Tray Dryer
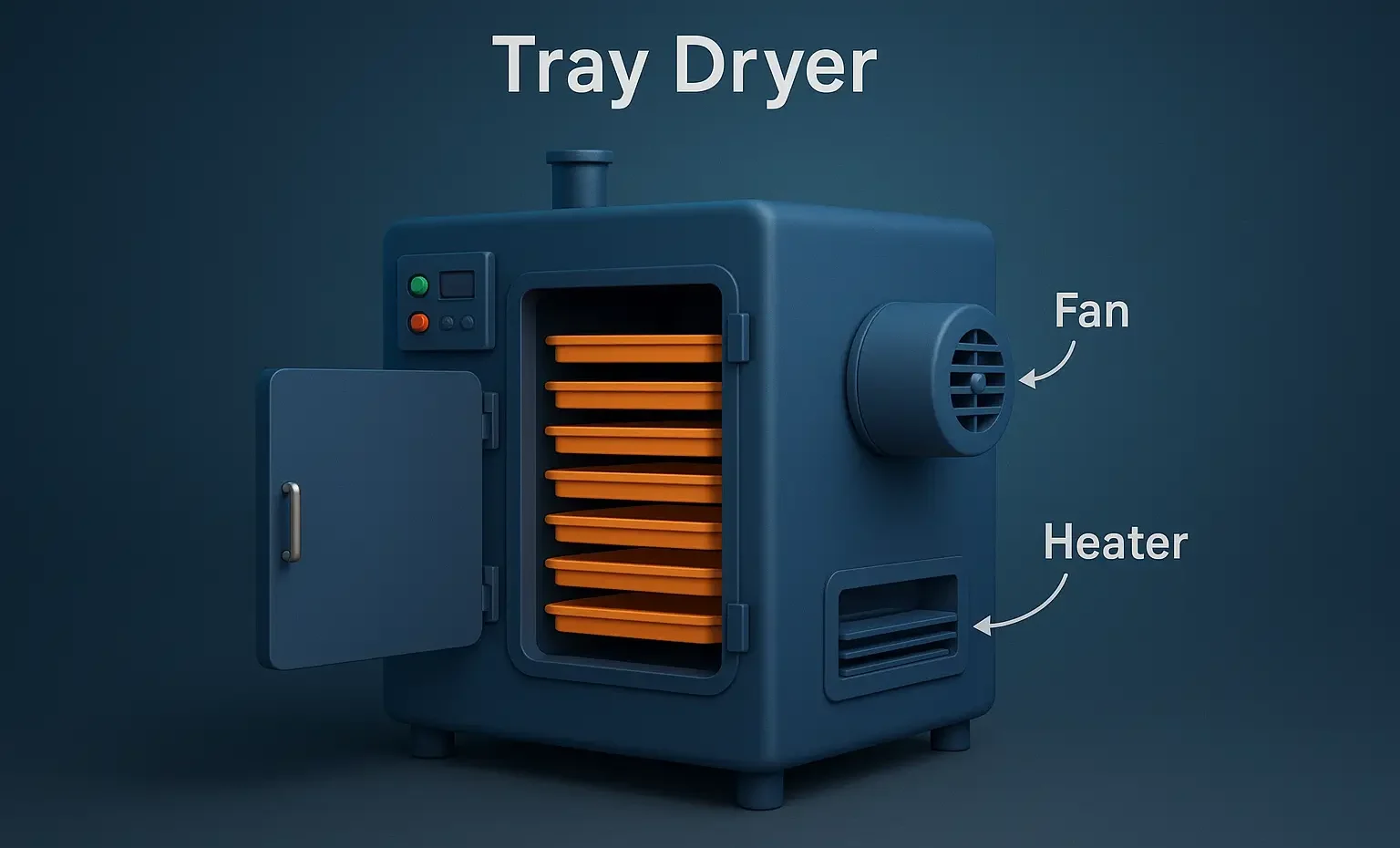
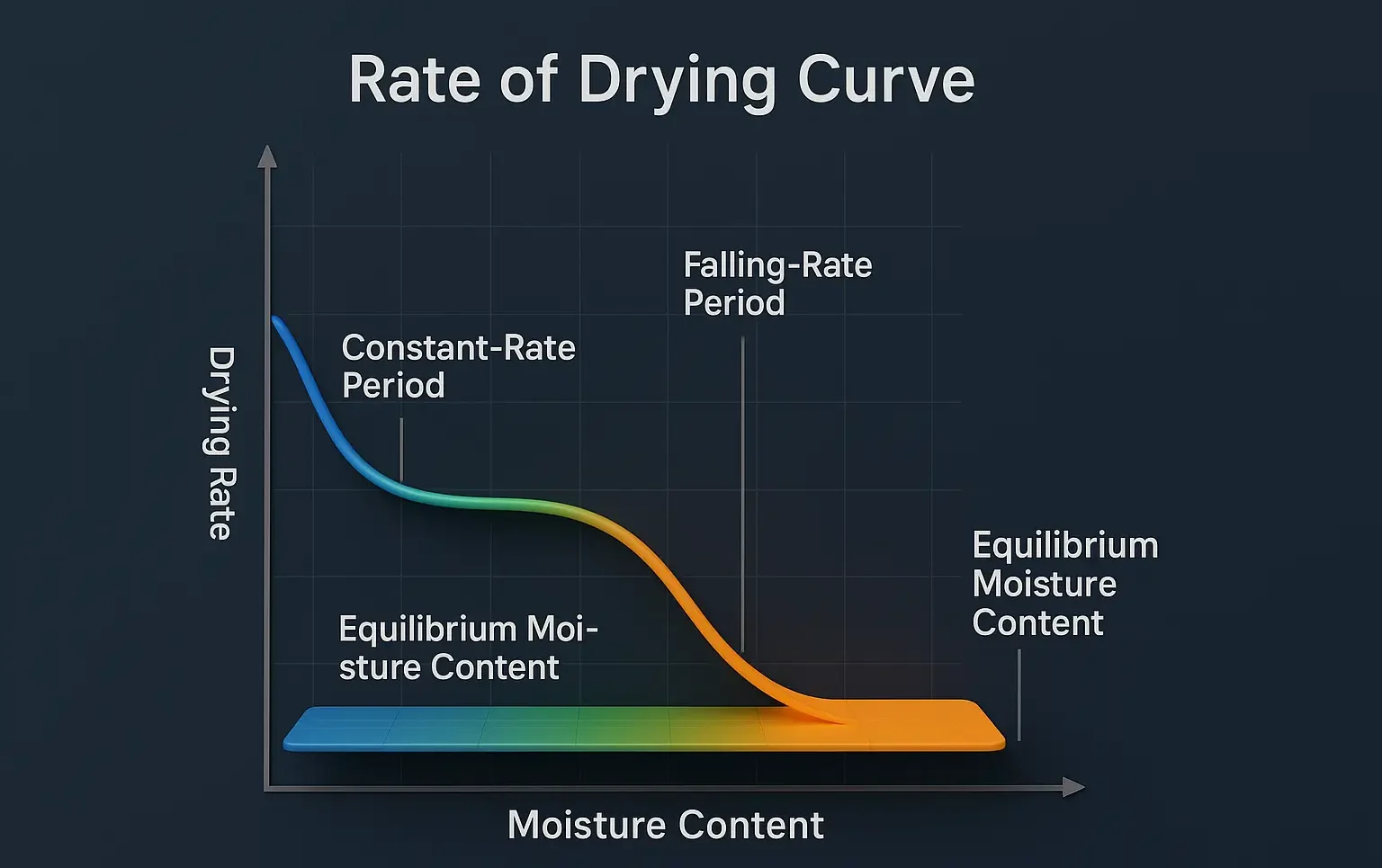
Principles of Tray Dryer A tray dryer operates on the principle of convection drying, where heated air circulates over the trays containing the wet material. The moisture from the material is transferred to the air and carried away, leaving the material dry. Construction of Tray Dryer Chamber: An insulated enclosure to maintain heat. Trays: Perforated … Read more