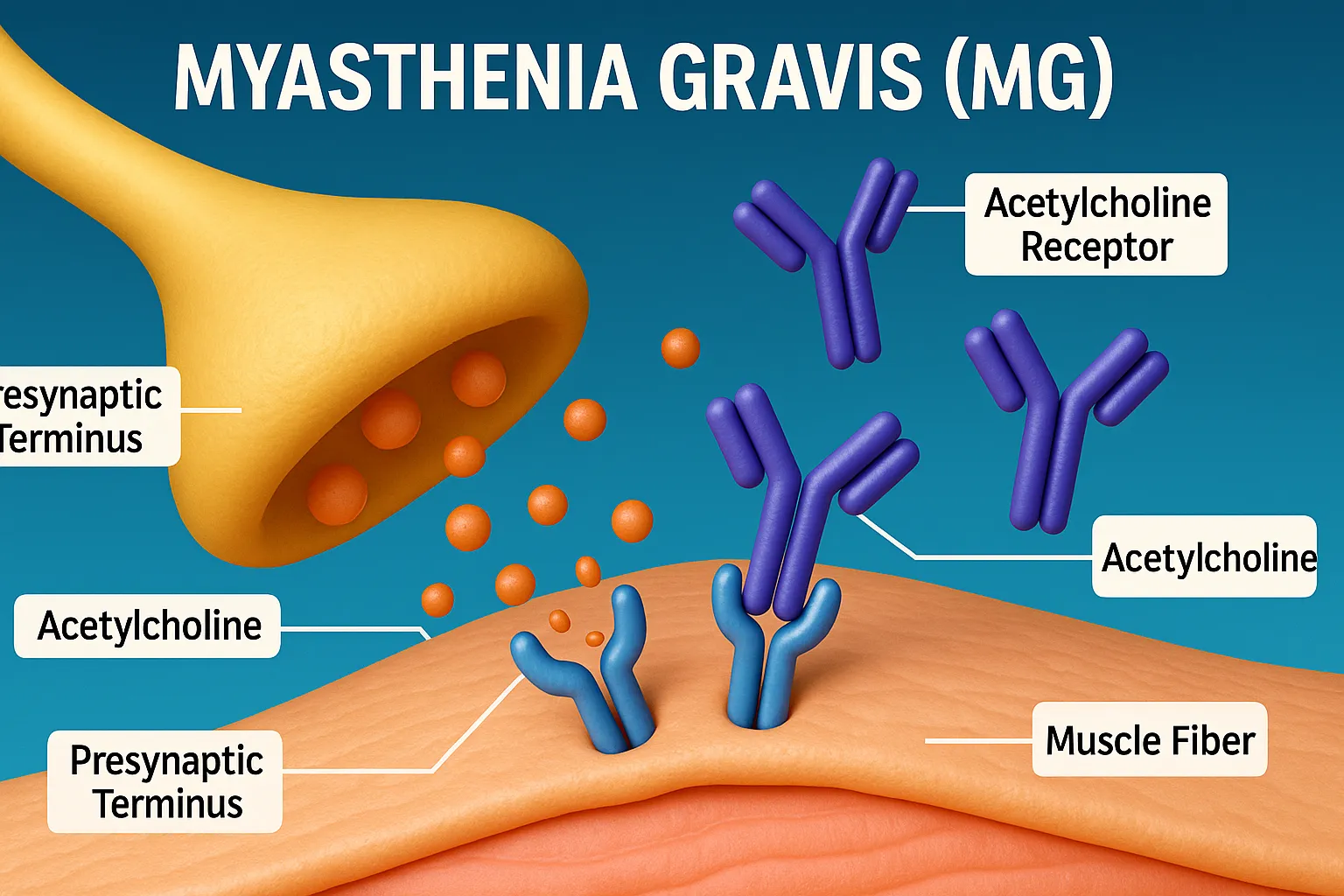
Glutamate
Glutamate is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS, crucial for learning, memory, and brain function. Function of Glutamate: Primary excitatory neurotransmitter. Crucial for synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. Receptors: Ionotropic: NMDA (N-Methyl-D-Aspartate) AMPA Kainate Metabotropic: mGluRs (G-protein-coupled) Synthesis Pathway of Glutamate: Glutamine (from astrocytes) → Glutamate Enzyme: Glutaminase Glutamate is packed into vesicles by … Read more