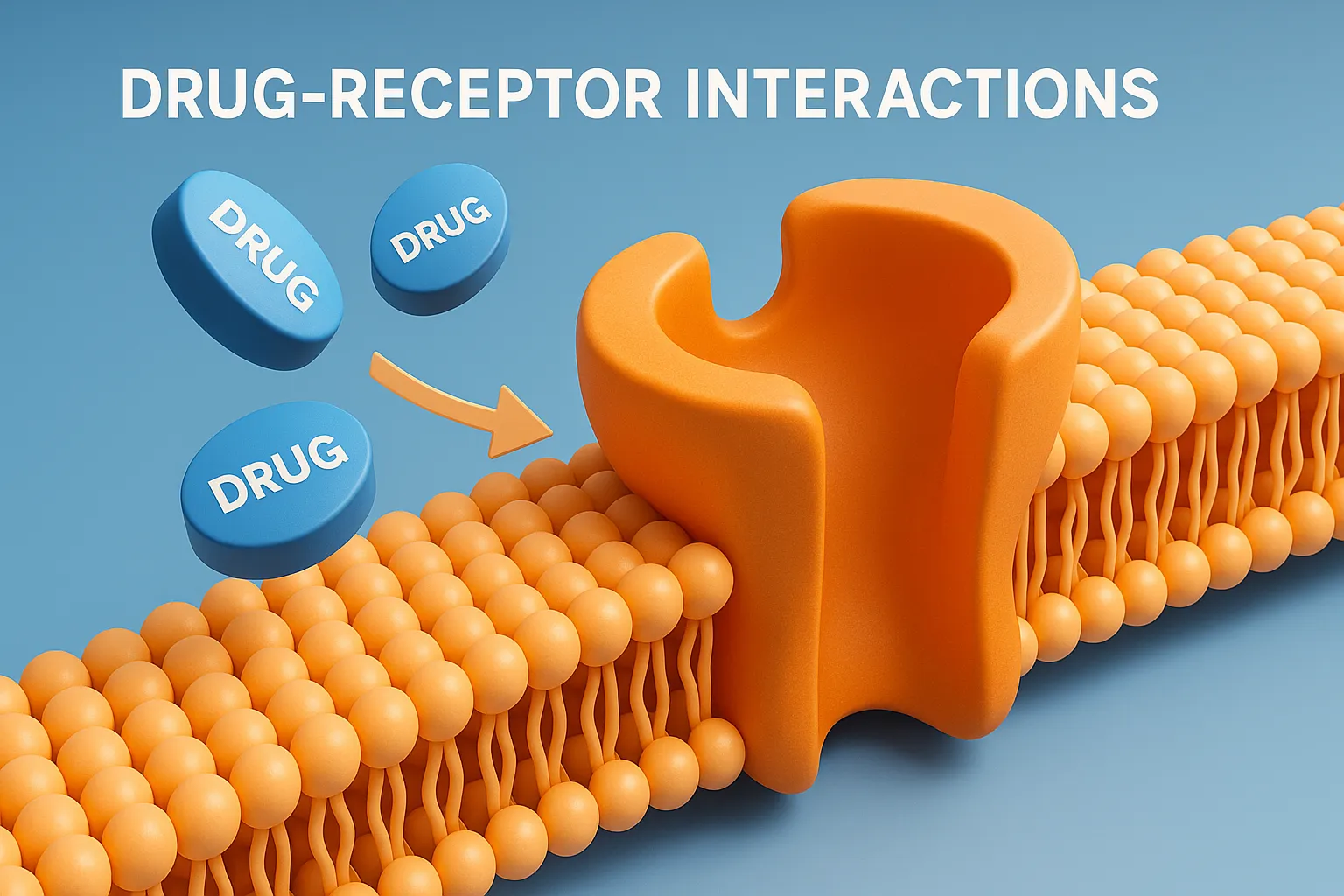
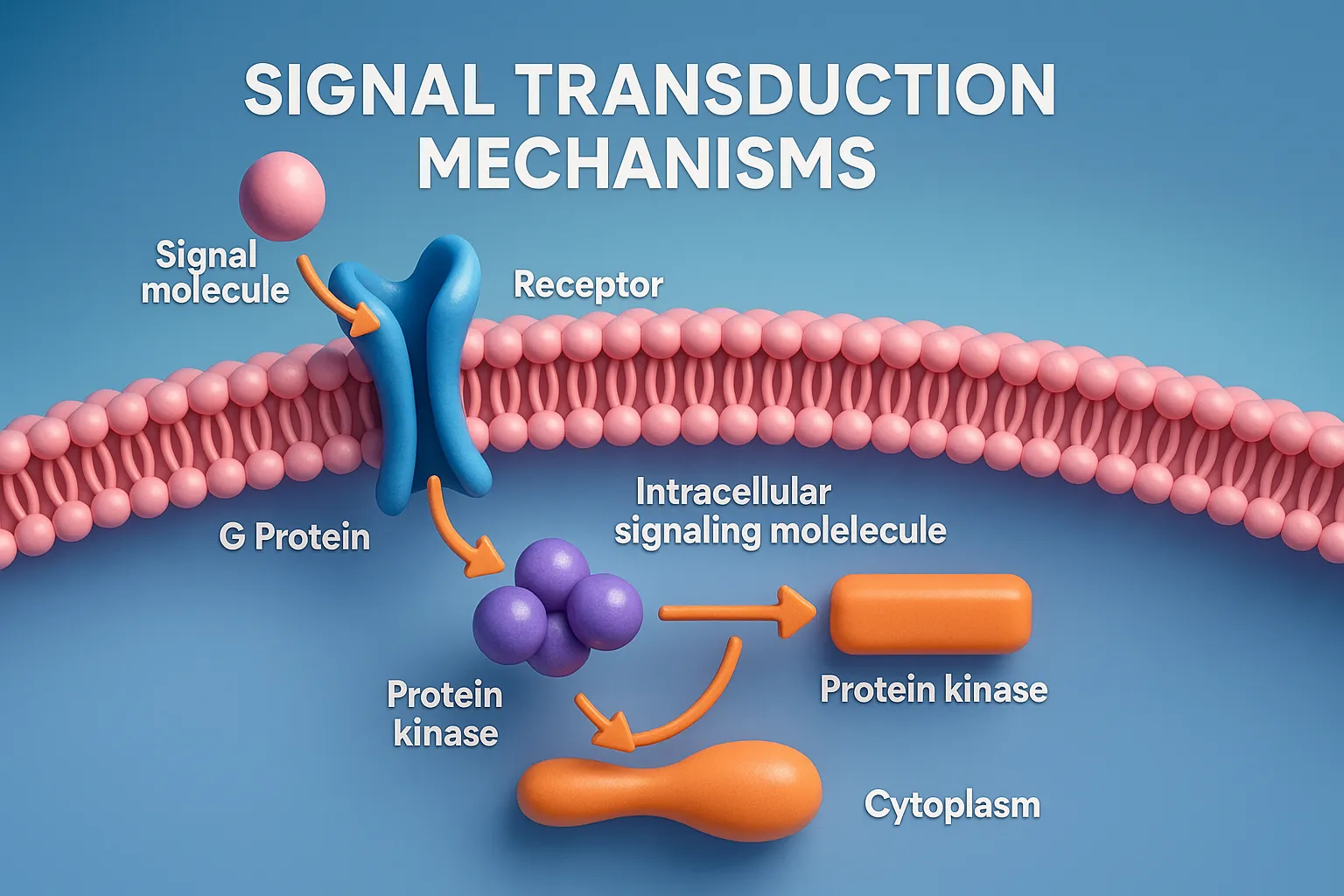
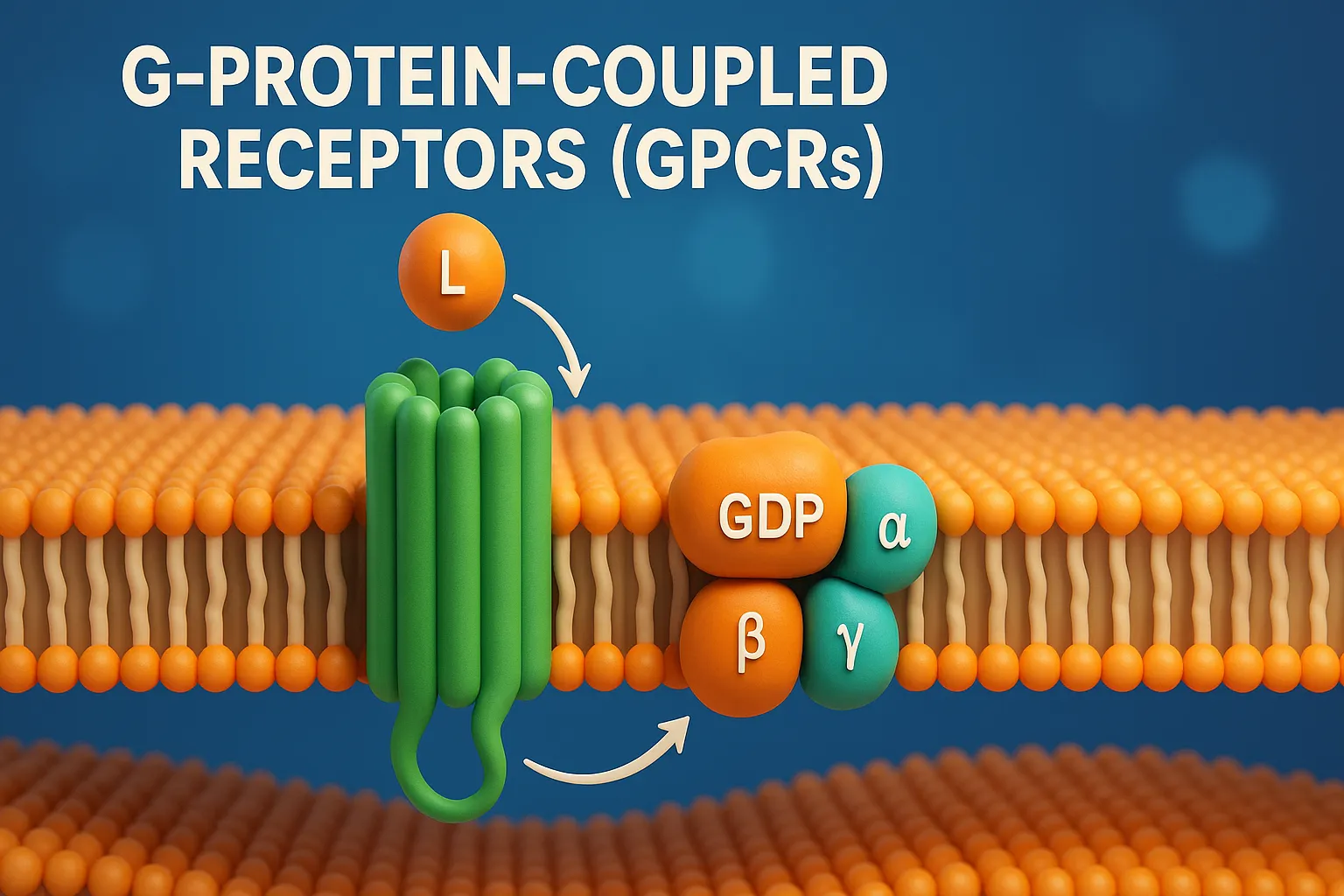
