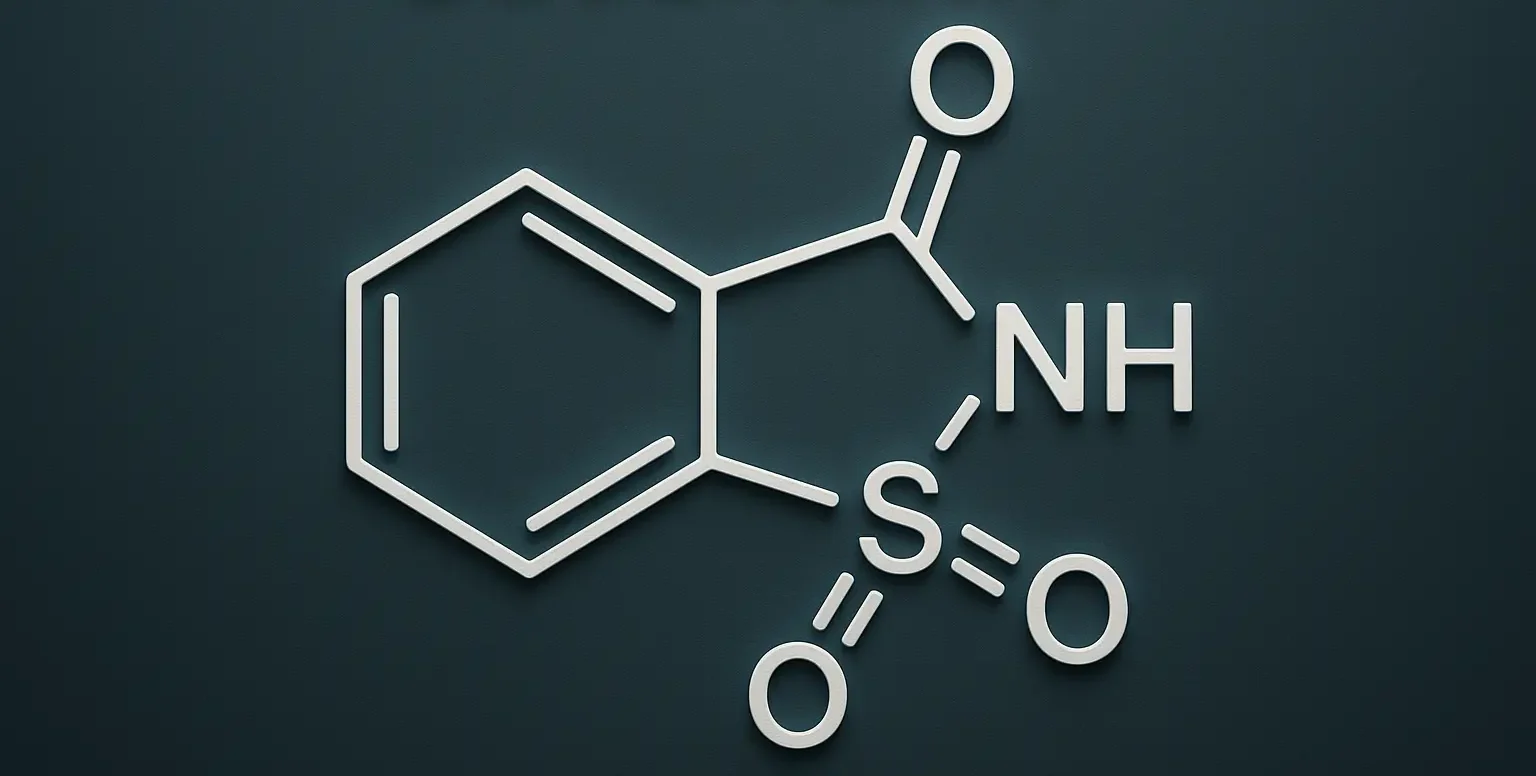
Saccharin
Structure of Saccharin: Chemical Formula: C₇H₅NO₃S Description: Saccharin is an artificial sweetener. Its structure consists of a benzene ring substituted with an amine group, a carbonyl group, and a sulfonyl group. Uses: Used as a non-nutritive sweetener in various food and beverage products, such as diet sodas, sugar-free candies, and tabletop sweeteners. Approximately 300 to … Read more