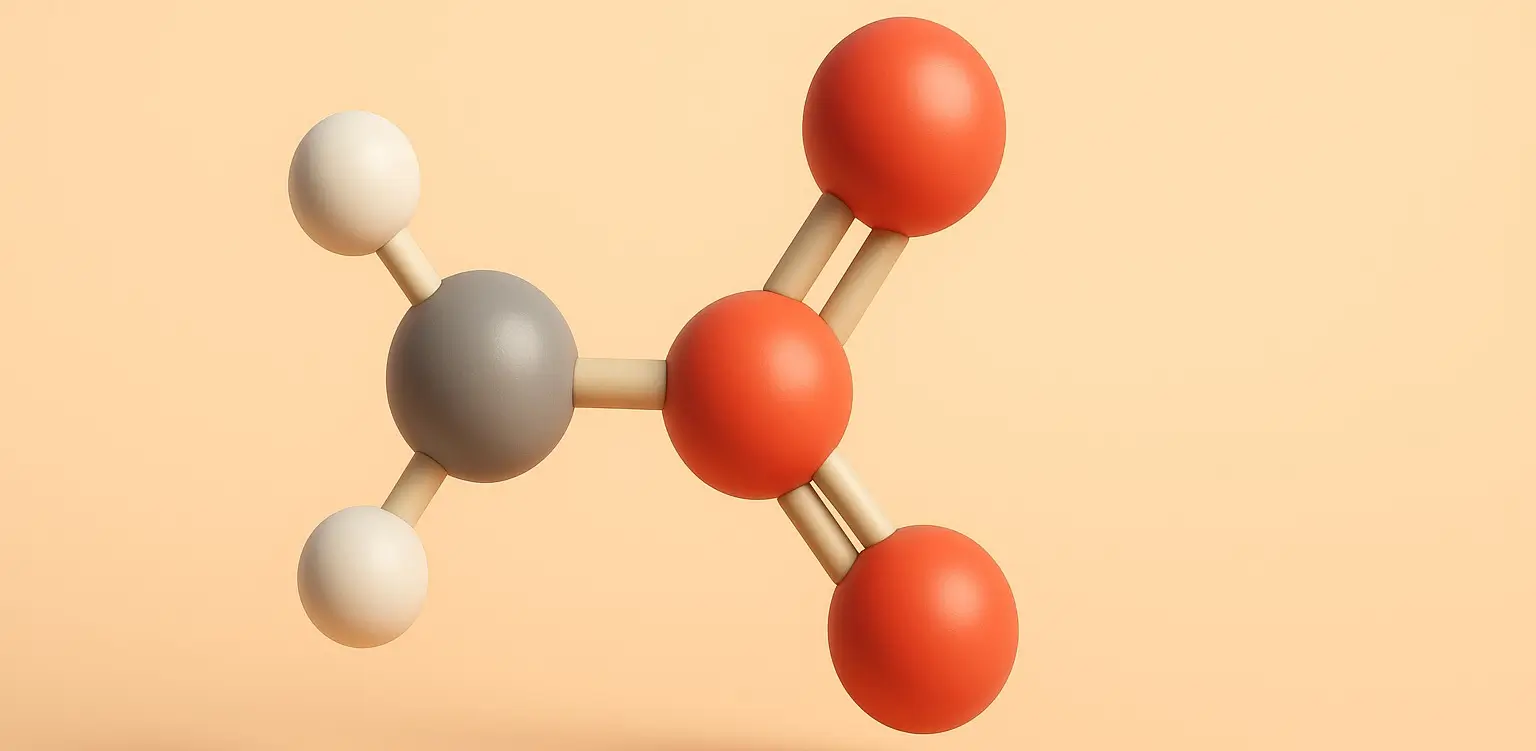
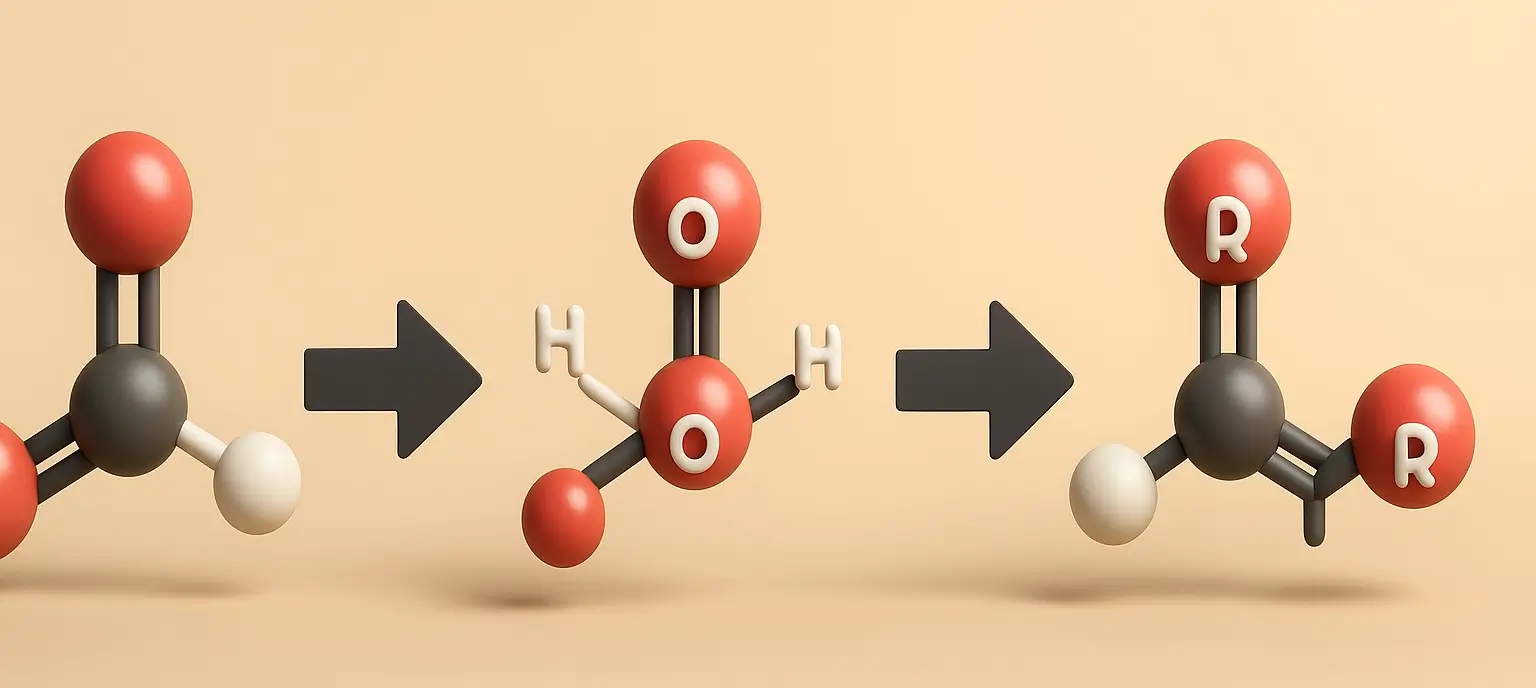
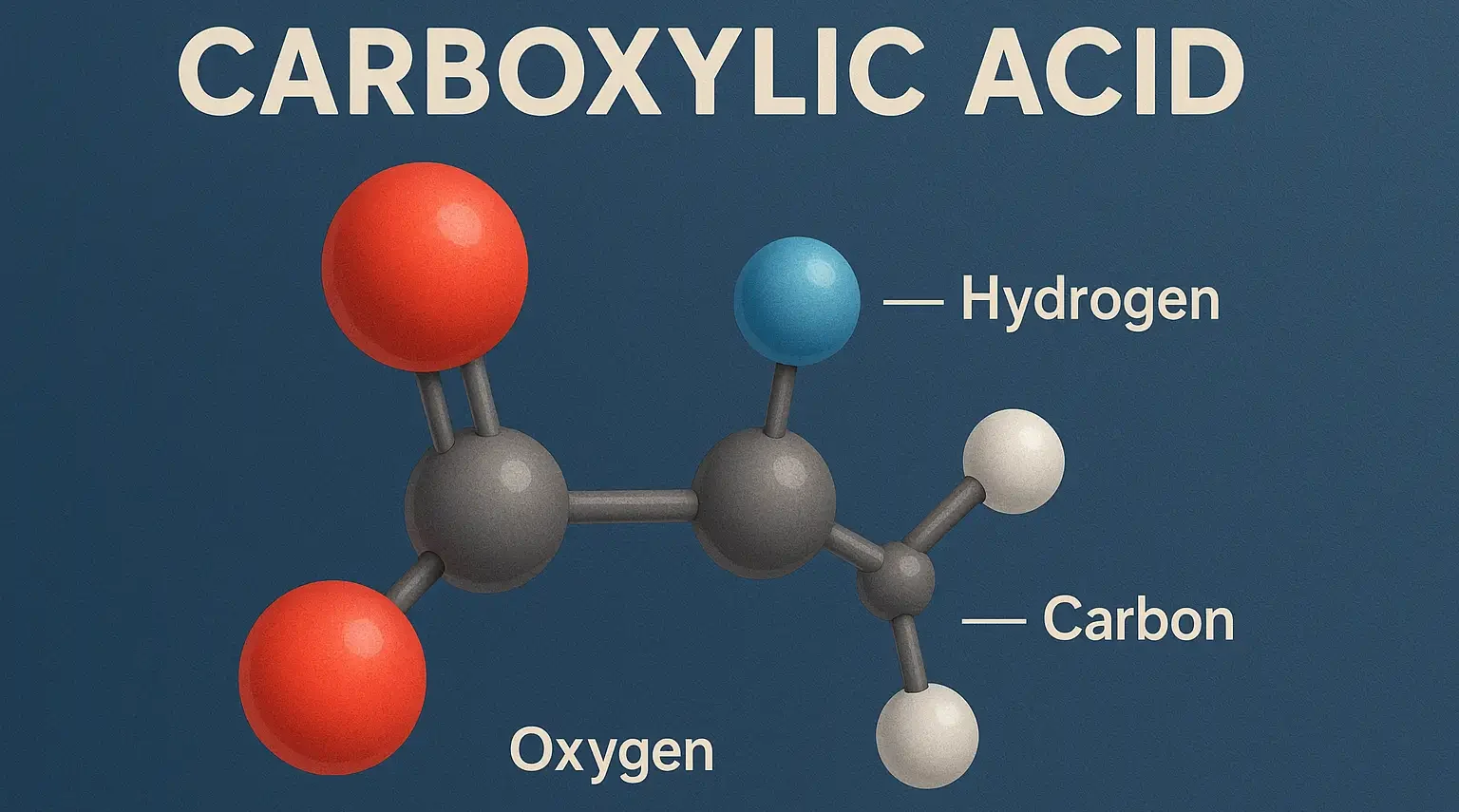
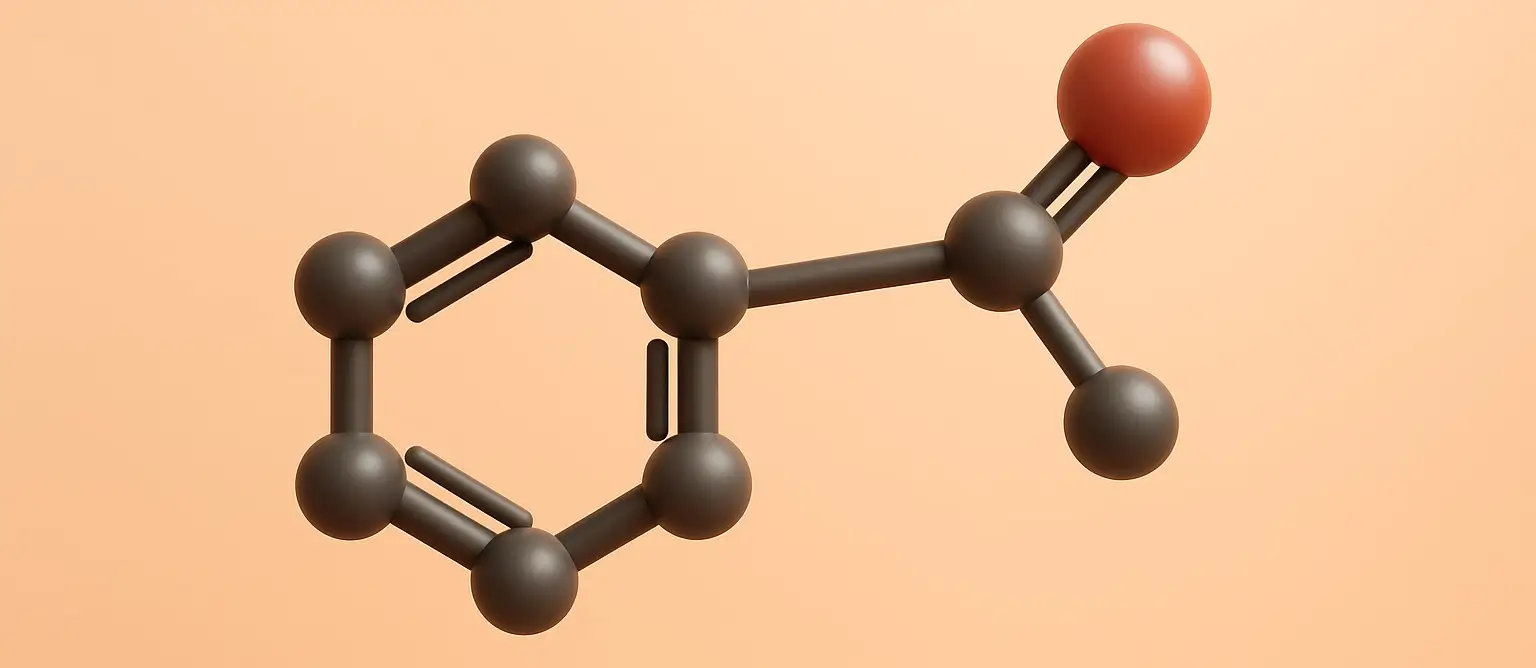
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids Effect of Substituents
acidity of carboxylic acids is influenced by substituents attached to the molecule, which can stabilize or destabilize the carboxylate anion formed upon deprotonation. acidity of carboxylic acids effect is primarily due to the inductive and resonance effects: Inductive Effect The inductive effect is the transmission of charge through a chain of atoms in a molecule, … Read more