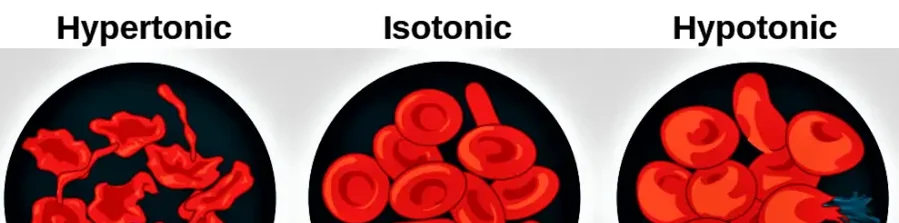
Oral Rehydration Salt (ORS): Electrolytes
Preparation of Oral Rehydration Salt ORS is a balanced mixture of electrolytes and glucose, formulated to prevent and treat dehydration caused by diarrhea or other conditions leading to fluid loss. Typical ORS Composition: Sodium chloride (NaCl) Potassium chloride (KCl) Trisodium citrate dihydrate (Na₃C₆H₅O₇·2H₂O) or sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) WHO-Recommended Composition: Sodium chloride: 2.6 g … Read more