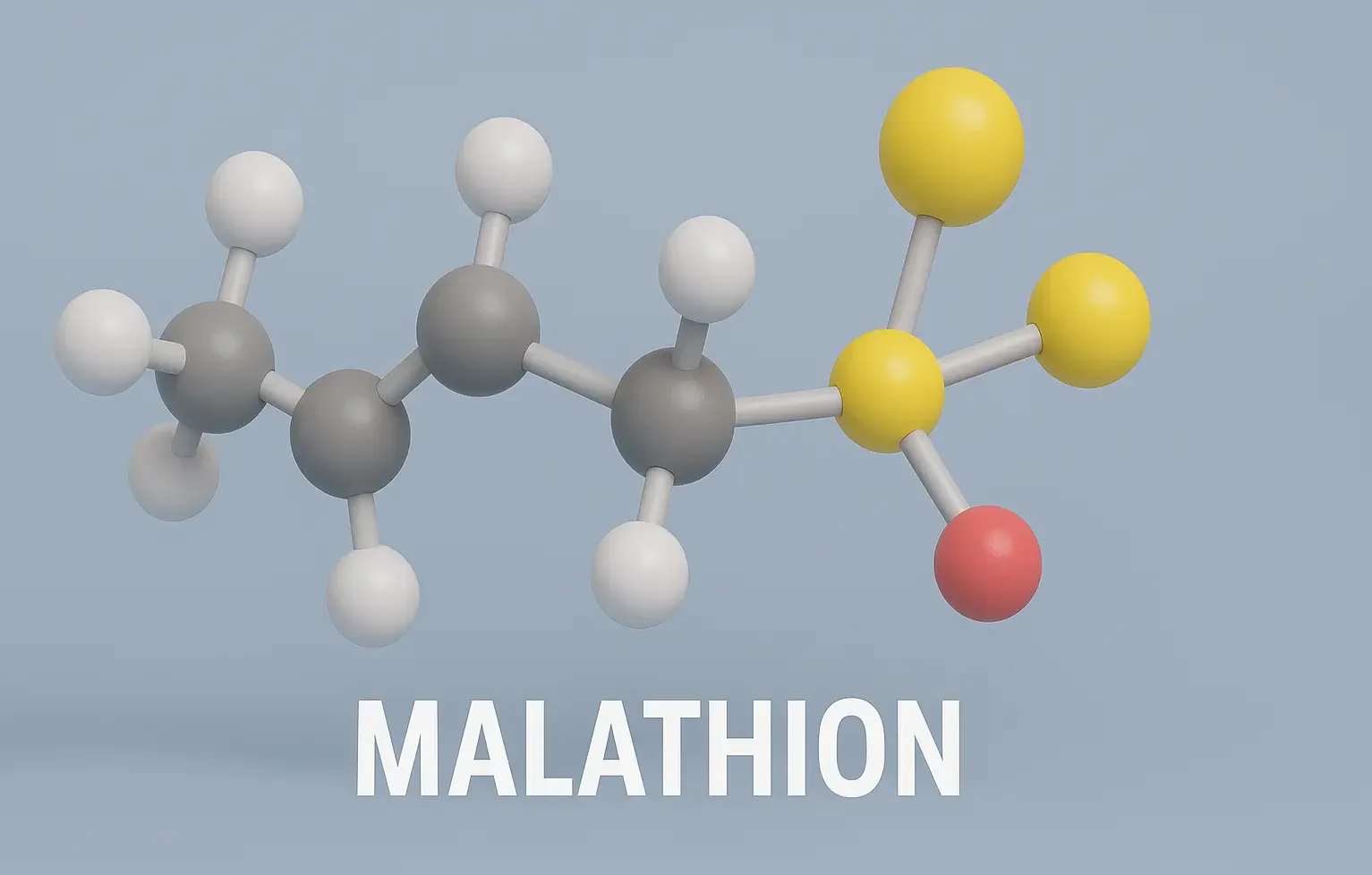
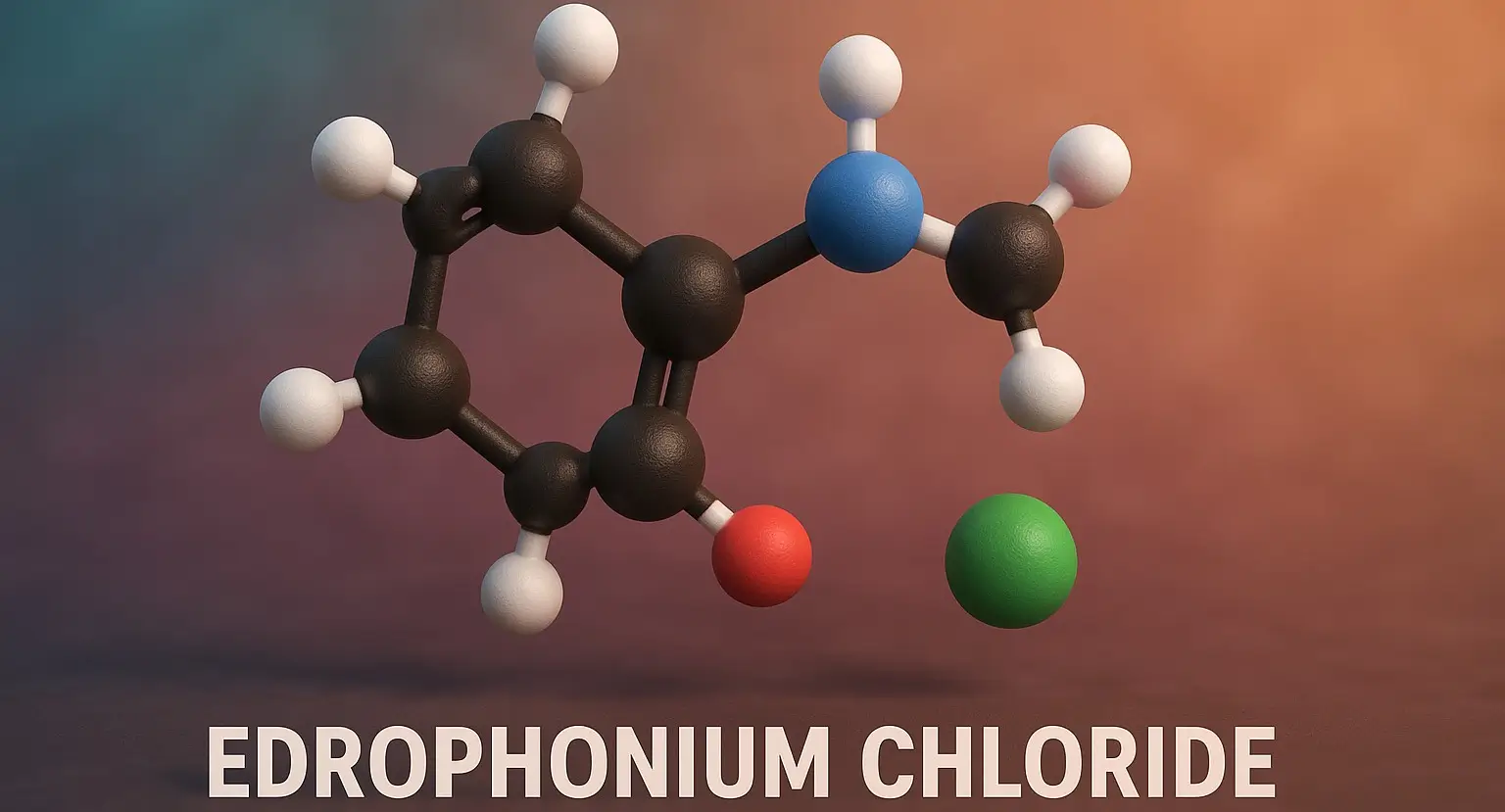
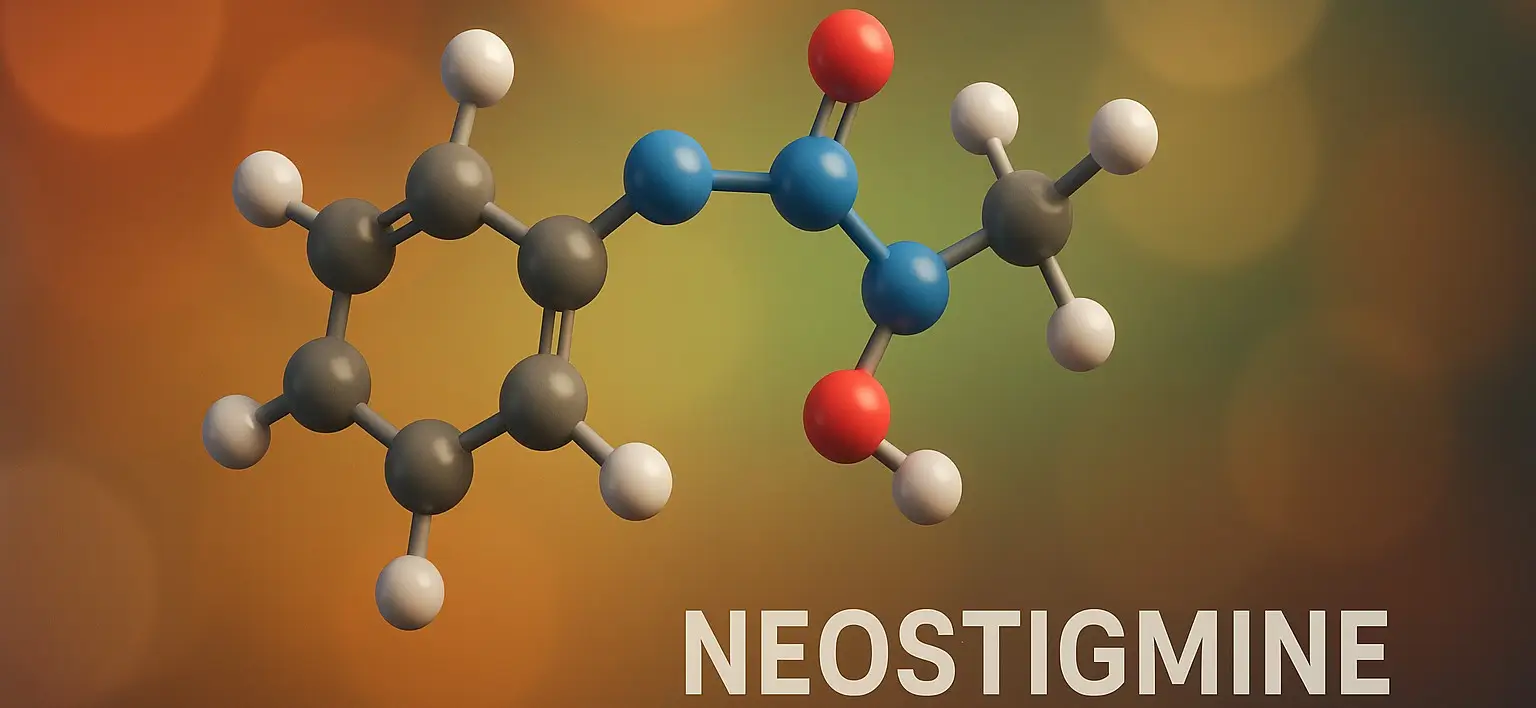
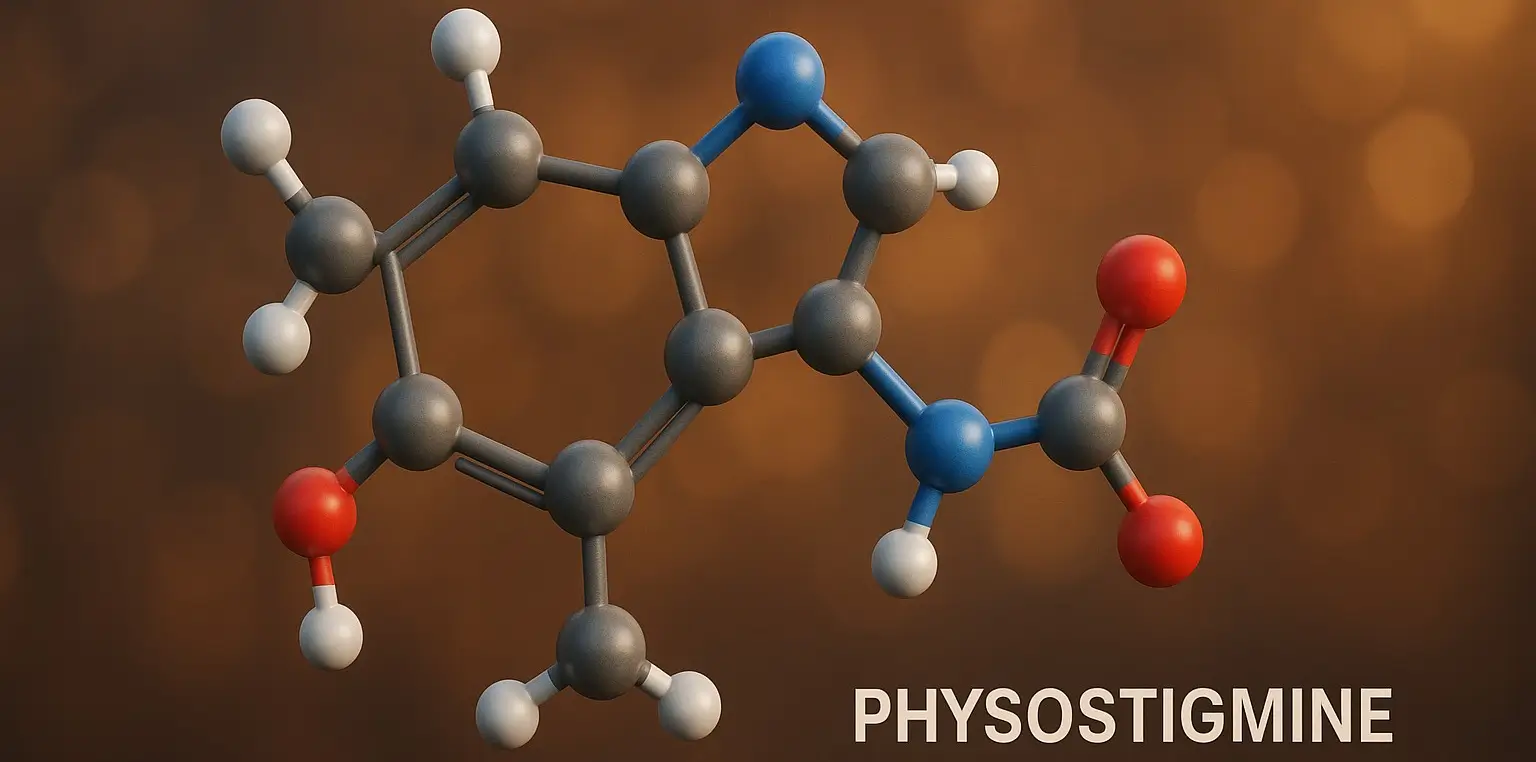
Malathion
Malathion is an organophosphate insecticide widely used to control pests in agriculture and public health. Malathion treats head lice, mosquito control, and protects crops, ensuring safety with proper dosage and handling. Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₁₉O₆PS₂ Mechanism of Action: Irreversible AChE inhibitor after conversion to malaoxon Uses of Malathion: Head lice treatment Scabies Agricultural pesticide Side Effects … Read more