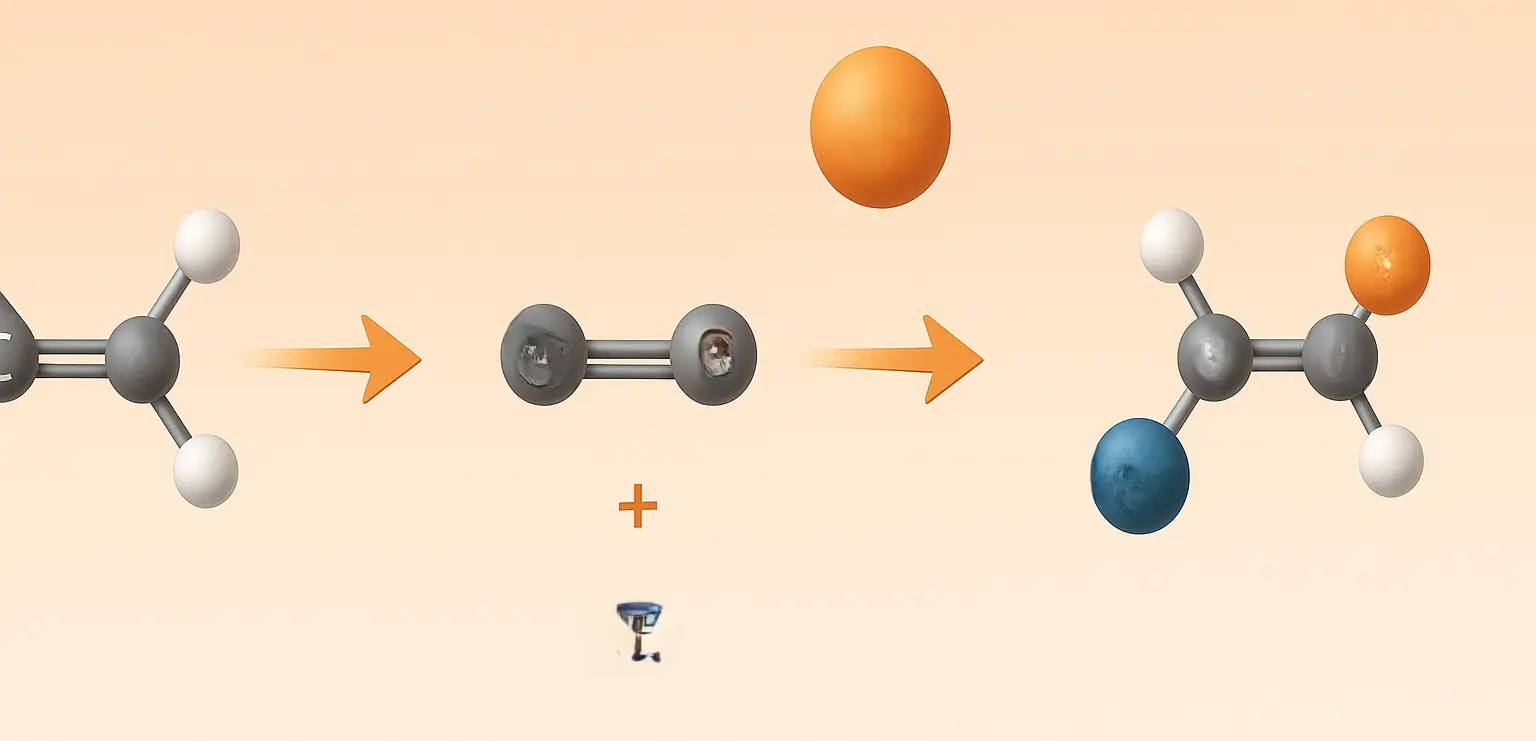
Chloroform (Trichloromethane)
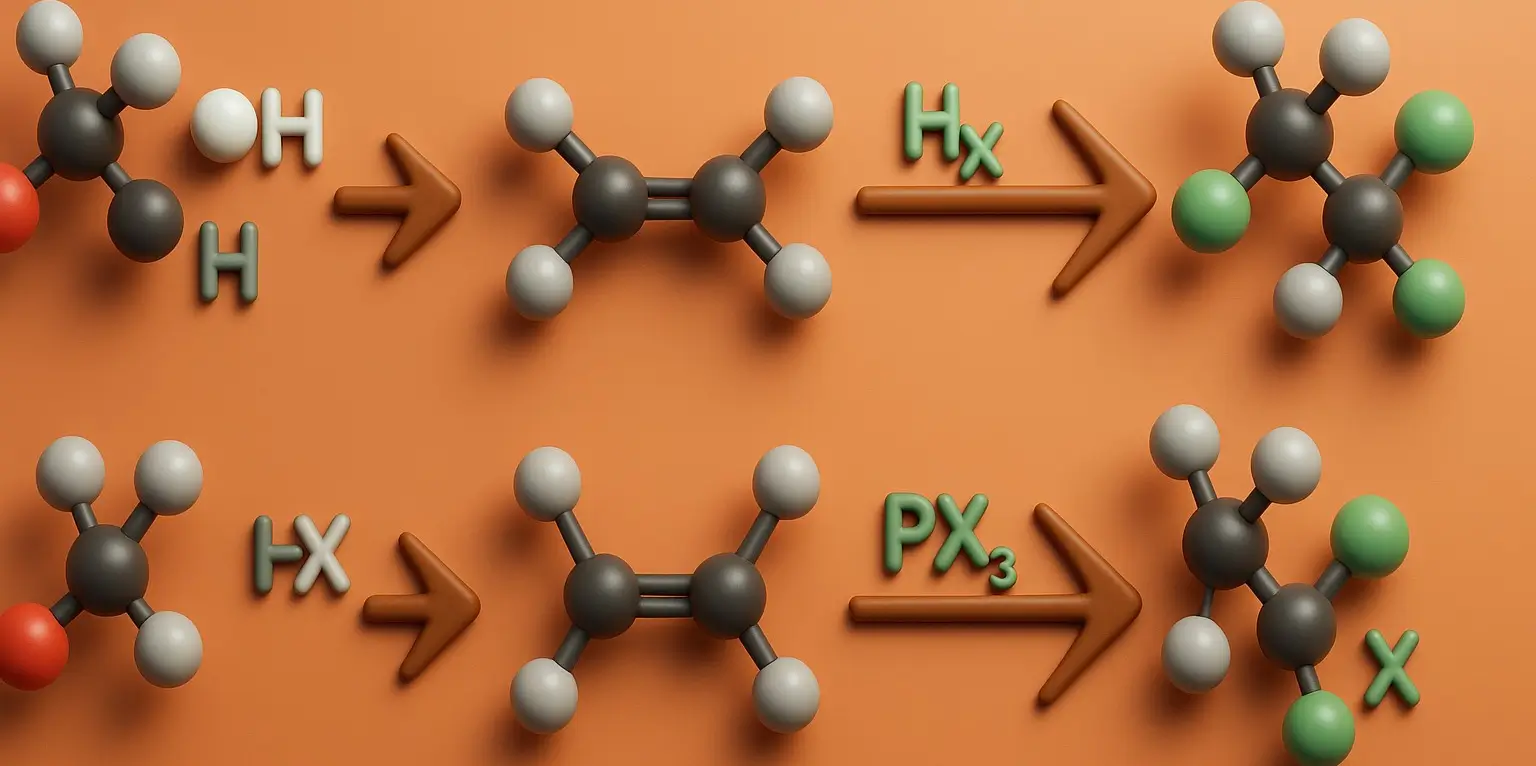
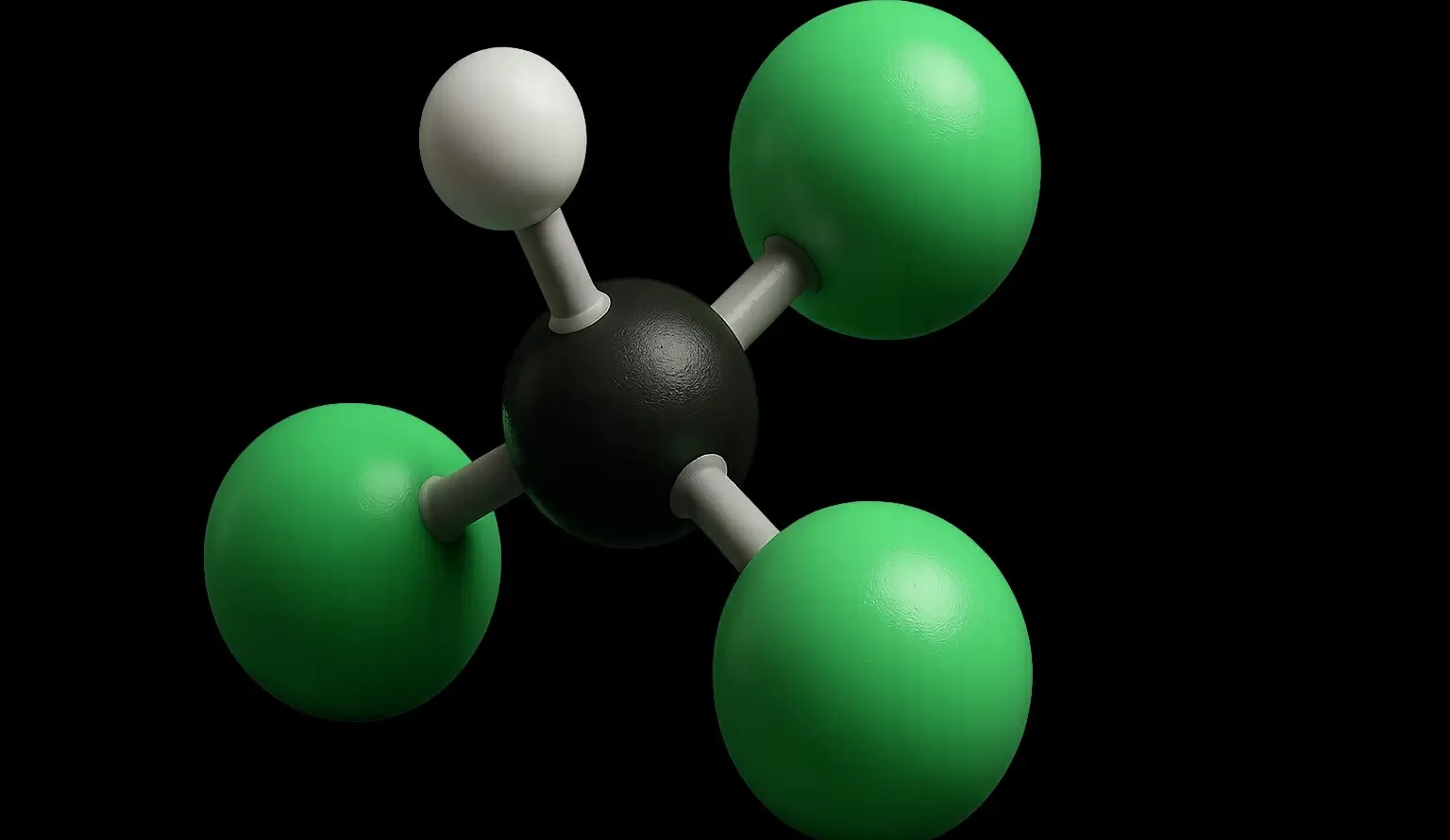
Chloroform (Trichloromethane) Definition Chloroform (Trichloromethane), also known by its IUPAC name trichloromethane (CHCl₃), is a colorless, volatile, and sweet-smelling liquid that is non-flammable and heavier than water. It belongs to the class of compounds called halogenated hydrocarbons and is primarily used as a solvent, reagent, and intermediate in the production of various chemicals, especially refrigerants … Read more