Acetone
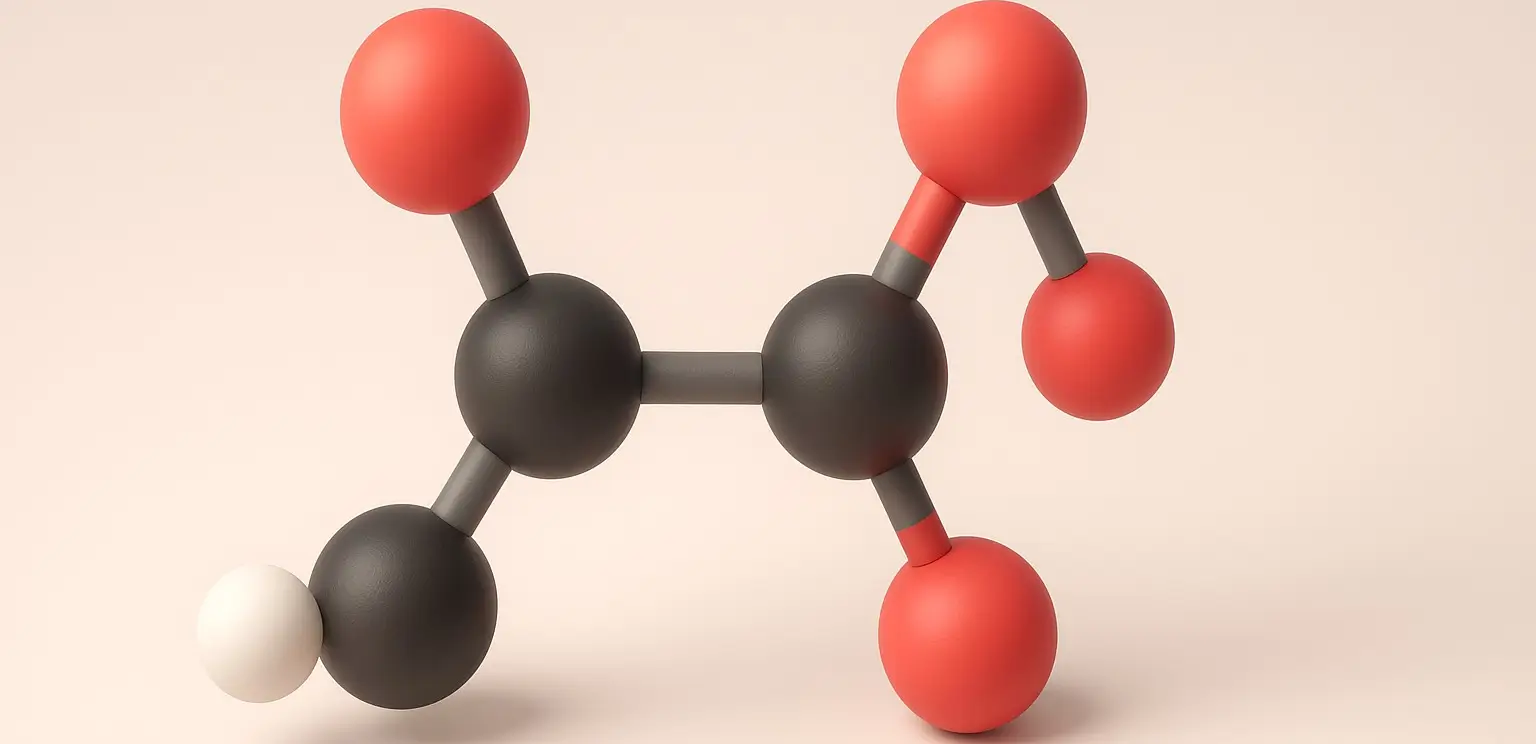
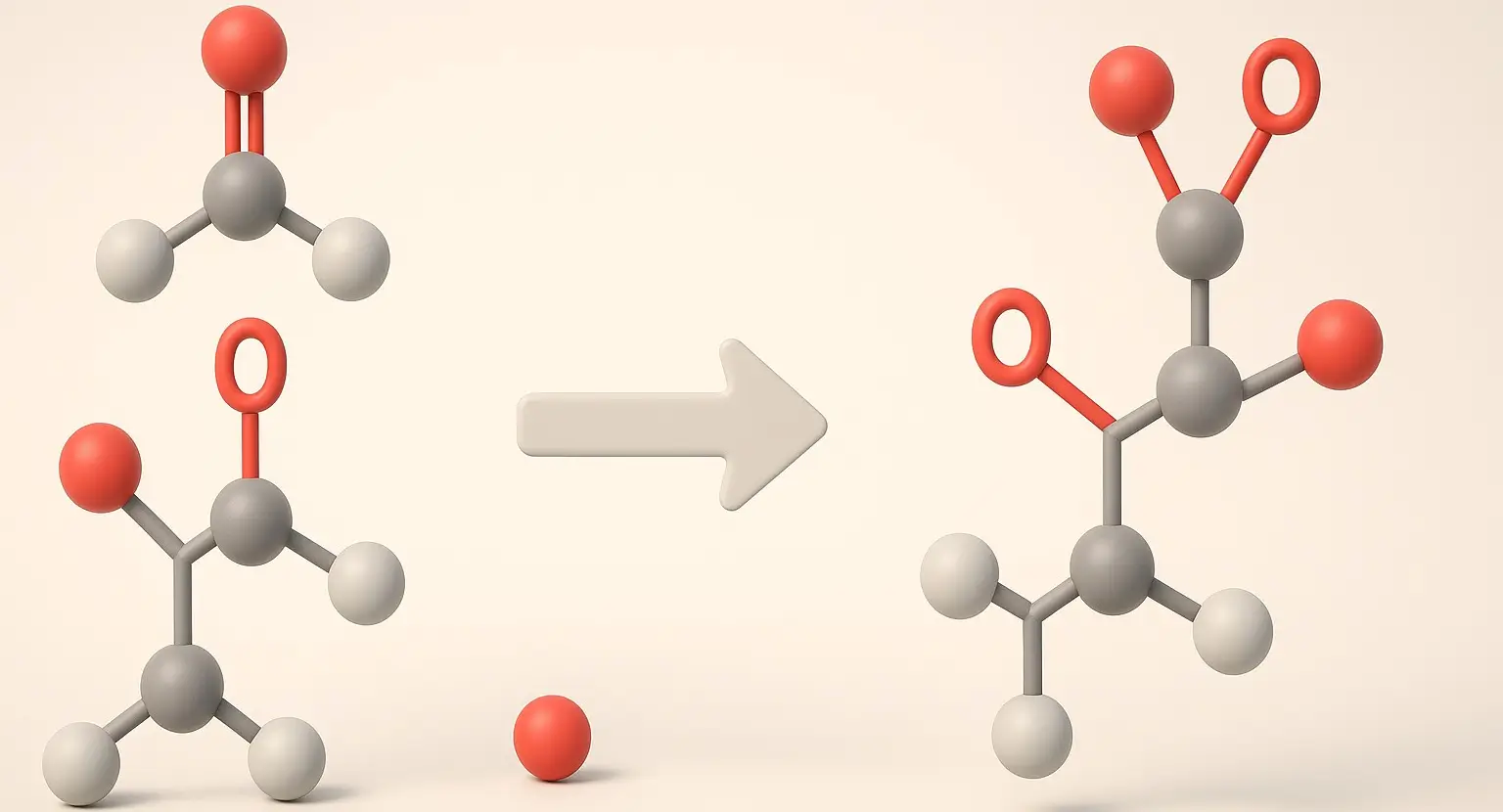
Acetone Definition Acetone is a colorless, volatile, flammable liquid organic compound with the chemical formula C₃H₆O. It is the simplest and smallest ketone, also known by its IUPAC name propanone. Structure: Chemical Formula: C₃H₆O Molecular Structure: A three-carbon chain with a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to the central carbon, with the remaining valencies filled by … Read more