Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS)
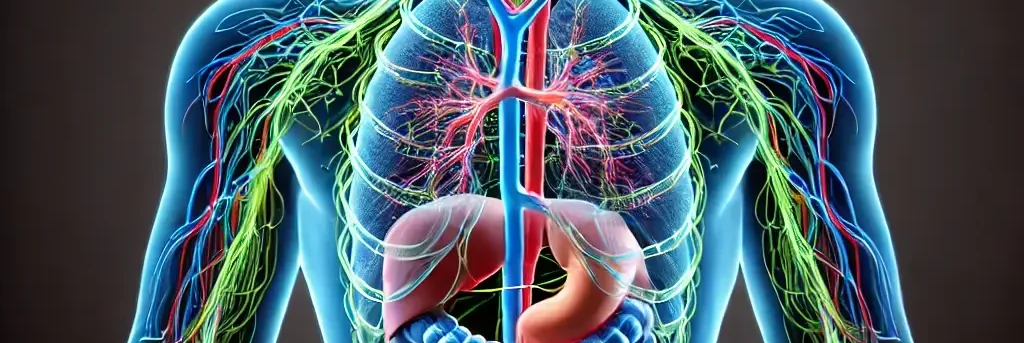
Structure of the Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS) The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) originates from the craniosacral region: it arises from the brainstem (cranial nerves) and sacral spinal cord (S2-S4). Cranial nerves involved include the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X), which innervates most thoracic and abdominal organs. Sacral nerves primarily innervate the pelvic organs. Preganglionic neurons: … Read more