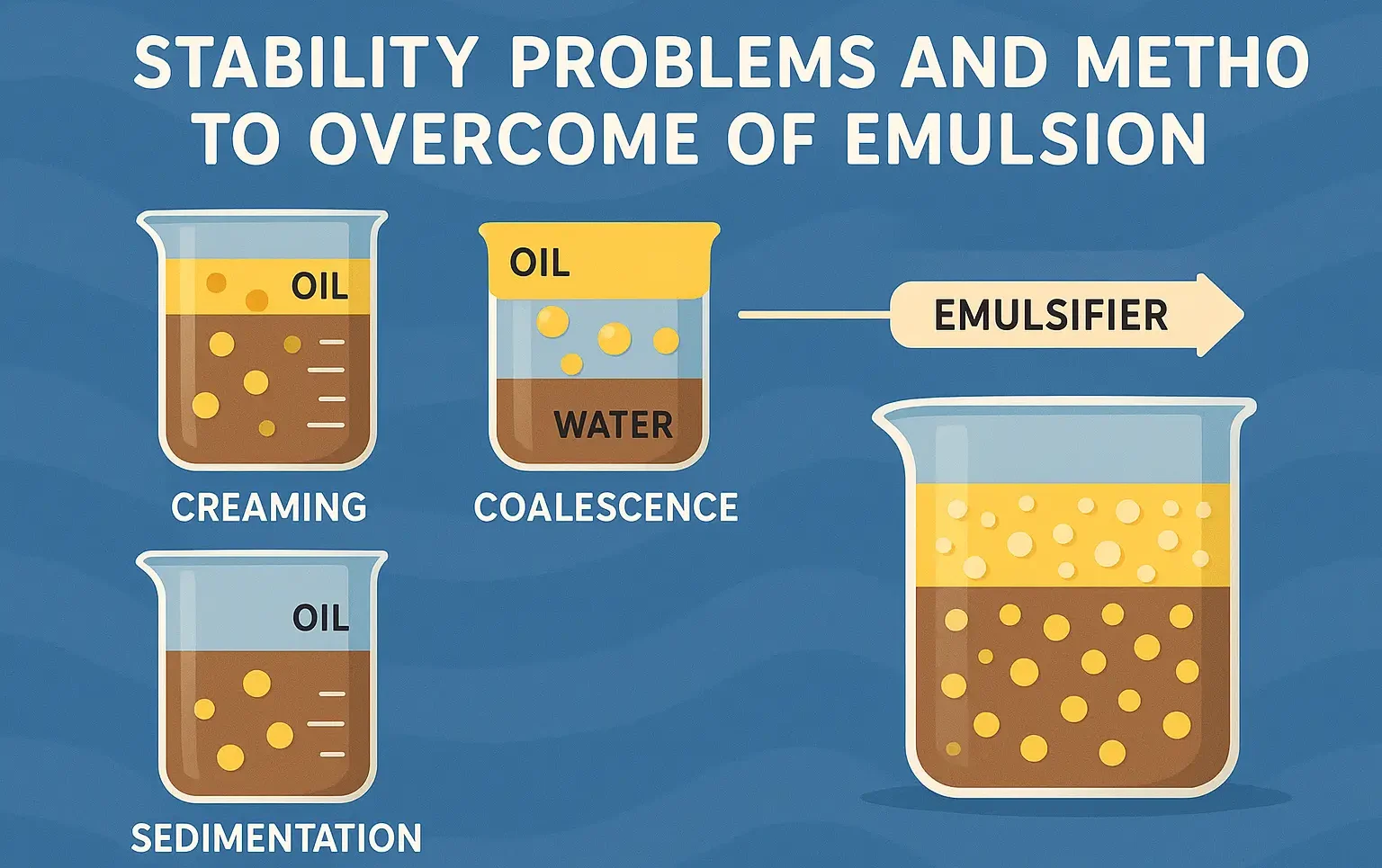
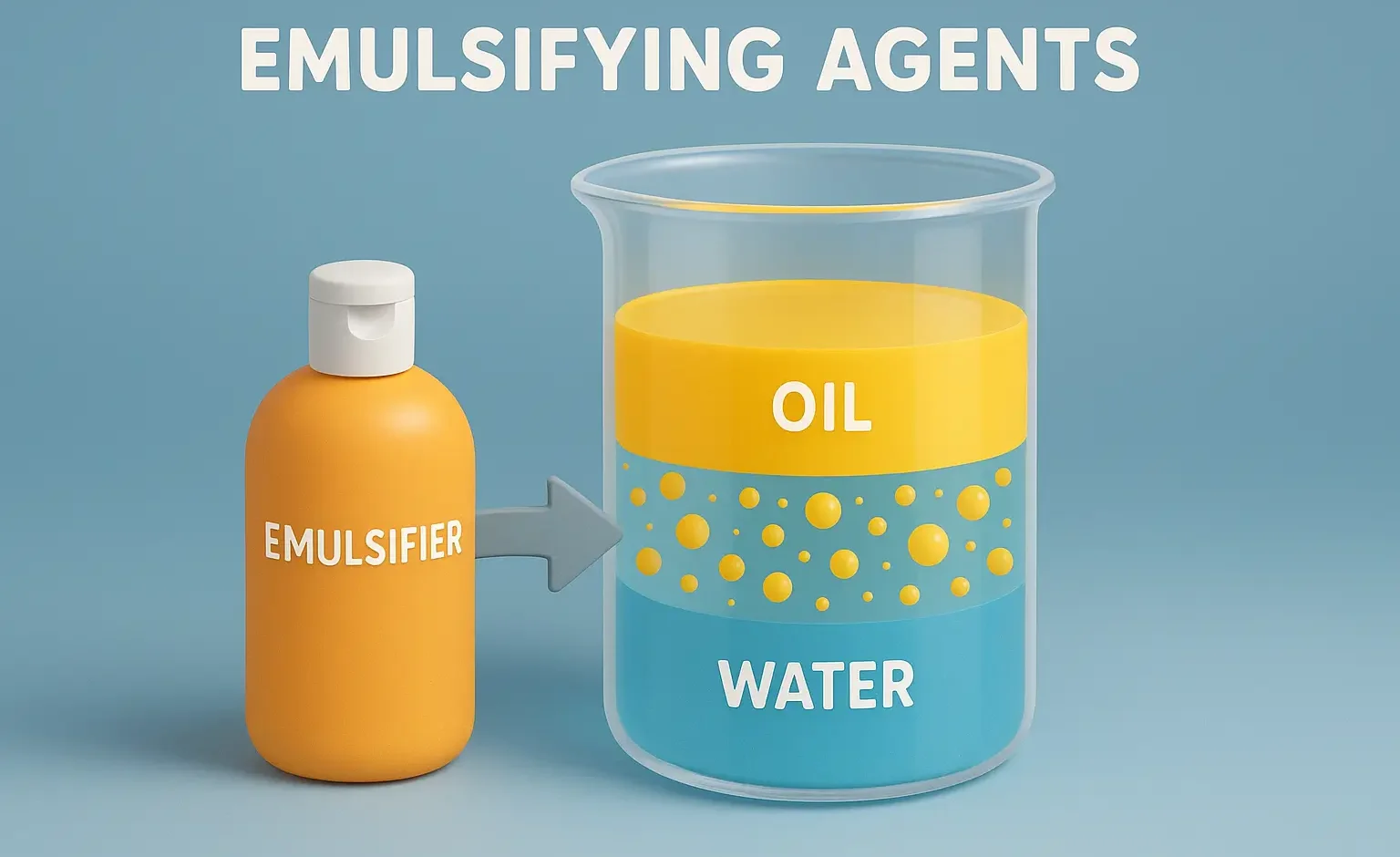
Stability problems and methods to overcome of emulsion
Emulsions can encounter several stability issues due to the immiscible nature of their components. Common problems include creaming, flocculation, coalescence, and phase separation. Below, we discuss these issues and provide methods to overcome them. 1. Creaming Definition: Creaming occurs when the dispersed droplets in an emulsion migrate toward the top or bottom of the system … Read more