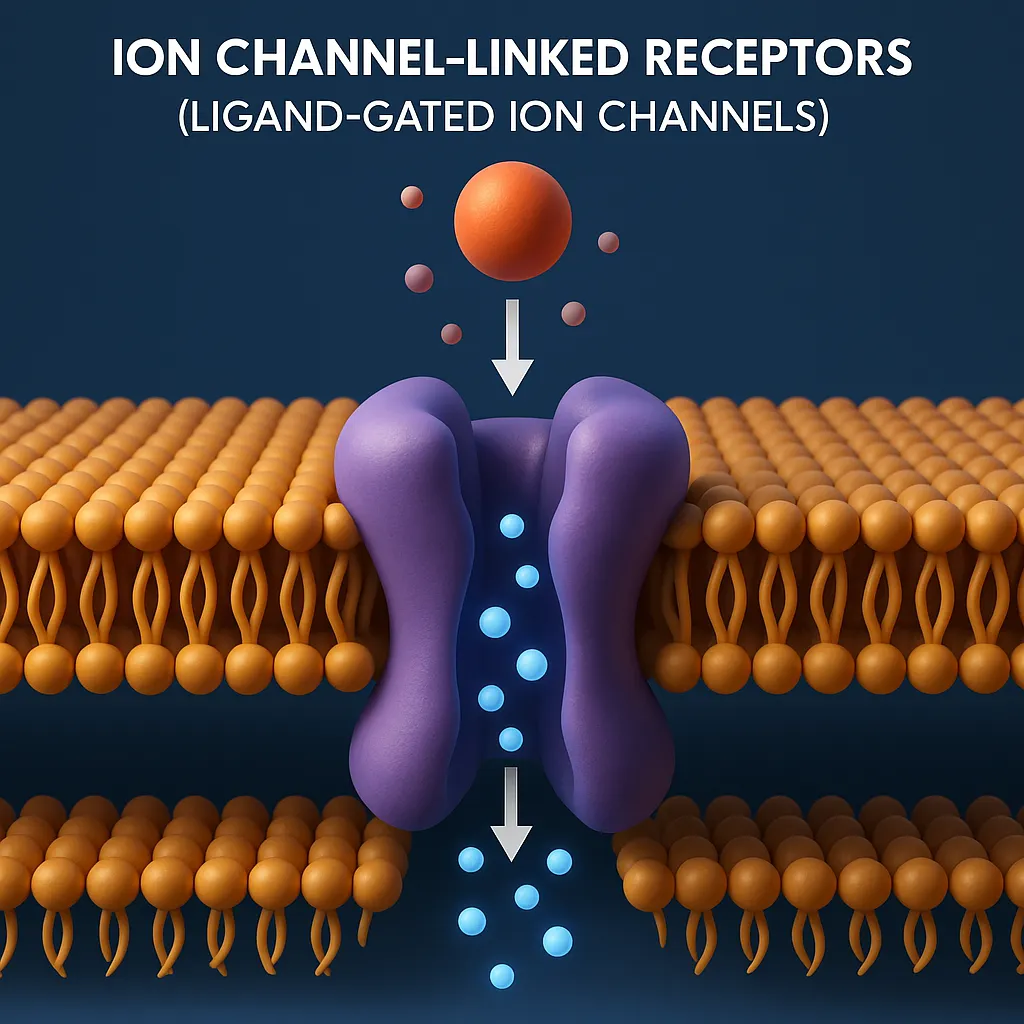
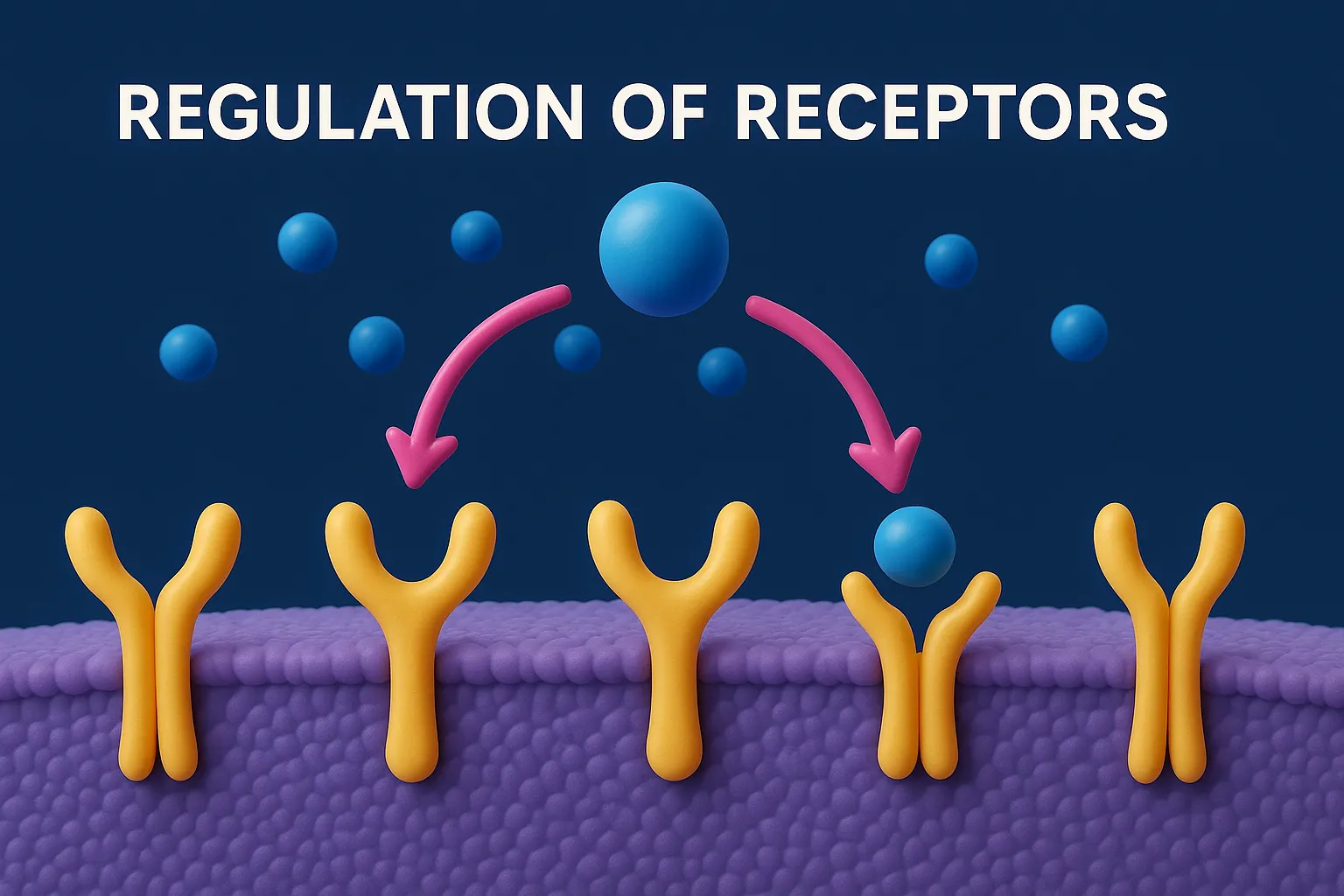
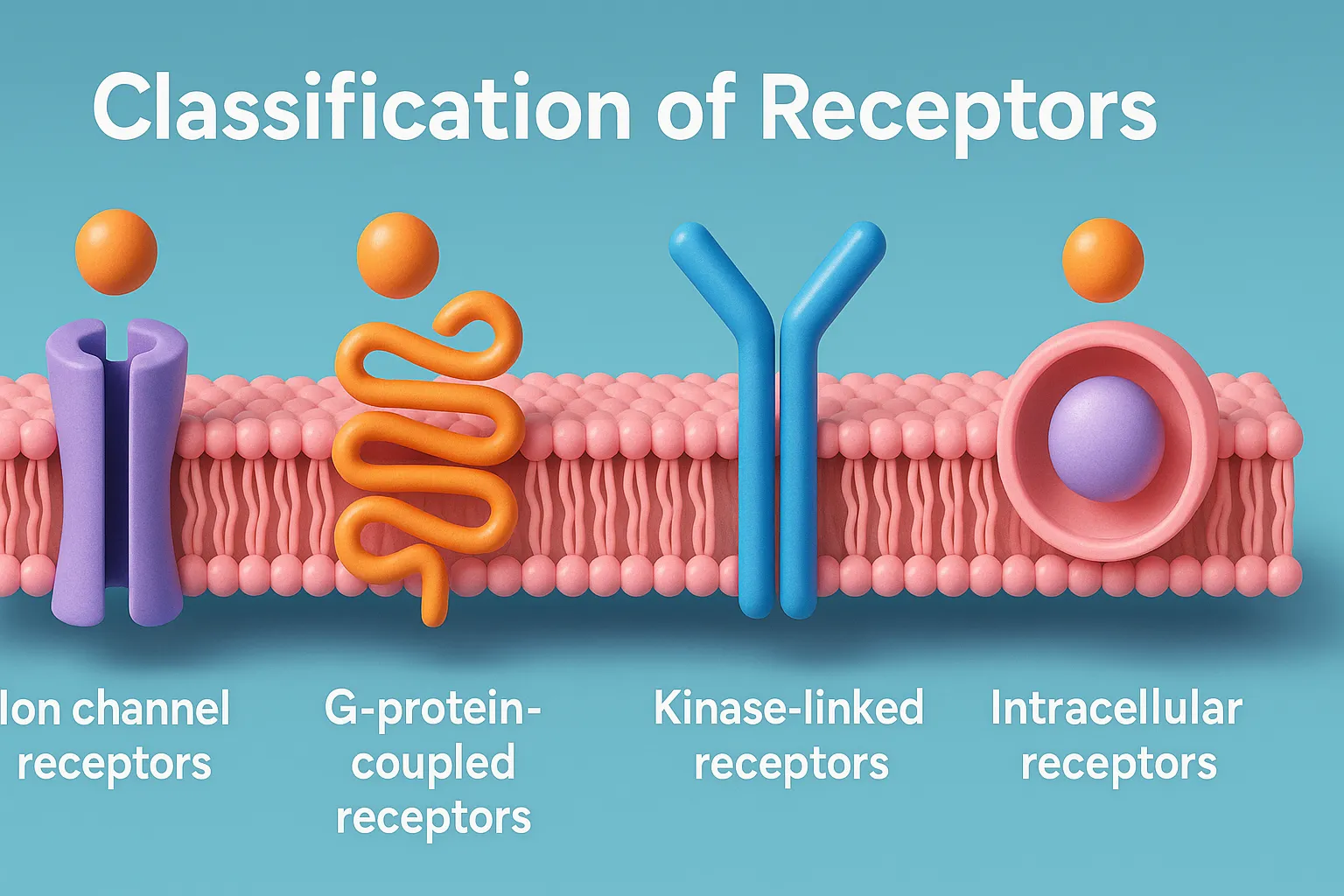
Drug Discovery Phase
Drug discovery phase involves identifying and designing new drug molecules with potential therapeutic effects. This is the initial stage in developing a new drug, focused on identifying compounds that could become safe and effective medicines. Key Steps for Drug Discovery Phase: Target Identification and Validation A target is usually a protein, enzyme, or receptor involved … Read more