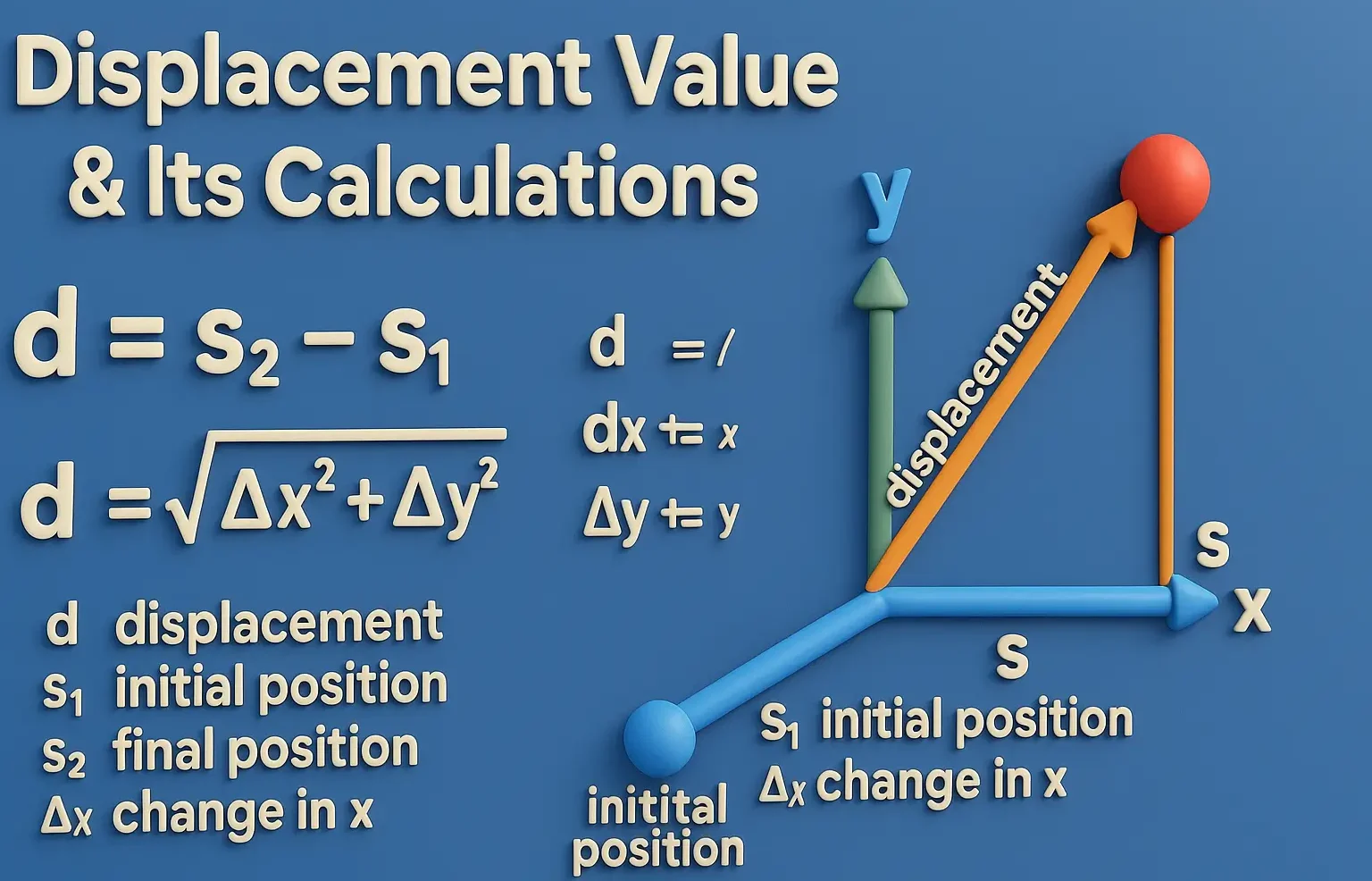
Types of Suppository bases
Suppository bases are vehicles that carry the active ingredients in suppositories. They are classified into two main categories: lipophilic (fat-soluble) and hydrophilic (water-soluble). The choice of base depends on factors such as drug solubility, stability, and release characteristics. 1. Lipophilic Bases Cocoa Butter (Theobroma Oil) A natural fat from cocoa beans, widely used in suppositories. … Read more