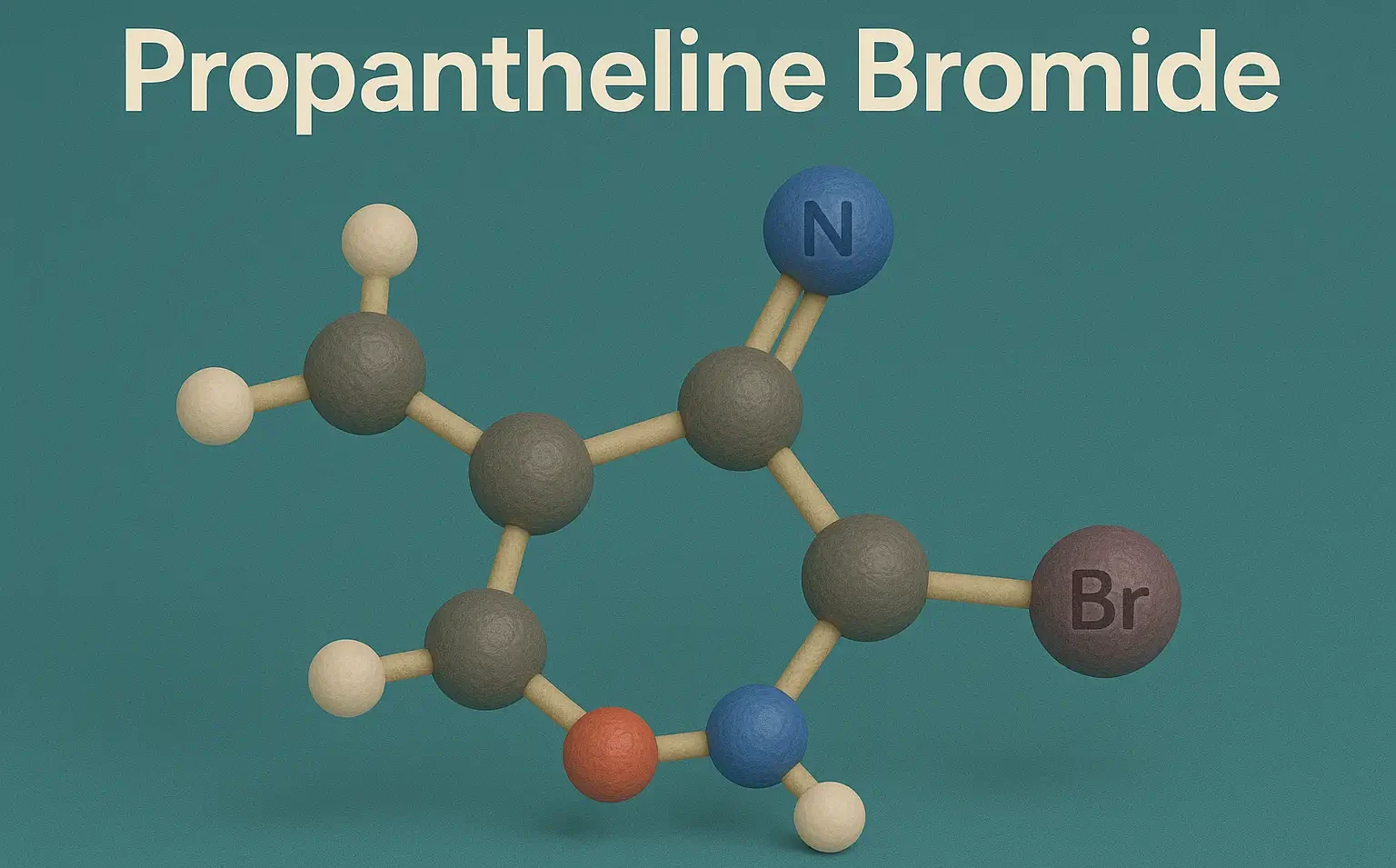
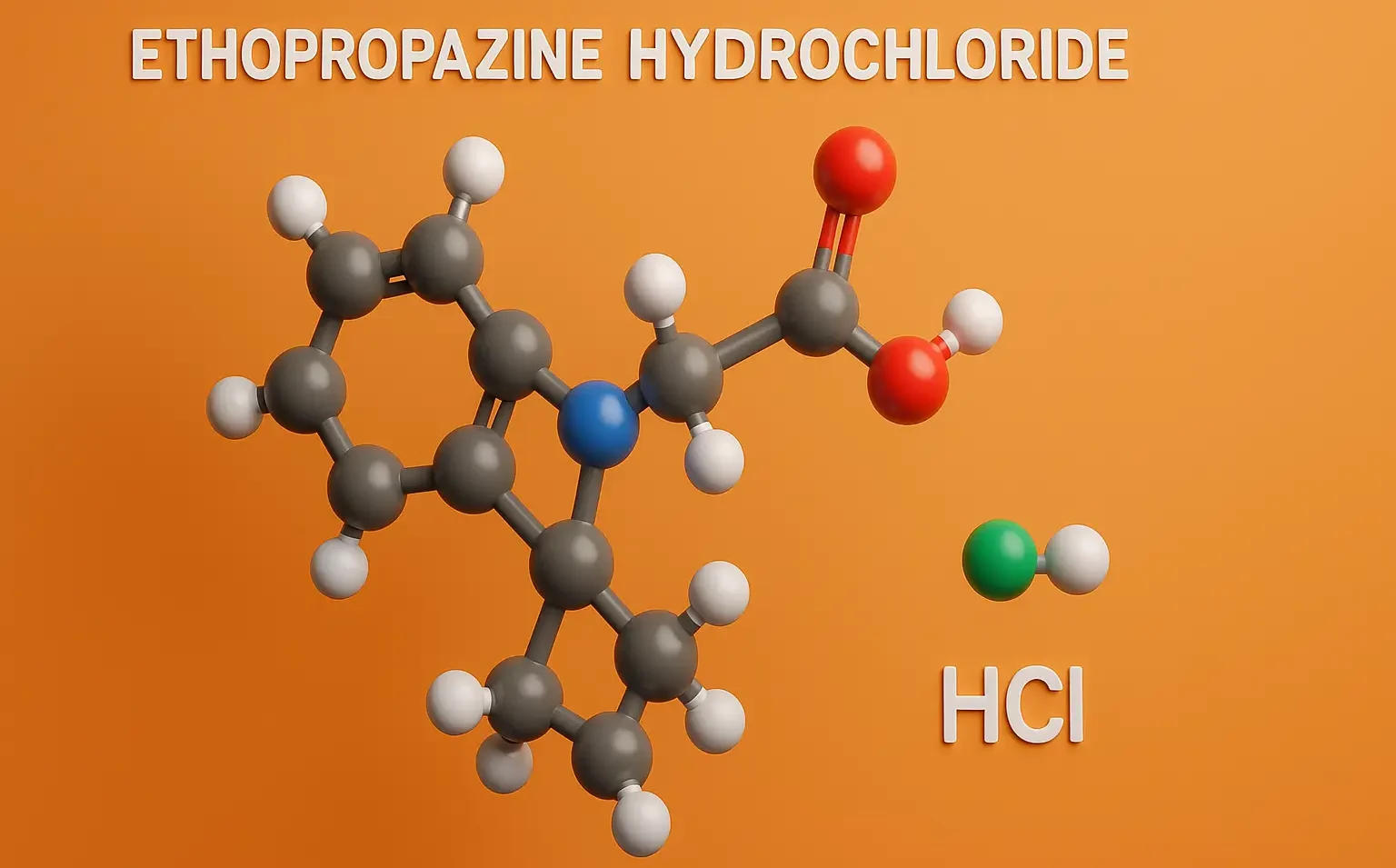
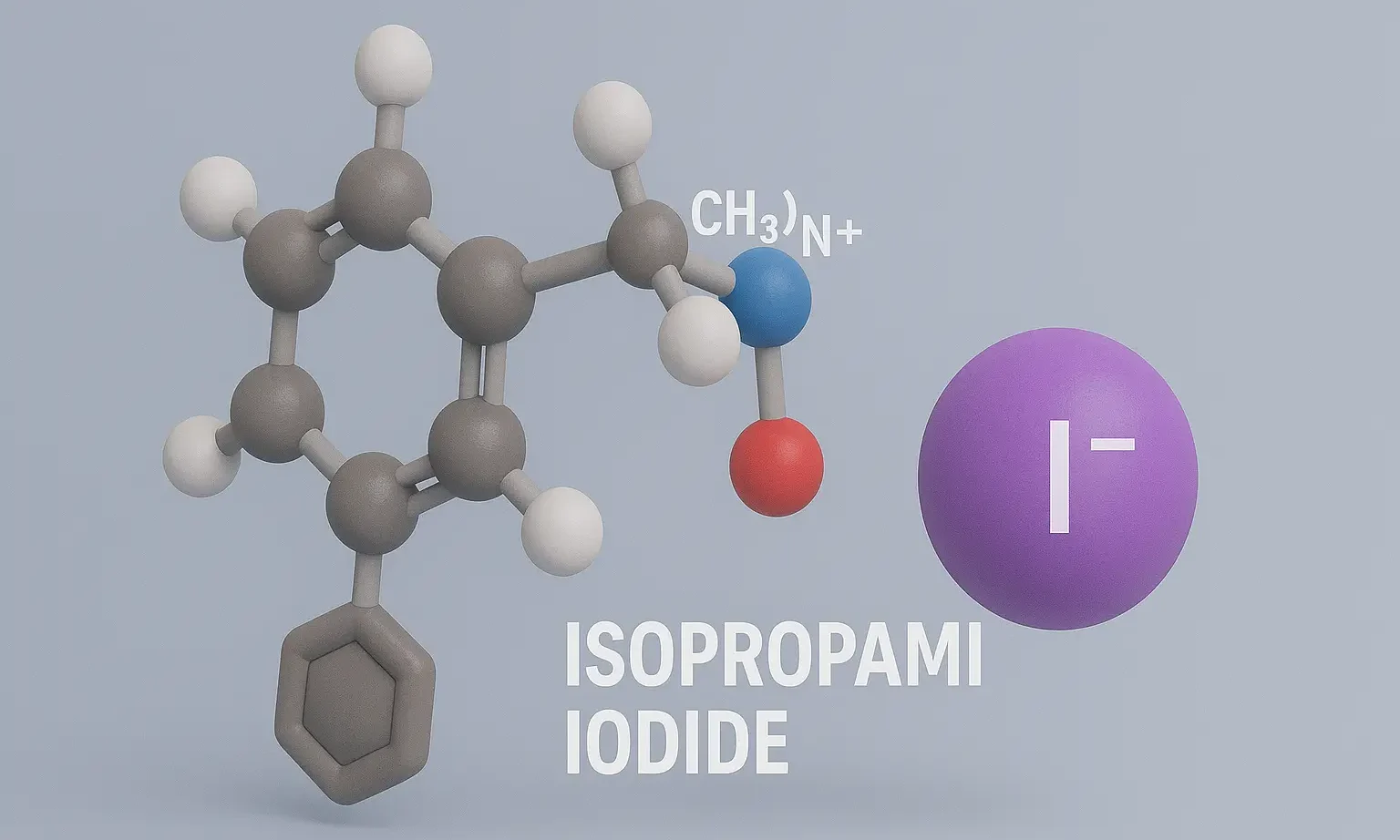
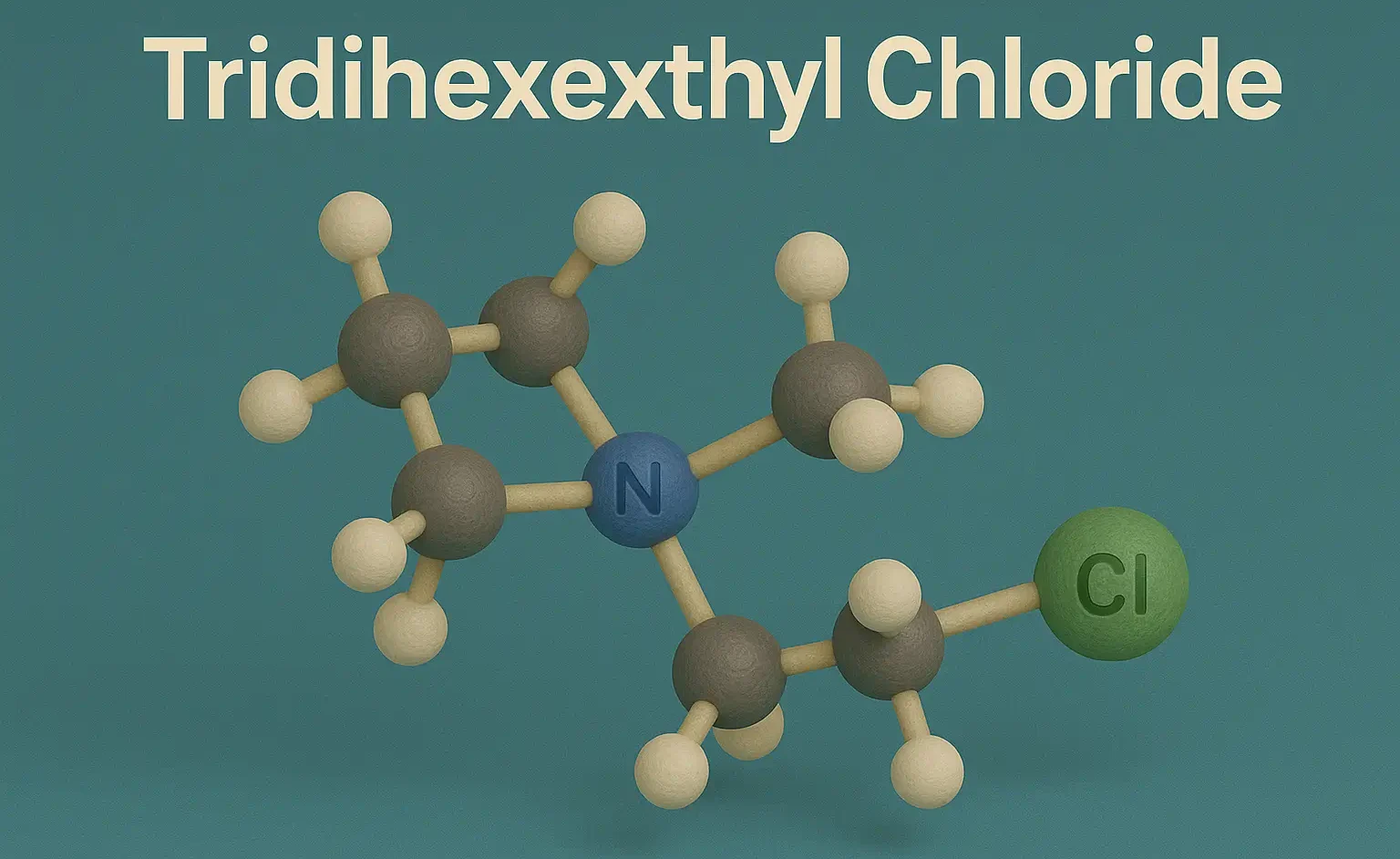
SAR of Benzodiazepines (BZDs)
SAR of Benzodiazepines (BZDs) highlights the importance of the 1,4-benzodiazepine nucleus for activity. SAR of Benzodiazepines (BZDs) shows how ring substitutions modify potency, duration, and receptor affinity. Benzodiazepines act primarily at the GABA-A receptor to enhance inhibitory neurotransmission. Key SAR of Benzodiazepines (BZDs) Points: Aromatic Ring at Position 5 (C-5): A phenyl group at C-5 … Read more