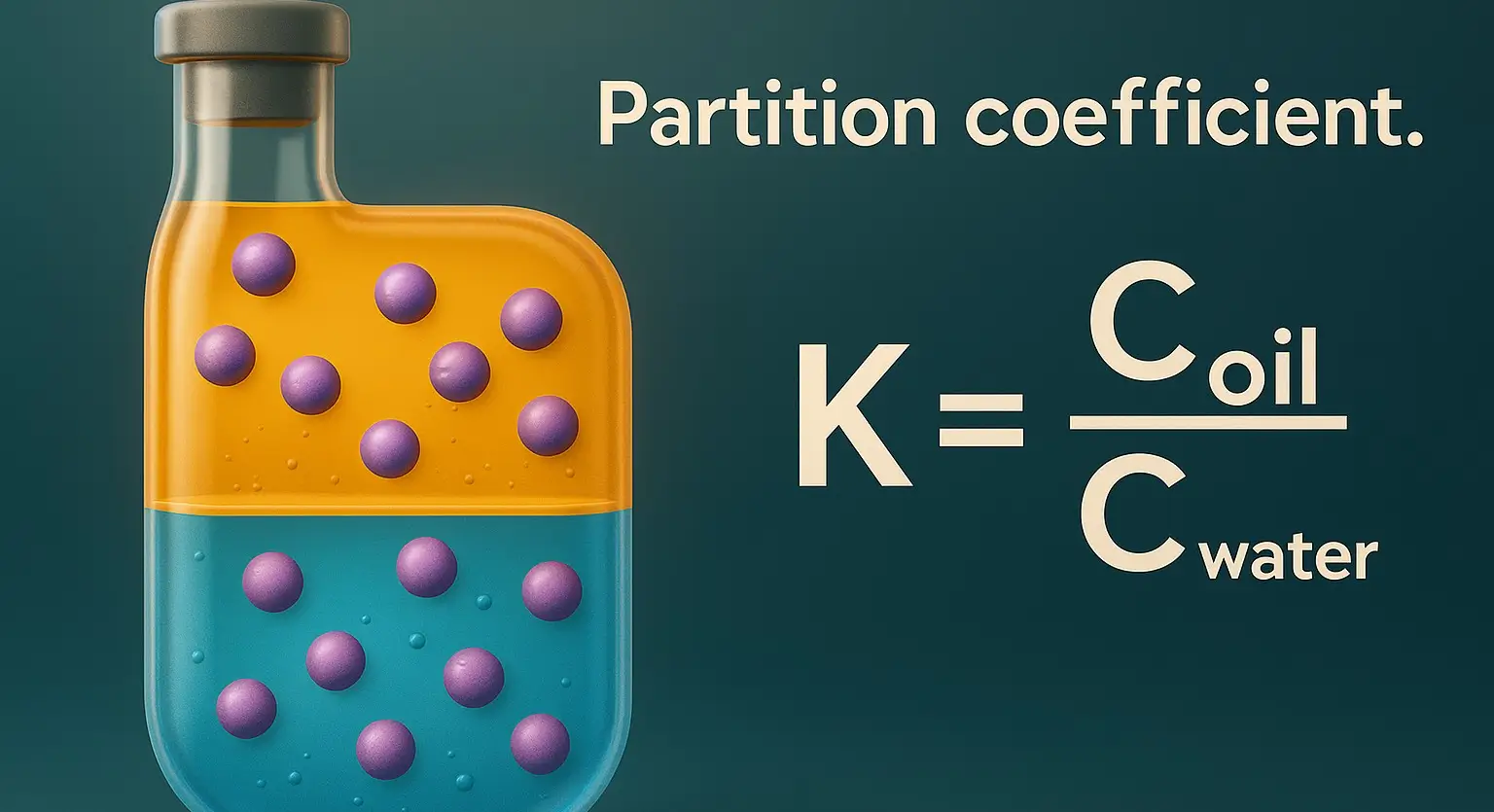Bioisosterism
Bioisosterism Definition: Bioisosterism are structurally similar chemical groups that mimic the biological activity of another. Importance in Drug Design: Improved Activity: Replacement of groups can enhance potency and reduce toxicity. Increased Stability: Bioisosteres improve metabolic stability. Reduced Side Effects: Modification helps improve drug safety. Examples: Sulfonamide (-SO₂NH₂) as a bioisostere of carboxyl (-COOH) in diuretics. Fluorine … Read more